Kelly S Peterson
VA Salt Lake City Health Care System, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA
Linking Symptom Inventories using Semantic Textual Similarity
Sep 08, 2023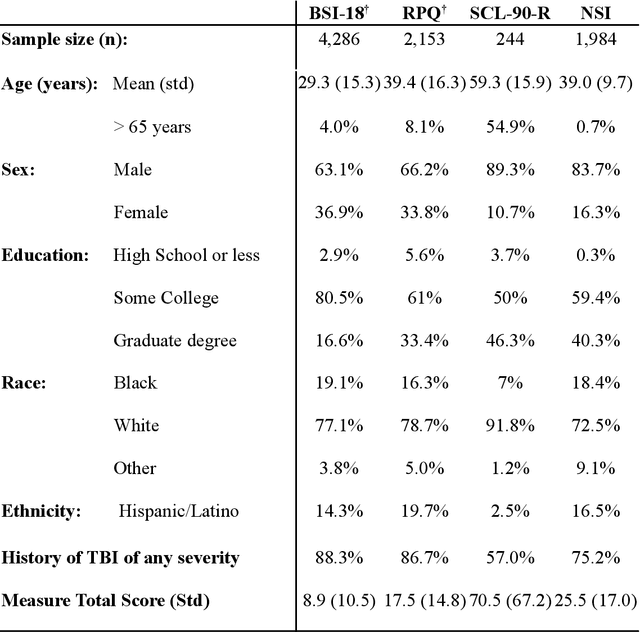
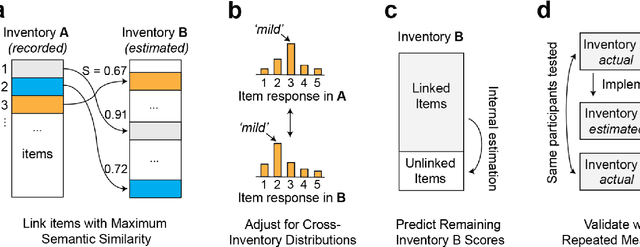
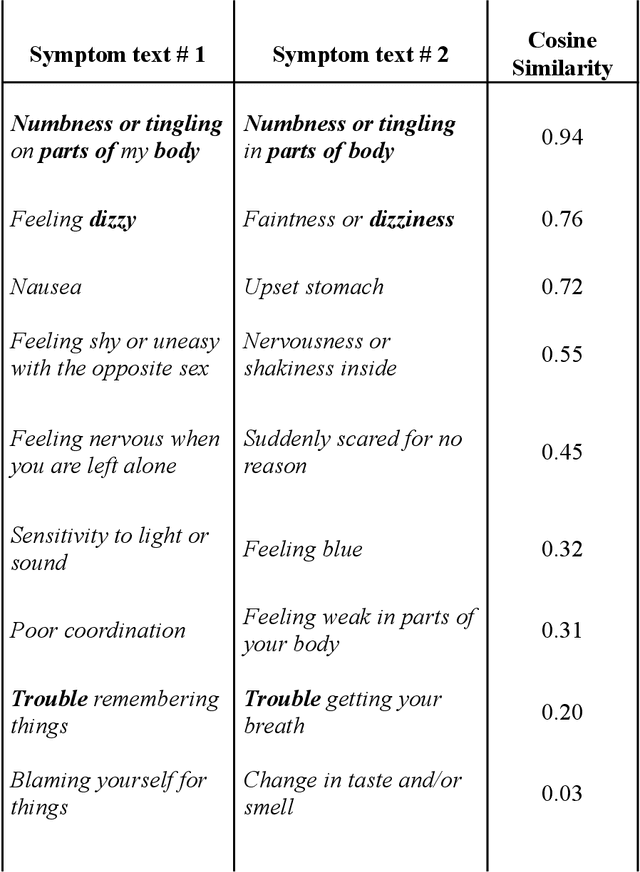
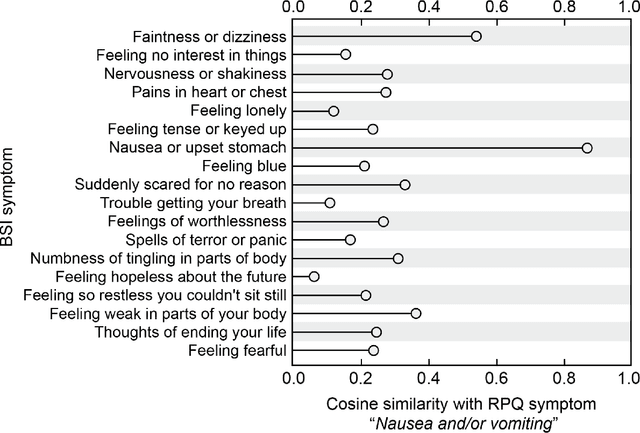
Abstract:An extensive library of symptom inventories has been developed over time to measure clinical symptoms, but this variety has led to several long standing issues. Most notably, results drawn from different settings and studies are not comparable, which limits reproducibility. Here, we present an artificial intelligence (AI) approach using semantic textual similarity (STS) to link symptoms and scores across previously incongruous symptom inventories. We tested the ability of four pre-trained STS models to screen thousands of symptom description pairs for related content - a challenging task typically requiring expert panels. Models were tasked to predict symptom severity across four different inventories for 6,607 participants drawn from 16 international data sources. The STS approach achieved 74.8% accuracy across five tasks, outperforming other models tested. This work suggests that incorporating contextual, semantic information can assist expert decision-making processes, yielding gains for both general and disease-specific clinical assessment.
Launching into clinical space with medspaCy: a new clinical text processing toolkit in Python
Jun 14, 2021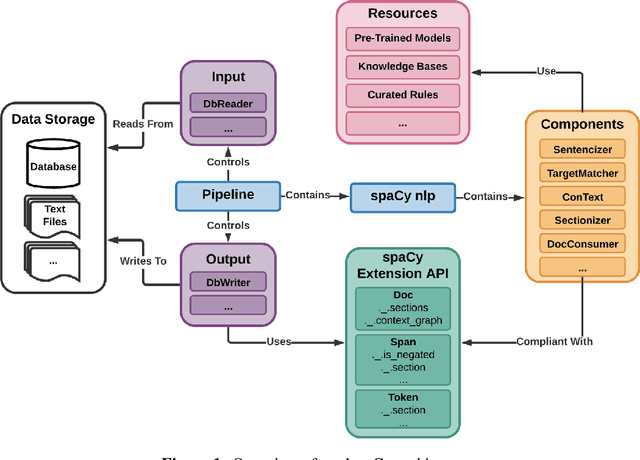
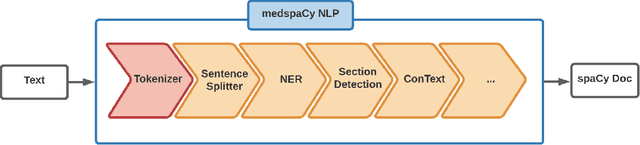
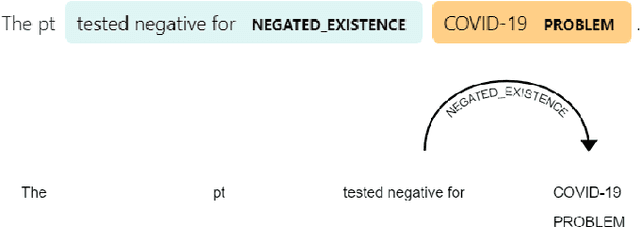
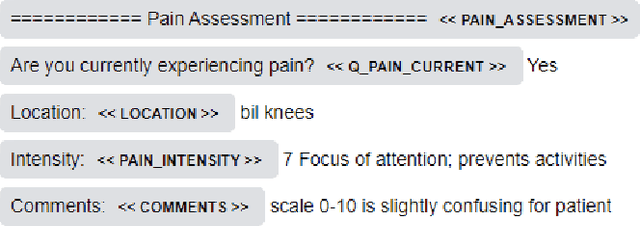
Abstract:Despite impressive success of machine learning algorithms in clinical natural language processing (cNLP), rule-based approaches still have a prominent role. In this paper, we introduce medspaCy, an extensible, open-source cNLP library based on spaCy framework that allows flexible integration of rule-based and machine learning-based algorithms adapted to clinical text. MedspaCy includes a variety of components that meet common cNLP needs such as context analysis and mapping to standard terminologies. By utilizing spaCy's clear and easy-to-use conventions, medspaCy enables development of custom pipelines that integrate easily with other spaCy-based modules. Our toolkit includes several core components and facilitates rapid development of pipelines for clinical text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge