Paul M Thompson
Tackling the dimensions in imaging genetics with CLUB-PLS
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:A major challenge in imaging genetics and similar fields is to link high-dimensional data in one domain, e.g., genetic data, to high dimensional data in a second domain, e.g., brain imaging data. The standard approach in the area are mass univariate analyses across genetic factors and imaging phenotypes. That entails executing one genome-wide association study (GWAS) for each pre-defined imaging measure. Although this approach has been tremendously successful, one shortcoming is that phenotypes must be pre-defined. Consequently, effects that are not confined to pre-selected regions of interest or that reflect larger brain-wide patterns can easily be missed. In this work we introduce a Partial Least Squares (PLS)-based framework, which we term Cluster-Bootstrap PLS (CLUB-PLS), that can work with large input dimensions in both domains as well as with large sample sizes. One key factor of the framework is to use cluster bootstrap to provide robust statistics for single input features in both domains. We applied CLUB-PLS to investigating the genetic basis of surface area and cortical thickness in a sample of 33,000 subjects from the UK Biobank. We found 107 genome-wide significant locus-phenotype pairs that are linked to 386 different genes. We found that a vast majority of these loci could be technically validated at a high rate: using classic GWAS or Genome-Wide Inferred Statistics (GWIS) we found that 85 locus-phenotype pairs exceeded the genome-wide suggestive (P<1e-05) threshold.
Linking Symptom Inventories using Semantic Textual Similarity
Sep 08, 2023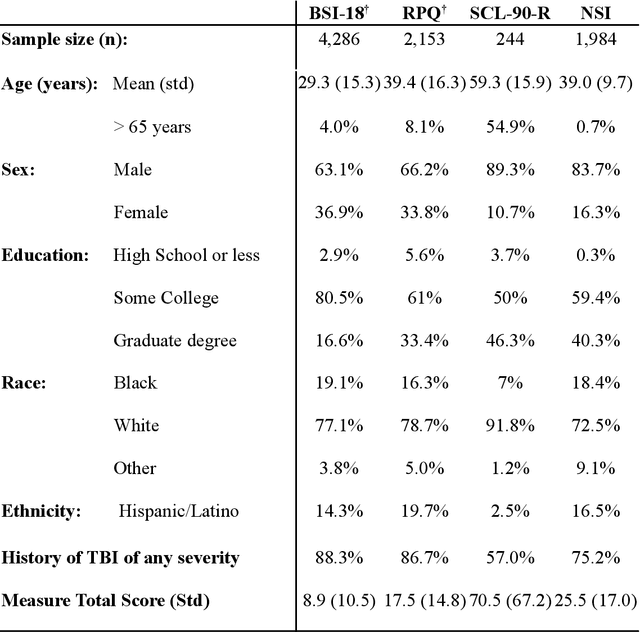
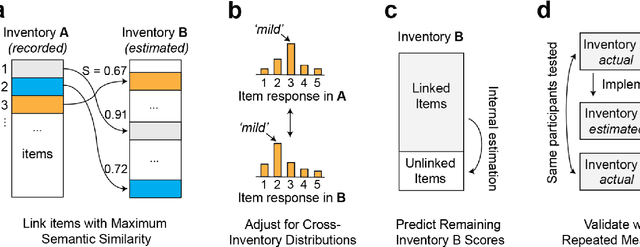
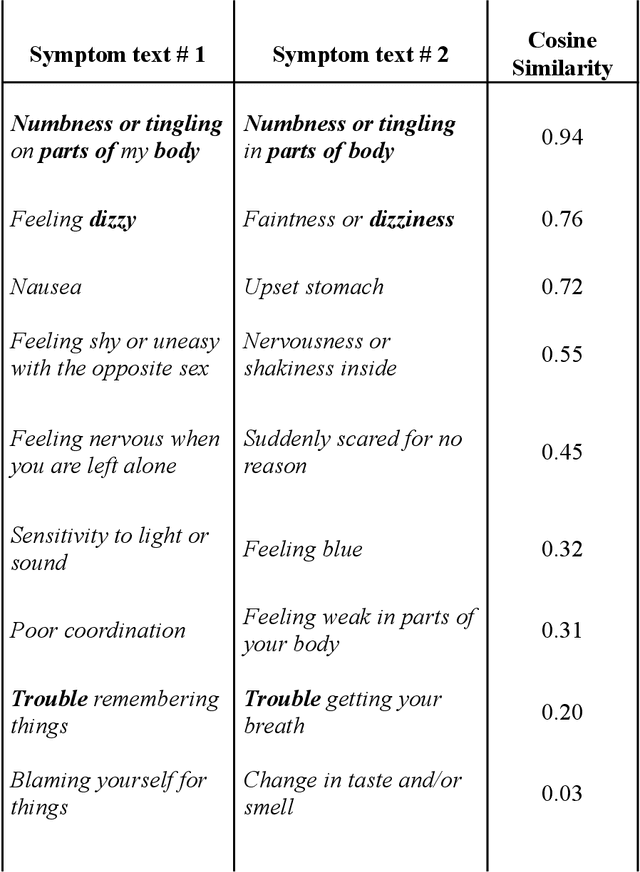
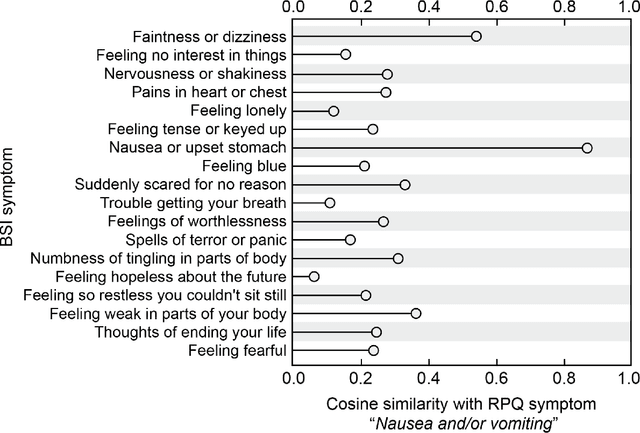
Abstract:An extensive library of symptom inventories has been developed over time to measure clinical symptoms, but this variety has led to several long standing issues. Most notably, results drawn from different settings and studies are not comparable, which limits reproducibility. Here, we present an artificial intelligence (AI) approach using semantic textual similarity (STS) to link symptoms and scores across previously incongruous symptom inventories. We tested the ability of four pre-trained STS models to screen thousands of symptom description pairs for related content - a challenging task typically requiring expert panels. Models were tasked to predict symptom severity across four different inventories for 6,607 participants drawn from 16 international data sources. The STS approach achieved 74.8% accuracy across five tasks, outperforming other models tested. This work suggests that incorporating contextual, semantic information can assist expert decision-making processes, yielding gains for both general and disease-specific clinical assessment.
Federated Learning in Distributed Medical Databases: Meta-Analysis of Large-Scale Subcortical Brain Data
Oct 22, 2018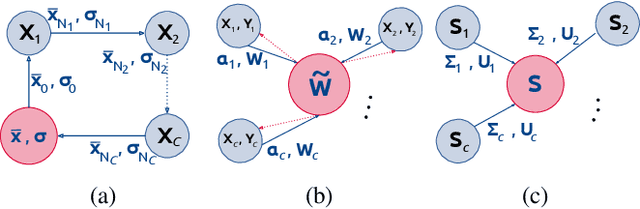
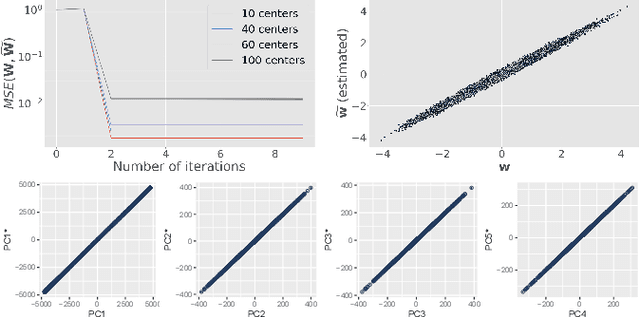
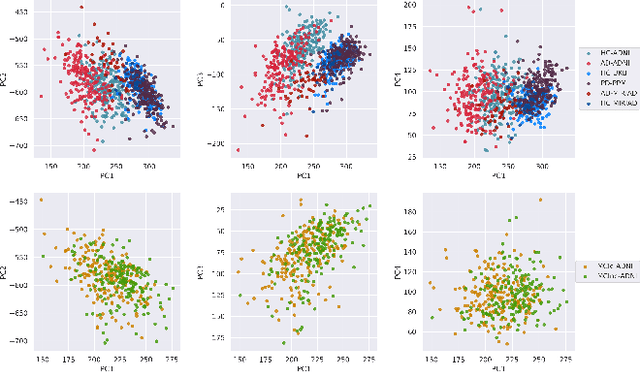
Abstract:At this moment, databanks worldwide contain brain images of previously unimaginable numbers. Combined with developments in data science, these massive data provide the potential to better understand the genetic underpinnings of brain diseases. However, different datasets, which are stored at different institutions, cannot always be shared directly due to privacy and legal concerns, thus limiting the full exploitation of big data in the study of brain disorders. Here we propose a federated learning framework for securely accessing and meta-analyzing any biomedical data without sharing individual information. We illustrate our framework by investigating brain structural relationships across diseases and clinical cohorts. The framework is first tested on synthetic data and then applied to multi-centric, multi-database studies including ADNI, PPMI, MIRIAD and UK Biobank, showing the potential of the approach for further applications in distributed analysis of multi-centric cohorts
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge