Pengcheng Wen
Glance-or-Gaze: Incentivizing LMMs to Adaptively Focus Search via Reinforcement Learning
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable success in visual understanding, yet they struggle with knowledge-intensive queries involving long-tail entities or evolving information due to static parametric knowledge. Recent search-augmented approaches attempt to address this limitation, but existing methods rely on indiscriminate whole-image retrieval that introduces substantial visual redundancy and noise, and lack deep iterative reflection, limiting their effectiveness on complex visual queries. To overcome these challenges, we propose Glance-or-Gaze (GoG), a fully autonomous framework that shifts from passive perception to active visual planning. GoG introduces a Selective Gaze mechanism that dynamically chooses whether to glance at global context or gaze into high-value regions, filtering irrelevant information before retrieval. We design a dual-stage training strategy: Reflective GoG Behavior Alignment via supervised fine-tuning instills the fundamental GoG paradigm, while Complexity-Adaptive Reinforcement Learning further enhances the model's capability to handle complex queries through iterative reasoning. Experiments across six benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. Ablation studies confirm that both Selective Gaze and complexity-adaptive RL are essential for effective visual search. We will release our data and models for further exploration soon.
AM$^3$Safety: Towards Data Efficient Alignment of Multi-modal Multi-turn Safety for MLLMs
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are increasingly deployed in interactive applications. However, their safety vulnerabilities become pronounced in multi-turn multi-modal scenarios, where harmful intent can be gradually reconstructed across turns, and security protocols fade into oblivion as the conversation progresses. Existing Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) alignment methods are largely developed for single-turn visual question-answer (VQA) task and often require costly manual preference annotations, limiting their effectiveness and scalability in dialogues. To address this challenge, we present InterSafe-V, an open-source multi-modal dialogue dataset containing 11,270 dialogues and 500 specially designed refusal VQA samples. This dataset, constructed through interaction between several models, is designed to more accurately reflect real-world scenarios and includes specialized VQA pairs tailored for specific domains. Building on this dataset, we propose AM$^3$Safety, a framework that combines a cold-start refusal phase with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) fine-tuning using turn-aware dual-objective rewards across entire dialogues. Experiments on Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct and LLaVA-NeXT-7B show more than 10\% decrease in Attack Success Rate (ASR) together with an increment of at least 8\% in harmless dimension and over 13\% in helpful dimension of MLLMs on multi-modal multi-turn safety benchmarks, while preserving their general abilities.
J1: Exploring Simple Test-Time Scaling for LLM-as-a-Judge
May 17, 2025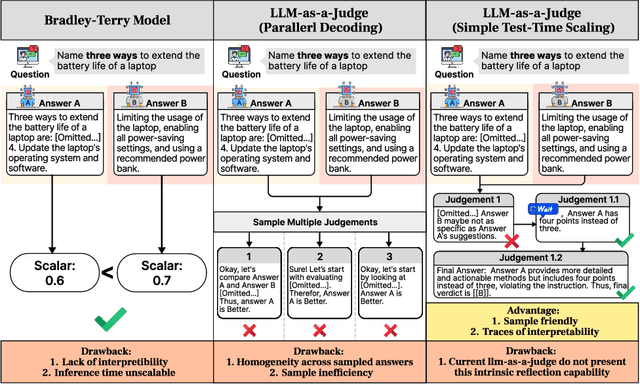
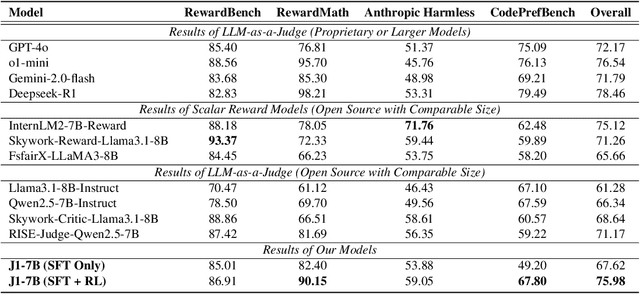
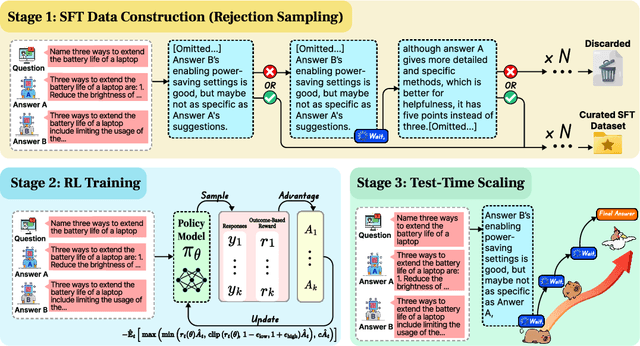
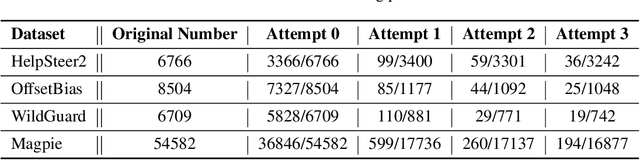
Abstract:The current focus of AI research is shifting from emphasizing model training towards enhancing evaluation quality, a transition that is crucial for driving further advancements in AI systems. Traditional evaluation methods typically rely on reward models assigning scalar preference scores to outputs. Although effective, such approaches lack interpretability, leaving users often uncertain about why a reward model rates a particular response as high or low. The advent of LLM-as-a-Judge provides a more scalable and interpretable method of supervision, offering insights into the decision-making process. Moreover, with the emergence of large reasoning models, which consume more tokens for deeper thinking and answer refinement, scaling test-time computation in the LLM-as-a-Judge paradigm presents an avenue for further boosting performance and providing more interpretability through reasoning traces. In this paper, we introduce $\textbf{J1-7B}$, which is first supervised fine-tuned on reflection-enhanced datasets collected via rejection-sampling and subsequently trained using Reinforcement Learning (RL) with verifiable rewards. At inference time, we apply Simple Test-Time Scaling (STTS) strategies for additional performance improvement. Experimental results demonstrate that $\textbf{J1-7B}$ surpasses the previous state-of-the-art LLM-as-a-Judge by $ \textbf{4.8}$\% and exhibits a $ \textbf{5.1}$\% stronger scaling trend under STTS. Additionally, we present three key findings: (1) Existing LLM-as-a-Judge does not inherently exhibit such scaling trend. (2) Model simply fine-tuned on reflection-enhanced datasets continues to demonstrate similarly weak scaling behavior. (3) Significant scaling trend emerges primarily during the RL phase, suggesting that effective STTS capability is acquired predominantly through RL training.
ThinkPatterns-21k: A Systematic Study on the Impact of Thinking Patterns in LLMs
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated enhanced performance through the \textit{Thinking then Responding} paradigm, where models generate internal thoughts before final responses (aka, System 2 thinking). However, existing research lacks a systematic understanding of the mechanisms underlying how thinking patterns affect performance across model sizes. In this work, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of the impact of various thinking types on model performance and introduce ThinkPatterns-21k, a curated dataset comprising 21k instruction-response pairs (QA) collected from existing instruction-following datasets with five thinking types. For each pair, we augment it with five distinct internal thinking patterns: one unstructured thinking (monologue) and four structured variants (decomposition, self-ask, self-debate and self-critic), while maintaining the same instruction and response. Through extensive evaluation across different model sizes (3B-32B parameters), we have two key findings: (1) smaller models (<30B parameters) can benefit from most of structured thinking patterns, while larger models (32B) with structured thinking like decomposition would degrade performance and (2) unstructured monologue demonstrates broad effectiveness across different model sizes. Finally, we released all of our datasets, checkpoints, training logs of diverse thinking patterns to reproducibility, aiming to facilitate further research in this direction.
SdCT-GAN: Reconstructing CT from Biplanar X-Rays with Self-driven Generative Adversarial Networks
Sep 10, 2023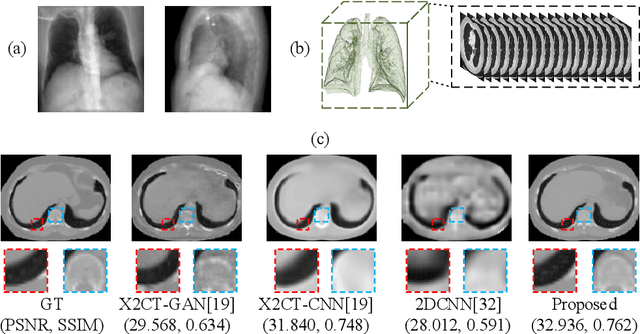
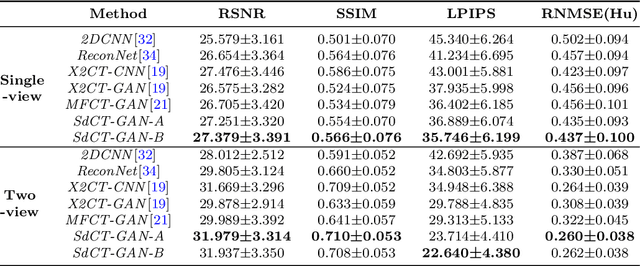
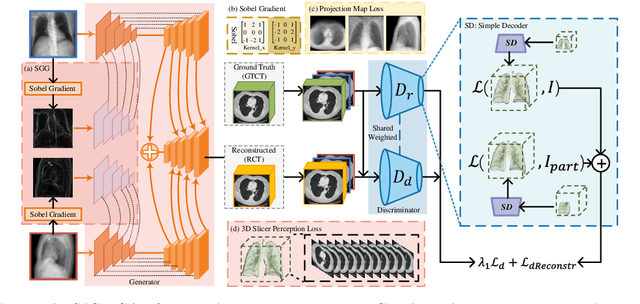
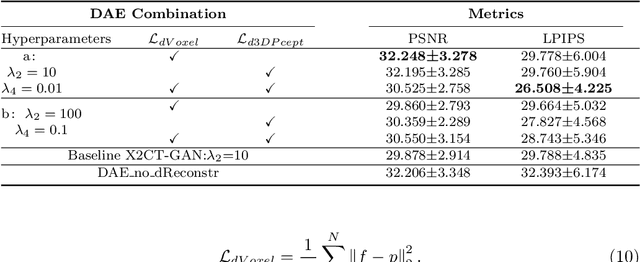
Abstract:Computed Tomography (CT) is a medical imaging modality that can generate more informative 3D images than 2D X-rays. However, this advantage comes at the expense of more radiation exposure, higher costs, and longer acquisition time. Hence, the reconstruction of 3D CT images using a limited number of 2D X-rays has gained significant importance as an economical alternative. Nevertheless, existing methods primarily prioritize minimizing pixel/voxel-level intensity discrepancies, often neglecting the preservation of textural details in the synthesized images. This oversight directly impacts the quality of the reconstructed images and thus affects the clinical diagnosis. To address the deficits, this paper presents a new self-driven generative adversarial network model (SdCT-GAN), which is motivated to pay more attention to image details by introducing a novel auto-encoder structure in the discriminator. In addition, a Sobel Gradient Guider (SGG) idea is applied throughout the model, where the edge information from the 2D X-ray image at the input can be integrated. Moreover, LPIPS (Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity) evaluation metric is adopted that can quantitatively evaluate the fine contours and textures of reconstructed images better than the existing ones. Finally, the qualitative and quantitative results of the empirical studies justify the power of the proposed model compared to mainstream state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge