Peyman Nejat
Zero-Shot Whole Slide Image Retrieval in Histopathology Using Embeddings of Foundation Models
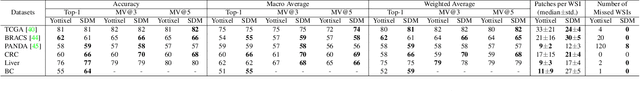
Sep 06, 2024Abstract:We have tested recently published foundation models for histopathology for image retrieval. We report macro average of F1 score for top-1 retrieval, majority of top-3 retrievals, and majority of top-5 retrievals. We perform zero-shot retrievals, i.e., we do not alter embeddings and we do not train any classifier. As test data, we used diagnostic slides of TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas, consisting of 23 organs and 117 cancer subtypes. As a search platform we used Yottixel that enabled us to perform WSI search using patches. Achieved F1 scores show low performance, e.g., for top-5 retrievals, 27% +/- 13% (Yottixel-DenseNet), 42% +/- 14% (Yottixel-UNI), 40%+/-13% (Yottixel-Virchow), and 41%+/-13% (Yottixel-GigaPath). The results for GigaPath WSI will be delayed due to the significant computational resources required for processing
SPLICE -- Streamlining Digital Pathology Image Processing
Apr 26, 2024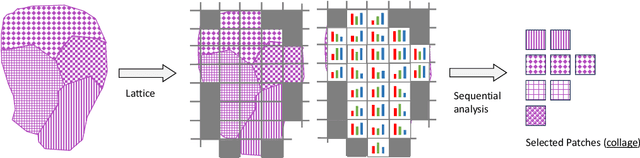
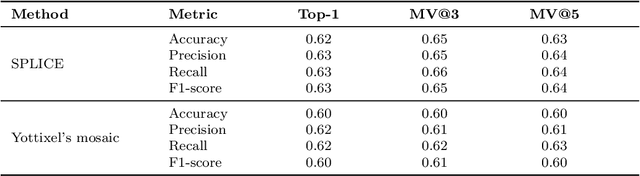
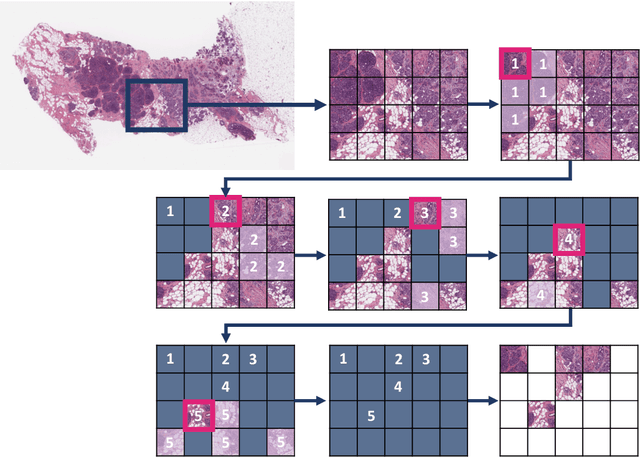
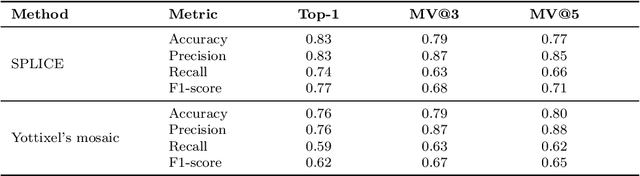
Abstract:Digital pathology and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) models have revolutionized histopathology, opening new opportunities. With the increasing availability of Whole Slide Images (WSIs), there's a growing demand for efficient retrieval, processing, and analysis of relevant images from vast biomedical archives. However, processing WSIs presents challenges due to their large size and content complexity. Full computer digestion of WSIs is impractical, and processing all patches individually is prohibitively expensive. In this paper, we propose an unsupervised patching algorithm, Sequential Patching Lattice for Image Classification and Enquiry (SPLICE). This novel approach condenses a histopathology WSI into a compact set of representative patches, forming a "collage" of WSI while minimizing redundancy. SPLICE prioritizes patch quality and uniqueness by sequentially analyzing a WSI and selecting non-redundant representative features. We evaluated SPLICE for search and match applications, demonstrating improved accuracy, reduced computation time, and storage requirements compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. As an unsupervised method, SPLICE effectively reduces storage requirements for representing tissue images by 50%. This reduction enables numerous algorithms in computational pathology to operate much more efficiently, paving the way for accelerated adoption of digital pathology.
Analysis and Validation of Image Search Engines in Histopathology
Jan 06, 2024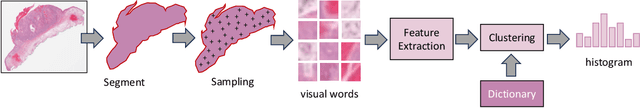
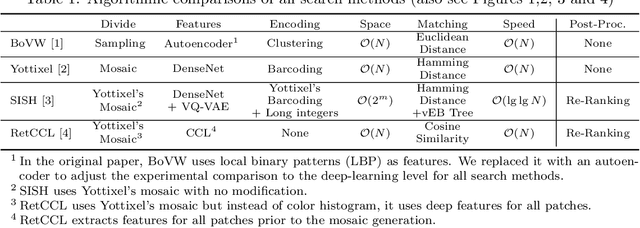
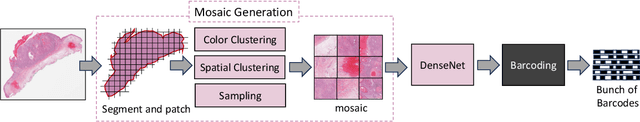
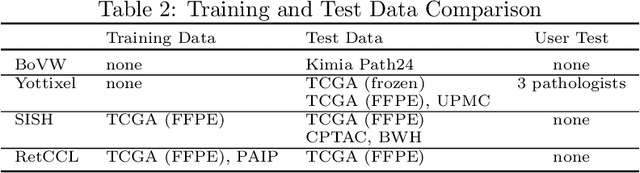
Abstract:Searching for similar images in archives of histology and histopathology images is a crucial task that may aid in patient matching for various purposes, ranging from triaging and diagnosis to prognosis and prediction. Whole slide images (WSIs) are highly detailed digital representations of tissue specimens mounted on glass slides. Matching WSI to WSI can serve as the critical method for patient matching. In this paper, we report extensive analysis and validation of four search methods bag of visual words (BoVW), Yottixel, SISH, RetCCL, and some of their potential variants. We analyze their algorithms and structures and assess their performance. For this evaluation, we utilized four internal datasets ($1269$ patients) and three public datasets ($1207$ patients), totaling more than $200,000$ patches from $38$ different classes/subtypes across five primary sites. Certain search engines, for example, BoVW, exhibit notable efficiency and speed but suffer from low accuracy. Conversely, search engines like Yottixel demonstrate efficiency and speed, providing moderately accurate results. Recent proposals, including SISH, display inefficiency and yield inconsistent outcomes, while alternatives like RetCCL prove inadequate in both accuracy and efficiency. Further research is imperative to address the dual aspects of accuracy and minimal storage requirements in histopathological image search.
Performance of externally validated machine learning models based on histopathology images for the diagnosis, classification, prognosis, or treatment outcome prediction in female breast cancer: A systematic review
Dec 09, 2023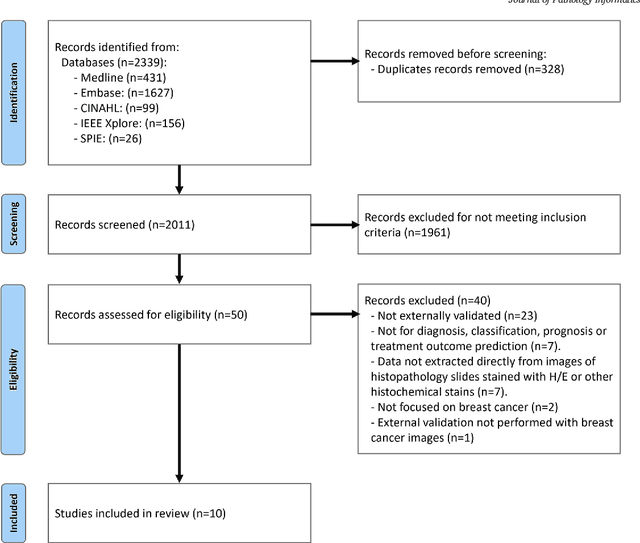
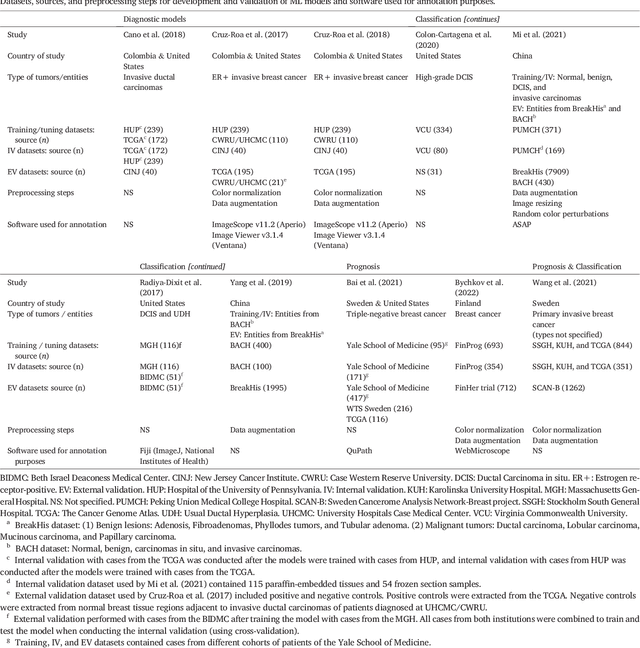
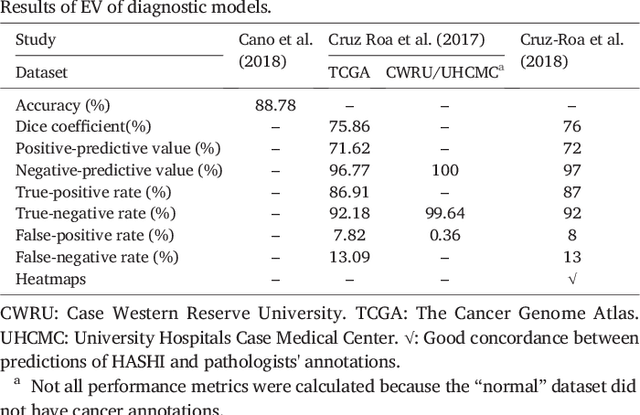
Abstract:Numerous machine learning (ML) models have been developed for breast cancer using various types of data. Successful external validation (EV) of ML models is important evidence of their generalizability. The aim of this systematic review was to assess the performance of externally validated ML models based on histopathology images for diagnosis, classification, prognosis, or treatment outcome prediction in female breast cancer. A systematic search of MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, IEEE, MICCAI, and SPIE conferences was performed for studies published between January 2010 and February 2022. The Prediction Model Risk of Bias Assessment Tool (PROBAST) was employed, and the results were narratively described. Of the 2011 non-duplicated citations, 8 journal articles and 2 conference proceedings met inclusion criteria. Three studies externally validated ML models for diagnosis, 4 for classification, 2 for prognosis, and 1 for both classification and prognosis. Most studies used Convolutional Neural Networks and one used logistic regression algorithms. For diagnostic/classification models, the most common performance metrics reported in the EV were accuracy and area under the curve, which were greater than 87% and 90%, respectively, using pathologists' annotations as ground truth. The hazard ratios in the EV of prognostic ML models were between 1.7 (95% CI, 1.2-2.6) and 1.8 (95% CI, 1.3-2.7) to predict distant disease-free survival; 1.91 (95% CI, 1.11-3.29) for recurrence, and between 0.09 (95% CI, 0.01-0.70) and 0.65 (95% CI, 0.43-0.98) for overall survival, using clinical data as ground truth. Despite EV being an important step before the clinical application of a ML model, it hasn't been performed routinely. The large variability in the training/validation datasets, methods, performance metrics, and reported information limited the comparison of the models and the analysis of their results (...)
Seeing the random forest through the decision trees. Supporting learning health systems from histopathology with machine learning models: Challenges and opportunities
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:This paper discusses some overlooked challenges faced when working with machine learning models for histopathology and presents a novel opportunity to support "Learning Health Systems" with them. Initially, the authors elaborate on these challenges after separating them according to their mitigation strategies: those that need innovative approaches, time, or future technological capabilities and those that require a conceptual reappraisal from a critical perspective. Then, a novel opportunity to support "Learning Health Systems" by integrating hidden information extracted by ML models from digitalized histopathology slides with other healthcare big data is presented.
Selection of Distinct Morphologies to Divide & Conquer Gigapixel Pathology Images
Nov 16, 2023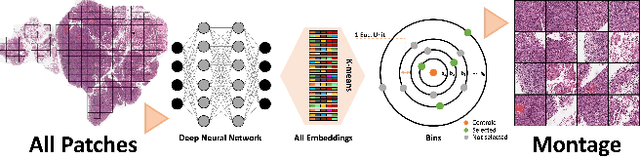
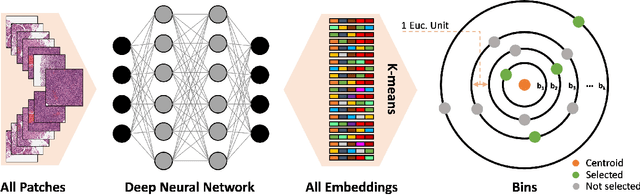
Abstract:Whole slide images (WSIs) are massive digital pathology files illustrating intricate tissue structures. Selecting a small, representative subset of patches from each WSI is essential yet challenging. Therefore, following the "Divide & Conquer" approach becomes essential to facilitate WSI analysis including the classification and the WSI matching in computational pathology. To this end, we propose a novel method termed "Selection of Distinct Morphologies" (SDM) to choose a subset of WSI patches. The aim is to encompass all inherent morphological variations within a given WSI while simultaneously minimizing the number of selected patches to represent these variations, ensuring a compact yet comprehensive set of patches. This systematically curated patch set forms what we term a "montage". We assess the representativeness of the SDM montage across various public and private histopathology datasets. This is conducted by using the leave-one-out WSI search and matching evaluation method, comparing it with the state-of-the-art Yottixel's mosaic. SDM demonstrates remarkable efficacy across all datasets during its evaluation. Furthermore, SDM eliminates the necessity for empirical parameterization, a crucial aspect of Yottixel's mosaic, by inherently optimizing the selection process to capture the distinct morphological features within the WSI.
Rotation-Agnostic Image Representation Learning for Digital Pathology
Nov 14, 2023

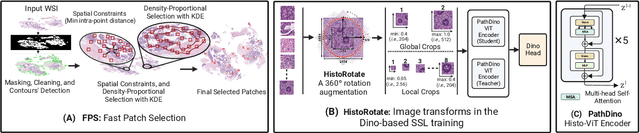
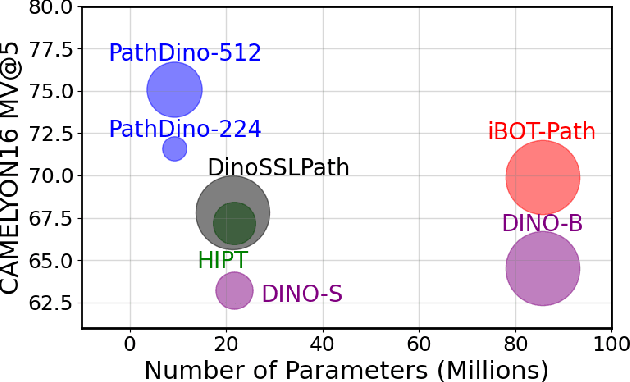
Abstract:This paper addresses complex challenges in histopathological image analysis through three key contributions. Firstly, it introduces a fast patch selection method, FPS, for whole-slide image (WSI) analysis, significantly reducing computational cost while maintaining accuracy. Secondly, it presents PathDino, a lightweight histopathology feature extractor with a minimal configuration of five Transformer blocks and only 9 million parameters, markedly fewer than alternatives. Thirdly, it introduces a rotation-agnostic representation learning paradigm using self-supervised learning, effectively mitigating overfitting. We also show that our compact model outperforms existing state-of-the-art histopathology-specific vision transformers on 12 diverse datasets, including both internal datasets spanning four sites (breast, liver, skin, and colorectal) and seven public datasets (PANDA, CAMELYON16, BRACS, DigestPath, Kather, PanNuke, and WSSS4LUAD). Notably, even with a training dataset of 6 million histopathology patches from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), our approach demonstrates an average 8.5% improvement in patch-level majority vote performance. These contributions provide a robust framework for enhancing image analysis in digital pathology, rigorously validated through extensive evaluation. Project Page: https://rhazeslab.github.io/PathDino-Page/
Creating an Atlas of Normal Tissue for Pruning WSI Patching Through Anomaly Detection
Oct 04, 2023Abstract:Patching gigapixel whole slide images (WSIs) is an important task in computational pathology. Some methods have been proposed to select a subset of patches as WSI representation for downstream tasks. While most of the computational pathology tasks are designed to classify or detect the presence of pathological lesions in each WSI, the confounding role and redundant nature of normal histology in tissue samples are generally overlooked in WSI representations. In this paper, we propose and validate the concept of an "atlas of normal tissue" solely using samples of WSIs obtained from normal tissue biopsies. Such atlases can be employed to eliminate normal fragments of tissue samples and hence increase the representativeness collection of patches. We tested our proposed method by establishing a normal atlas using 107 normal skin WSIs and demonstrated how established indexes and search engines like Yottixel can be improved. We used 553 WSIs of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) to show the advantage. We also validated our method applied to an external dataset of 451 breast WSIs. The number of selected WSI patches was reduced by 30% to 50% after utilizing the proposed normal atlas while maintaining the same indexing and search performance in leave-one-patinet-out validation for both datasets. We show that the proposed normal atlas shows promise for unsupervised selection of the most representative patches of the abnormal/malignant WSI lesions.
When is a Foundation Model a Foundation Model
Sep 14, 2023

Abstract:Recently, several studies have reported on the fine-tuning of foundation models for image-text modeling in the field of medicine, utilizing images from online data sources such as Twitter and PubMed. Foundation models are large, deep artificial neural networks capable of learning the context of a specific domain through training on exceptionally extensive datasets. Through validation, we have observed that the representations generated by such models exhibit inferior performance in retrieval tasks within digital pathology when compared to those generated by significantly smaller, conventional deep networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge