Phoebe Chua
Department of Information Systems and Analytics, National University of Singapore
EmoSign: A Multimodal Dataset for Understanding Emotions in American Sign Language
May 20, 2025Abstract:Unlike spoken languages where the use of prosodic features to convey emotion is well studied, indicators of emotion in sign language remain poorly understood, creating communication barriers in critical settings. Sign languages present unique challenges as facial expressions and hand movements simultaneously serve both grammatical and emotional functions. To address this gap, we introduce EmoSign, the first sign video dataset containing sentiment and emotion labels for 200 American Sign Language (ASL) videos. We also collect open-ended descriptions of emotion cues. Annotations were done by 3 Deaf ASL signers with professional interpretation experience. Alongside the annotations, we include baseline models for sentiment and emotion classification. This dataset not only addresses a critical gap in existing sign language research but also establishes a new benchmark for understanding model capabilities in multimodal emotion recognition for sign languages. The dataset is made available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/catfang/emosign.
AffectMachine-Classical: A novel system for generating affective classical music
Apr 11, 2023


Abstract:This work introduces a new music generation system, called AffectMachine-Classical, that is capable of generating affective Classic music in real-time. AffectMachine was designed to be incorporated into biofeedback systems (such as brain-computer-interfaces) to help users become aware of, and ultimately mediate, their own dynamic affective states. That is, this system was developed for music-based MedTech to support real-time emotion self-regulation in users. We provide an overview of the rule-based, probabilistic system architecture, describing the main aspects of the system and how they are novel. We then present the results of a listener study that was conducted to validate the ability of the system to reliably convey target emotions to listeners. The findings indicate that AffectMachine-Classical is very effective in communicating various levels of Arousal ($R^2 = .96$) to listeners, and is also quite convincing in terms of Valence (R^2 = .90). Future work will embed AffectMachine-Classical into biofeedback systems, to leverage the efficacy of the affective music for emotional well-being in listeners.
Predicting emotion from music videos: exploring the relative contribution of visual and auditory information to affective responses
Feb 19, 2022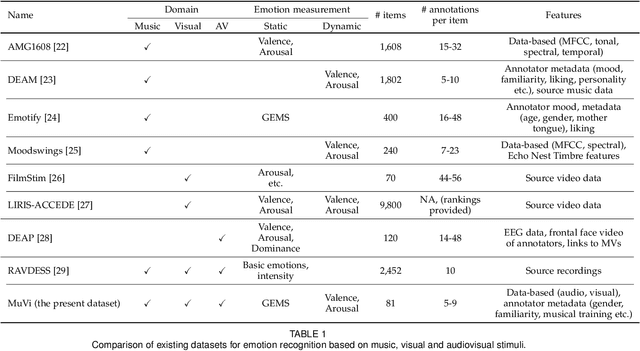

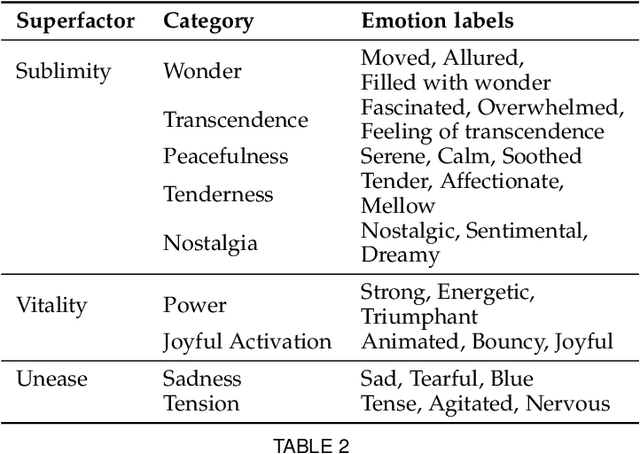
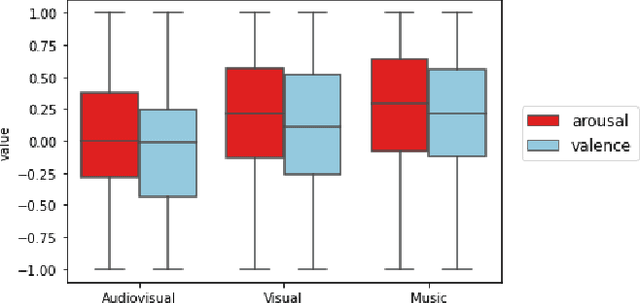
Abstract:Although media content is increasingly produced, distributed, and consumed in multiple combinations of modalities, how individual modalities contribute to the perceived emotion of a media item remains poorly understood. In this paper we present MusicVideos (MuVi), a novel dataset for affective multimedia content analysis to study how the auditory and visual modalities contribute to the perceived emotion of media. The data were collected by presenting music videos to participants in three conditions: music, visual, and audiovisual. Participants annotated the music videos for valence and arousal over time, as well as the overall emotion conveyed. We present detailed descriptive statistics for key measures in the dataset and the results of feature importance analyses for each condition. Finally, we propose a novel transfer learning architecture to train Predictive models Augmented with Isolated modality Ratings (PAIR) and demonstrate the potential of isolated modality ratings for enhancing multimodal emotion recognition. Our results suggest that perceptions of arousal are influenced primarily by auditory information, while perceptions of valence are more subjective and can be influenced by both visual and auditory information. The dataset is made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge