Paul Sajda
Structure Enables Effective Self-Localization of Errors in LLMs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Self-correction in language models remains elusive. In this work, we explore whether language models can explicitly localize errors in incorrect reasoning, as a path toward building AI systems that can effectively correct themselves. We introduce a prompting method that structures reasoning as discrete, semantically coherent thought steps, and show that models are able to reliably localize errors within this structure, while failing to do so in conventional, unstructured chain-of-thought reasoning. Motivated by how the human brain monitors errors at discrete decision points and resamples alternatives, we introduce Iterative Correction Sampling of Thoughts (Thought-ICS), a self-correction framework. Thought-ICS iteratively prompts the model to generate reasoning one discrete and complete thought at a time--where each thought represents a deliberate decision by the model--creating natural boundaries for precise error localization. Upon verification, the model localizes the first erroneous step, and the system backtracks to generate alternative reasoning from the last correct point. When asked to correct reasoning verified as incorrect by an oracle, Thought-ICS achieves 20-40% self-correction lift. In a completely autonomous setting without external verification, it outperforms contemporary self-correction baselines.
Internalizing Self-Consistency in Language Models: Multi-Agent Consensus Alignment
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Language Models (LMs) are inconsistent reasoners, often generating contradictory responses to identical prompts. While inference-time methods can mitigate these inconsistencies, they fail to address the core problem: LMs struggle to reliably select reasoning pathways leading to consistent outcomes under exploratory sampling. To address this, we formalize self-consistency as an intrinsic property of well-aligned reasoning models and introduce Multi-Agent Consensus Alignment (MACA), a reinforcement learning framework that post-trains models to favor reasoning trajectories aligned with their internal consensus using majority/minority outcomes from multi-agent debate. These trajectories emerge from deliberative exchanges where agents ground reasoning in peer arguments, not just aggregation of independent attempts, creating richer consensus signals than single-round majority voting. MACA enables agents to teach themselves to be more decisive and concise, and better leverage peer insights in multi-agent settings without external supervision, driving substantial improvements across self-consistency (+27.6% on GSM8K), single-agent reasoning (+23.7% on MATH), sampling-based inference (+22.4% Pass@20 on MATH), and multi-agent ensemble decision-making (+42.7% on MathQA). These findings, coupled with strong generalization to unseen benchmarks (+16.3% on GPQA, +11.6% on CommonsenseQA), demonstrate robust self-alignment that more reliably unlocks latent reasoning potential of language models.
Brain2Model Transfer: Training sensory and decision models with human neural activity as a teacher
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Transfer learning enhances the training of novel sensory and decision models by employing rich feature representations from large, pre-trained teacher models. Cognitive neuroscience shows that the human brain creates low-dimensional, abstract representations for efficient sensorimotor coding. Importantly, the brain can learn these representations with significantly fewer data points and less computational power than artificial models require. We introduce Brain2Model Transfer Learning (B2M), a framework where neural activity from human sensory and decision-making tasks acts as the teacher model for training artificial neural networks. We propose two B2M strategies: (1) Brain Contrastive Transfer, which aligns brain activity and network activations through a contrastive objective; and (2) Brain Latent Transfer, which projects latent dynamics from similar cognitive tasks onto student networks via supervised regression of brain-derived features. We validate B2M in memory-based decision-making with a recurrent neural network and scene reconstruction for autonomous driving with a variational autoencoder. The results show that student networks benefiting from brain-based transfer converge faster and achieve higher predictive accuracy than networks trained in isolation. Our findings indicate that the brain's representations are valuable for artificial learners, paving the way for more efficient learning of complex decision-making representations, which would be costly or slow through purely artificial training.
Physiologically-Informed Predictability of a Teammate's Future Actions Forecasts Team Performance
Jan 25, 2025



Abstract:In collaborative environments, a deep understanding of multi-human teaming dynamics is essential for optimizing performance. However, the relationship between individuals' behavioral and physiological markers and their combined influence on overall team performance remains poorly understood. To explore this, we designed a triadic human collaborative sensorimotor task in virtual reality (VR) and introduced a novel predictability metric to examine team dynamics and performance. Our findings reveal a strong connection between team performance and the predictability of a team member's future actions based on other team members' behavioral and physiological data. Contrary to conventional wisdom that high-performing teams are highly synchronized, our results suggest that physiological and behavioral synchronizations among team members have a limited correlation with team performance. These insights provide a new quantitative framework for understanding multi-human teaming, paving the way for deeper insights into team dynamics and performance.
EEG-estimated functional connectivity, and not behavior, differentiates Parkinson's patients from health controls during the Simon conflict task
Oct 09, 2024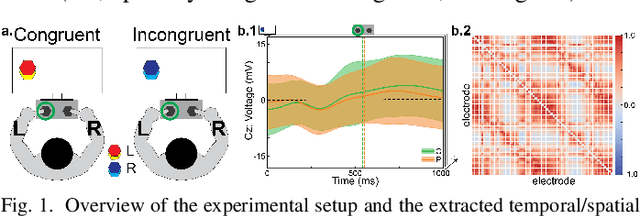
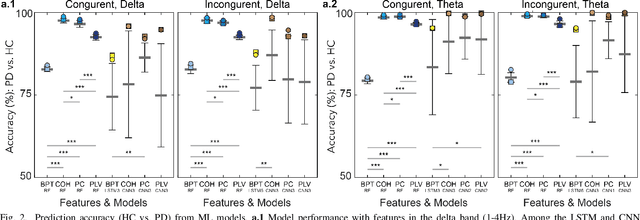
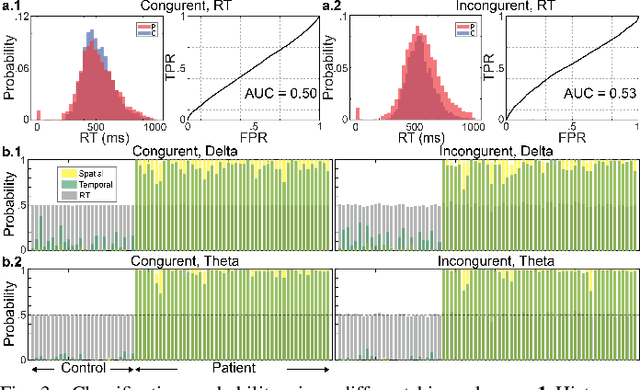
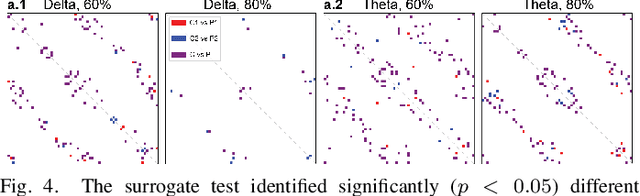
Abstract:Neural biomarkers that can classify or predict disease are of broad interest to the neurological and psychiatric communities. Such biomarkers can be informative of disease state or treatment efficacy, even before there are changes in symptoms and/or behavior. This work investigates EEG-estimated functional connectivity (FC) as a Parkinson's Disease (PD) biomarker. Specifically, we investigate FC mediated via neural oscillations and consider such activity during the Simons conflict task. This task yields sensory-motor conflict, and one might expect differences in behavior between PD patients and healthy controls (HCs). In addition to considering spatially focused approaches, such as FC, as a biomarker, we also consider temporal biomarkers, which are more sensitive to ongoing changes in neural activity. We find that FC, estimated from delta (1-4Hz) and theta (4-7Hz) oscillations, yields spatial FC patterns significantly better at distinguishing PD from HC than temporal features or behavior. This study reinforces that FC in spectral bands is informative of differences in brain-wide processes and can serve as a biomarker distinguishing normal brain function from that seen in disease.
Enabling Multi-Robot Collaboration from Single-Human Guidance
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Learning collaborative behaviors is essential for multi-agent systems. Traditionally, multi-agent reinforcement learning solves this implicitly through a joint reward and centralized observations, assuming collaborative behavior will emerge. Other studies propose to learn from demonstrations of a group of collaborative experts. Instead, we propose an efficient and explicit way of learning collaborative behaviors in multi-agent systems by leveraging expertise from only a single human. Our insight is that humans can naturally take on various roles in a team. We show that agents can effectively learn to collaborate by allowing a human operator to dynamically switch between controlling agents for a short period and incorporating a human-like theory-of-mind model of teammates. Our experiments showed that our method improves the success rate of a challenging collaborative hide-and-seek task by up to 58$% with only 40 minutes of human guidance. We further demonstrate our findings transfer to the real world by conducting multi-robot experiments.
Circular Clustering with Polar Coordinate Reconstruction
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:There is a growing interest in characterizing circular data found in biological systems. Such data are wide ranging and varied, from signal phase in neural recordings to nucleotide sequences in round genomes. Traditional clustering algorithms are often inadequate due to their limited ability to distinguish differences in the periodic component. Current clustering schemes that work in a polar coordinate system have limitations, such as being only angle-focused or lacking generality. To overcome these limitations, we propose a new analysis framework that utilizes projections onto a cylindrical coordinate system to better represent objects in a polar coordinate system. Using the mathematical properties of circular data, we show our approach always finds the correct clustering result within the reconstructed dataset, given sufficient periodic repetitions of the data. Our approach is generally applicable and adaptable and can be incorporated into most state-of-the-art clustering algorithms. We demonstrate on synthetic and real data that our method generates more appropriate and consistent clustering results compared to standard methods. In summary, our proposed analysis framework overcomes the limitations of existing polar coordinate-based clustering methods and provides a more accurate and efficient way to cluster circular data.
Fixating on Attention: Integrating Human Eye Tracking into Vision Transformers
Aug 26, 2023



Abstract:Modern transformer-based models designed for computer vision have outperformed humans across a spectrum of visual tasks. However, critical tasks, such as medical image interpretation or autonomous driving, still require reliance on human judgments. This work demonstrates how human visual input, specifically fixations collected from an eye-tracking device, can be integrated into transformer models to improve accuracy across multiple driving situations and datasets. First, we establish the significance of fixation regions in left-right driving decisions, as observed in both human subjects and a Vision Transformer (ViT). By comparing the similarity between human fixation maps and ViT attention weights, we reveal the dynamics of overlap across individual heads and layers. This overlap is exploited for model pruning without compromising accuracy. Thereafter, we incorporate information from the driving scene with fixation data, employing a "joint space-fixation" (JSF) attention setup. Lastly, we propose a "fixation-attention intersection" (FAX) loss to train the ViT model to attend to the same regions that humans fixated on. We find that the ViT performance is improved in accuracy and number of training epochs when using JSF and FAX. These results hold significant implications for human-guided artificial intelligence.
Bayesian Beta-Bernoulli Process Sparse Coding with Deep Neural Networks
Mar 14, 2023



Abstract:Several approximate inference methods have been proposed for deep discrete latent variable models. However, non-parametric methods which have previously been successfully employed for classical sparse coding models have largely been unexplored in the context of deep models. We propose a non-parametric iterative algorithm for learning discrete latent representations in such deep models. Additionally, to learn scale invariant discrete features, we propose local data scaling variables. Lastly, to encourage sparsity in our representations, we propose a Beta-Bernoulli process prior on the latent factors. We evaluate our spare coding model coupled with different likelihood models. We evaluate our method across datasets with varying characteristics and compare our results to current amortized approximate inference methods.
Inferring latent neural sources via deep transcoding of simultaneously acquired EEG and fMRI
Nov 27, 2022Abstract:Simultaneous EEG-fMRI is a multi-modal neuroimaging technique that provides complementary spatial and temporal resolution. Challenging has been developing principled and interpretable approaches for fusing the modalities, specifically approaches enabling inference of latent source spaces representative of neural activity. In this paper, we address this inference problem within the framework of transcoding -- mapping from a specific encoding (modality) to a decoding (the latent source space) and then encoding the latent source space to the other modality. Specifically, we develop a symmetric method consisting of a cyclic convolutional transcoder that transcodes EEG to fMRI and vice versa. Without any prior knowledge of either the hemodynamic response function or lead field matrix, the complete data-driven method exploits the temporal and spatial relationships between the modalities and latent source spaces to learn these mappings. We quantify, for both the simulated and real EEG-fMRI data, how well the modalities can be transcoded from one to another as well as the source spaces that are recovered, all evaluated on unseen data. In addition to enabling a new way to symmetrically infer a latent source space, the method can also be seen as low-cost computational neuroimaging -- i.e. generating an 'expensive' fMRI BOLD image from 'low cost' EEG data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge