EEG-estimated functional connectivity, and not behavior, differentiates Parkinson's patients from health controls during the Simon conflict task
Paper and Code
Oct 09, 2024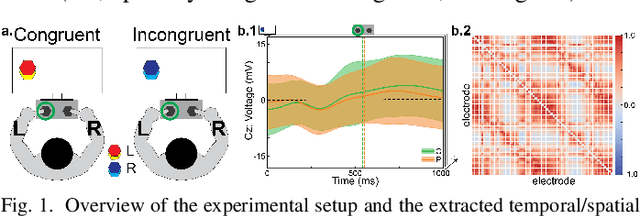
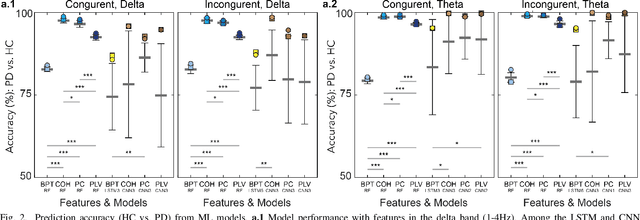
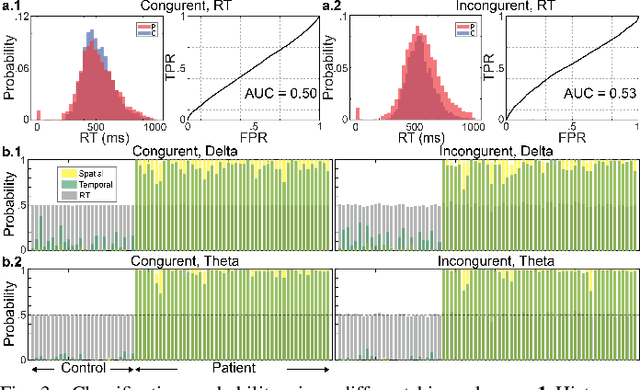
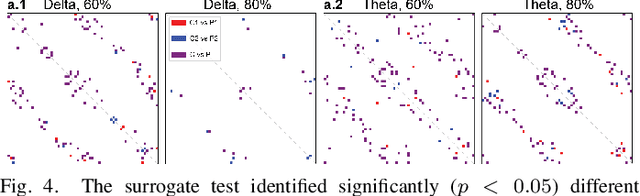
Neural biomarkers that can classify or predict disease are of broad interest to the neurological and psychiatric communities. Such biomarkers can be informative of disease state or treatment efficacy, even before there are changes in symptoms and/or behavior. This work investigates EEG-estimated functional connectivity (FC) as a Parkinson's Disease (PD) biomarker. Specifically, we investigate FC mediated via neural oscillations and consider such activity during the Simons conflict task. This task yields sensory-motor conflict, and one might expect differences in behavior between PD patients and healthy controls (HCs). In addition to considering spatially focused approaches, such as FC, as a biomarker, we also consider temporal biomarkers, which are more sensitive to ongoing changes in neural activity. We find that FC, estimated from delta (1-4Hz) and theta (4-7Hz) oscillations, yields spatial FC patterns significantly better at distinguishing PD from HC than temporal features or behavior. This study reinforces that FC in spectral bands is informative of differences in brain-wide processes and can serve as a biomarker distinguishing normal brain function from that seen in disease.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge