Pica Johansson
Cheap Learning: Maximising Performance of Language Models for Social Data Science Using Minimal Data
Jan 22, 2024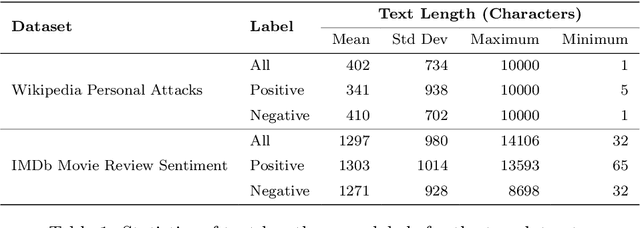
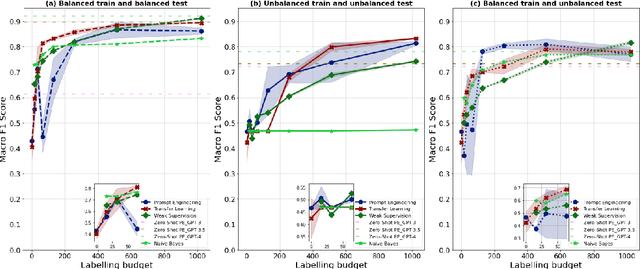
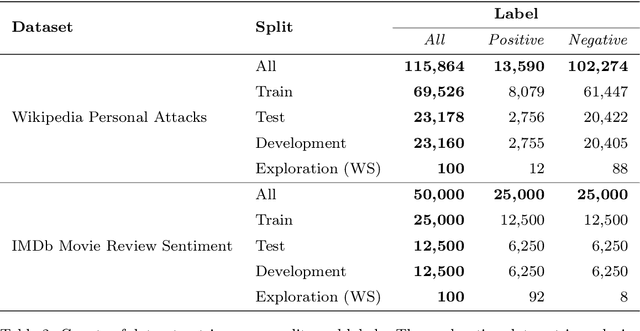
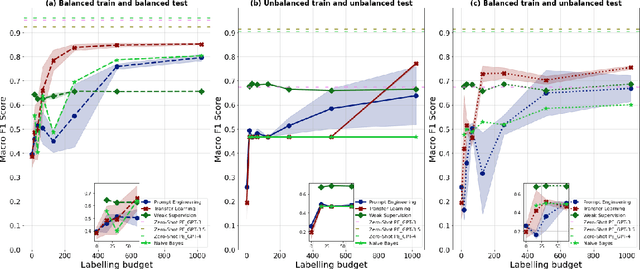
Abstract:The field of machine learning has recently made significant progress in reducing the requirements for labelled training data when building new models. These `cheaper' learning techniques hold significant potential for the social sciences, where development of large labelled training datasets is often a significant practical impediment to the use of machine learning for analytical tasks. In this article we review three `cheap' techniques that have developed in recent years: weak supervision, transfer learning and prompt engineering. For the latter, we also review the particular case of zero-shot prompting of large language models. For each technique we provide a guide of how it works and demonstrate its application across six different realistic social science applications (two different tasks paired with three different dataset makeups). We show good performance for all techniques, and in particular we demonstrate how prompting of large language models can achieve high accuracy at very low cost. Our results are accompanied by a code repository to make it easy for others to duplicate our work and use it in their own research. Overall, our article is intended to stimulate further uptake of these techniques in the social sciences.
DoDo Learning: DOmain-DemOgraphic Transfer in Language Models for Detecting Abuse Targeted at Public Figures
Aug 21, 2023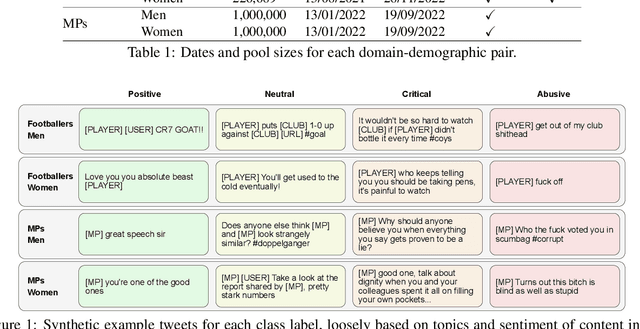
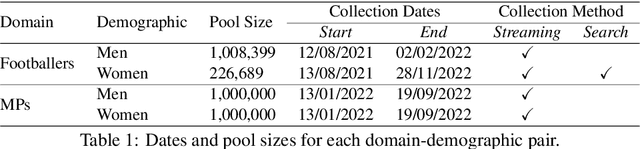
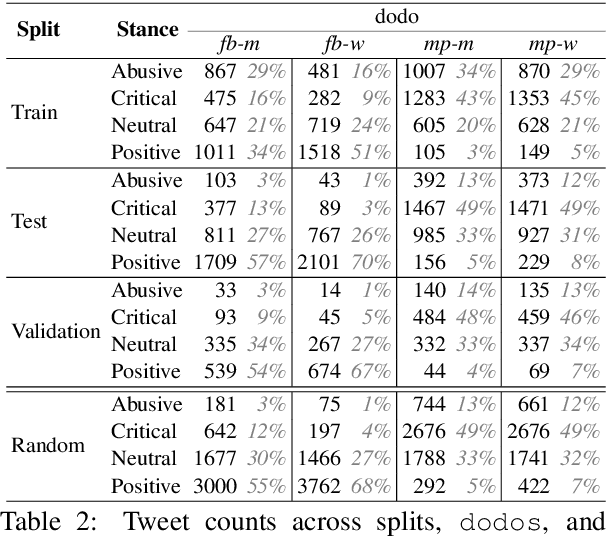
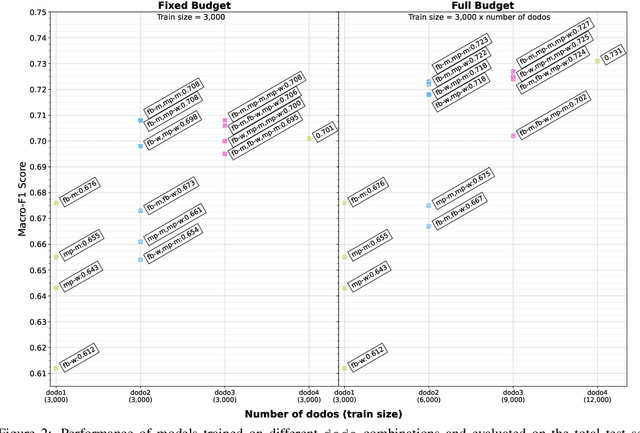
Abstract:Public figures receive a disproportionate amount of abuse on social media, impacting their active participation in public life. Automated systems can identify abuse at scale but labelling training data is expensive, complex and potentially harmful. So, it is desirable that systems are efficient and generalisable, handling both shared and specific aspects of online abuse. We explore the dynamics of cross-group text classification in order to understand how well classifiers trained on one domain or demographic can transfer to others, with a view to building more generalisable abuse classifiers. We fine-tune language models to classify tweets targeted at public figures across DOmains (sport and politics) and DemOgraphics (women and men) using our novel DODO dataset, containing 28,000 labelled entries, split equally across four domain-demographic pairs. We find that (i) small amounts of diverse data are hugely beneficial to generalisation and model adaptation; (ii) models transfer more easily across demographics but models trained on cross-domain data are more generalisable; (iii) some groups contribute more to generalisability than others; and (iv) dataset similarity is a signal of transferability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge