Peiqin Zhuang
RadarQA: Multi-modal Quality Analysis of Weather Radar Forecasts
Aug 17, 2025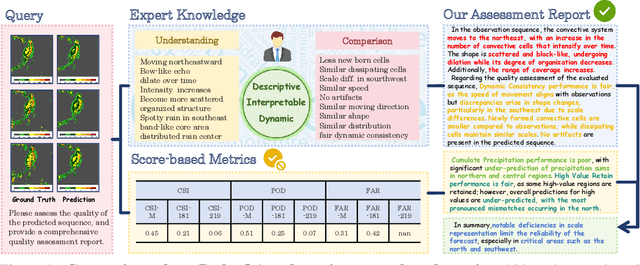
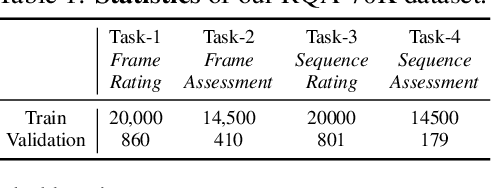

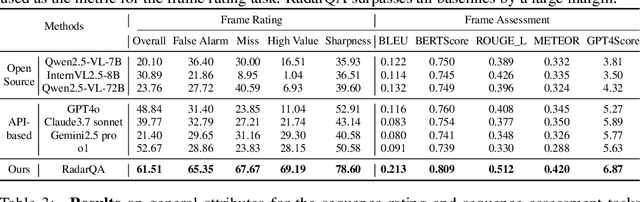
Abstract:Quality analysis of weather forecasts is an essential topic in meteorology. Although traditional score-based evaluation metrics can quantify certain forecast errors, they are still far from meteorological experts in terms of descriptive capability, interpretability, and understanding of dynamic evolution. With the rapid development of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), these models become potential tools to overcome the above challenges. In this work, we introduce an MLLM-based weather forecast analysis method, RadarQA, integrating key physical attributes with detailed assessment reports. We introduce a novel and comprehensive task paradigm for multi-modal quality analysis, encompassing both single frame and sequence, under both rating and assessment scenarios. To support training and benchmarking, we design a hybrid annotation pipeline that combines human expert labeling with automated heuristics. With such an annotation method, we construct RQA-70K, a large-scale dataset with varying difficulty levels for radar forecast quality evaluation. We further design a multi-stage training strategy that iteratively improves model performance at each stage. Extensive experiments show that RadarQA outperforms existing general MLLMs across all evaluation settings, highlighting its potential for advancing quality analysis in weather prediction.
Swarm Intelligence Enhanced Reasoning: A Density-Driven Framework for LLM-Based Multi-Agent Optimization
May 21, 2025Abstract:Recently, many approaches, such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting and Multi-Agent Debate (MAD), have been proposed to further enrich Large Language Models' (LLMs) complex problem-solving capacities in reasoning scenarios. However, these methods may fail to solve complex problems due to the lack of ability to find optimal solutions. Swarm Intelligence has been serving as a powerful tool for finding optima in the field of traditional optimization problems. To this end, we propose integrating swarm intelligence into the reasoning process by introducing a novel Agent-based Swarm Intelligence (ASI) paradigm. In this paradigm, we formulate LLM reasoning as an optimization problem and use a swarm intelligence scheme to guide a group of LLM-based agents in collaboratively searching for optimal solutions. To avoid swarm intelligence getting trapped in local optima, we further develop a Swarm Intelligence Enhancing Reasoning (SIER) framework, which develops a density-driven strategy to enhance the reasoning ability. To be specific, we propose to perform kernel density estimation and non-dominated sorting to optimize both solution quality and diversity simultaneously. In this case, SIER efficiently enhances solution space exploration through expanding the diversity of the reasoning path. Besides, a step-level quality evaluation is used to help agents improve solution quality by correcting low-quality intermediate steps. Then, we use quality thresholds to dynamically control the termination of exploration and the selection of candidate steps, enabling a more flexible and efficient reasoning process. Extensive experiments are ...
Transferable Knowledge-Based Multi-Granularity Aggregation Network for Temporal Action Localization: Submission to ActivityNet Challenge 2021
Jul 27, 2021



Abstract:This technical report presents an overview of our solution used in the submission to 2021 HACS Temporal Action Localization Challenge on both Supervised Learning Track and Weakly-Supervised Learning Track. Temporal Action Localization (TAL) requires to not only precisely locate the temporal boundaries of action instances, but also accurately classify the untrimmed videos into specific categories. However, Weakly-Supervised TAL indicates locating the action instances using only video-level class labels. In this paper, to train a supervised temporal action localizer, we adopt Temporal Context Aggregation Network (TCANet) to generate high-quality action proposals through ``local and global" temporal context aggregation and complementary as well as progressive boundary refinement. As for the WSTAL, a novel framework is proposed to handle the poor quality of CAS generated by simple classification network, which can only focus on local discriminative parts, rather than locate the entire interval of target actions. Further inspired by the transfer learning method, we also adopt an additional module to transfer the knowledge from trimmed videos (HACS Clips dataset) to untrimmed videos (HACS Segments dataset), aiming at promoting the classification performance on untrimmed videos. Finally, we employ a boundary regression module embedded with Outer-Inner-Contrastive (OIC) loss to automatically predict the boundaries based on the enhanced CAS. Our proposed scheme achieves 39.91 and 29.78 average mAP on the challenge testing set of supervised and weakly-supervised temporal action localization track respectively.
Learning Attentive Pairwise Interaction for Fine-Grained Classification
Feb 24, 2020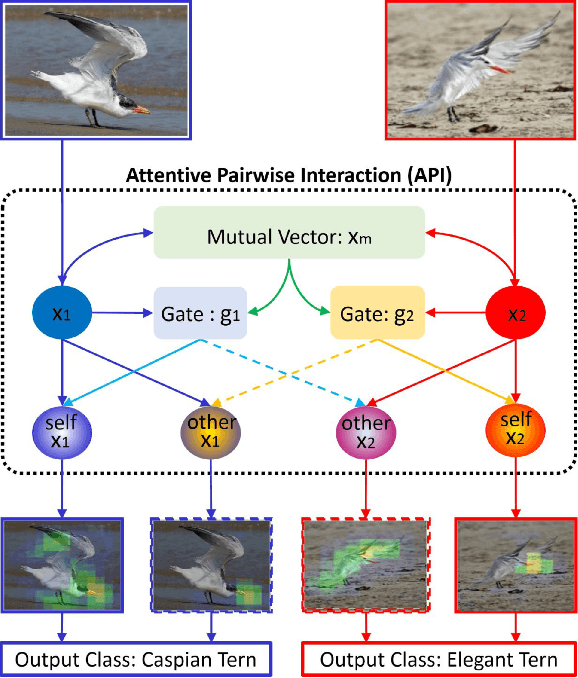

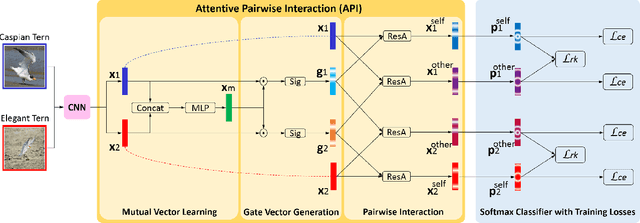

Abstract:Fine-grained classification is a challenging problem, due to subtle differences among highly-confused categories. Most approaches address this difficulty by learning discriminative representation of individual input image. On the other hand, humans can effectively identify contrastive clues by comparing image pairs. Inspired by this fact, this paper proposes a simple but effective Attentive Pairwise Interaction Network (API-Net), which can progressively recognize a pair of fine-grained images by interaction. Specifically, API-Net first learns a mutual feature vector to capture semantic differences in the input pair. It then compares this mutual vector with individual vectors to generate gates for each input image. These distinct gate vectors inherit mutual context on semantic differences, which allow API-Net to attentively capture contrastive clues by pairwise interaction between two images. Additionally, we train API-Net in an end-to-end manner with a score ranking regularization, which can further generalize API-Net by taking feature priorities into account. We conduct extensive experiments on five popular benchmarks in fine-grained classification. API-Net outperforms the recent SOTA methods, i.e., CUB-200-2011 (90.0%), Aircraft(93.9%), Stanford Cars (95.3%), Stanford Dogs (90.3%), and NABirds (88.1%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge