Patrícia Alves-Oliveira
Painted Heart Beats
Nov 19, 2025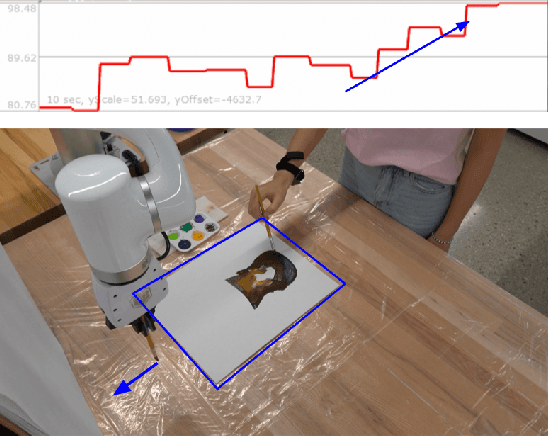
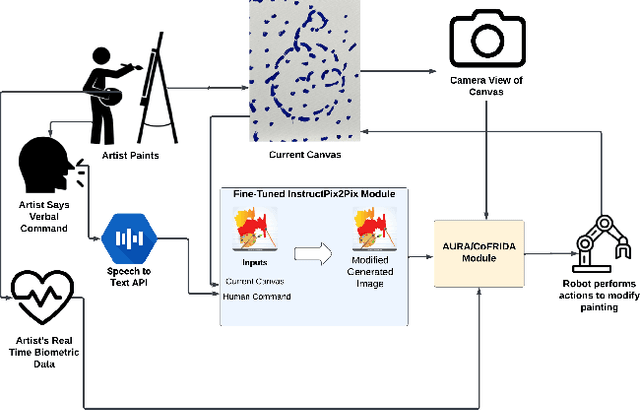
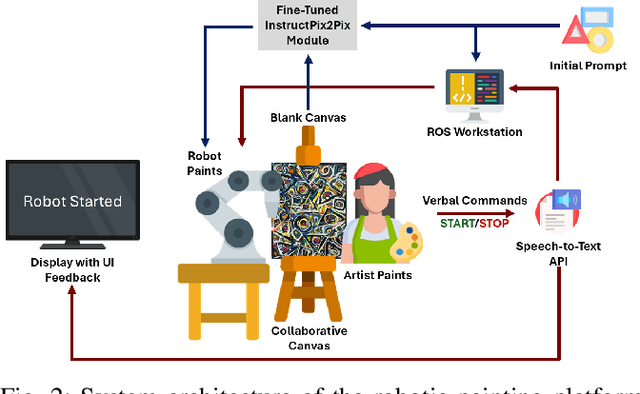
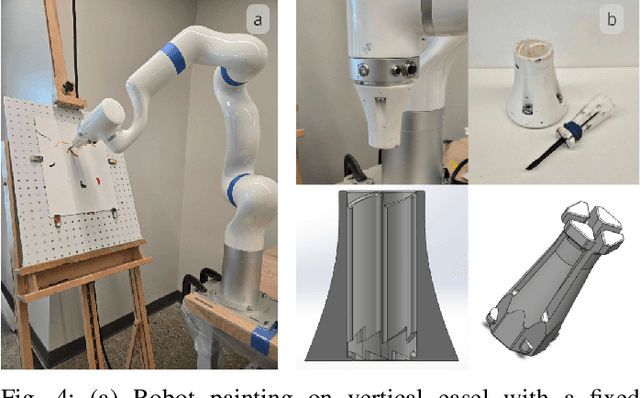
Abstract:In this work we present AURA, a framework for synergistic human-artist painting. We developed a robot arm that collaboratively paints with a human artist. The robot has an awareness of the artist's heartbeat through the EmotiBit sensor, which provides the arousal levels of the painter. Given the heartbeat detected, the robot decides to increase proximity to the artist's workspace or retract. If a higher heartbeat is detected, which is associated with increased arousal in human artists, the robot will move away from that area of the canvas. If the artist's heart rate is detected as neutral, indicating the human artist's baseline state, the robot will continue its painting actions across the entire canvas. We also demonstrate and propose alternative robot-artist interactions using natural language and physical touch. This work combines the biometrics of a human artist to inform fluent artistic interactions.
Artists' Views on Robotics Involvement in Painting Productions
Oct 08, 2025

Abstract:As robotic technologies evolve, their potential in artistic creation becomes an increasingly relevant topic of inquiry. This study explores how professional abstract artists perceive and experience co-creative interactions with an autonomous painting robotic arm. Eight artists engaged in six painting sessions -- three with a human partner, followed by three with the robot -- and subsequently participated in semi-structured interviews analyzed through reflexive thematic analysis. Human-human interactions were described as intuitive, dialogic, and emotionally engaging, whereas human-robot sessions felt more playful and reflective, offering greater autonomy and prompting for novel strategies to overcome the system's limitations. This work offers one of the first empirical investigations into artists' lived experiences with a robot, highlighting the value of long-term engagement and a multidisciplinary approach to human-robot co-creation.
Multiple Ways of Working with Users to Develop Physically Assistive Robots
Mar 07, 2024
Abstract:Despite the growth of physically assistive robotics (PAR) research over the last decade, nearly half of PAR user studies do not involve participants with the target disabilities. There are several reasons for this -- recruitment challenges, small sample sizes, and transportation logistics -- all influenced by systemic barriers that people with disabilities face. However, it is well-established that working with end-users results in technology that better addresses their needs and integrates with their lived circumstances. In this paper, we reflect on multiple approaches we have taken to working with people with motor impairments across the design, development, and evaluation of three PAR projects: (a) assistive feeding with a robot arm; (b) assistive teleoperation with a mobile manipulator; and (c) shared control with a robot arm. We discuss these approaches to working with users along three dimensions -- individual vs. community-level insight, logistic burden on end-users vs. researchers, and benefit to researchers vs. community -- and share recommendations for how other PAR researchers can incorporate users into their work.
Software architecture for YOLO, a creativity-stimulating robot
Sep 24, 2019



Abstract:YOLO is a social robot designed and developed to stimulate creativity in children through storytelling activities. Children use it as a character in their stories. This article details the artificial intelligence software developed for YOLO. The implemented software schedules through several Creativity Behaviors to find the ones that stimulate creativity more effectively. YOLO can choose between convergent and divergent thinking techniques, two important processes of creative thought. These techniques were developed based on the psychological theories of creativity development and on research from creativity experts who work with children. Additionally, this software allows the creation of Social Behaviors that enable the robot to behave as a believable character. On top of our framework, we built 3 main social behavior parameters: Exuberant, Aloof, and Harmonious. These behaviors are meant to ease immersive play and the process of character creation. The 3 social behaviors were based on psychological theories of personality and developed using children's input during co-design studies. Overall, this work presents an attempt to design, develop, and deploy social robots that nurture intrinsic human abilities, such as the ability to be creative.
An extended framework for characterizing social robots
Jul 23, 2019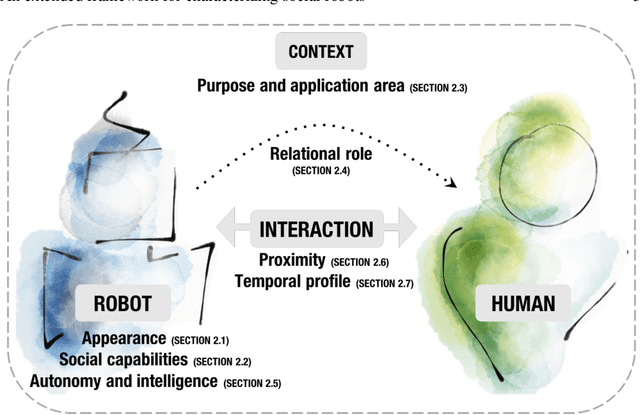
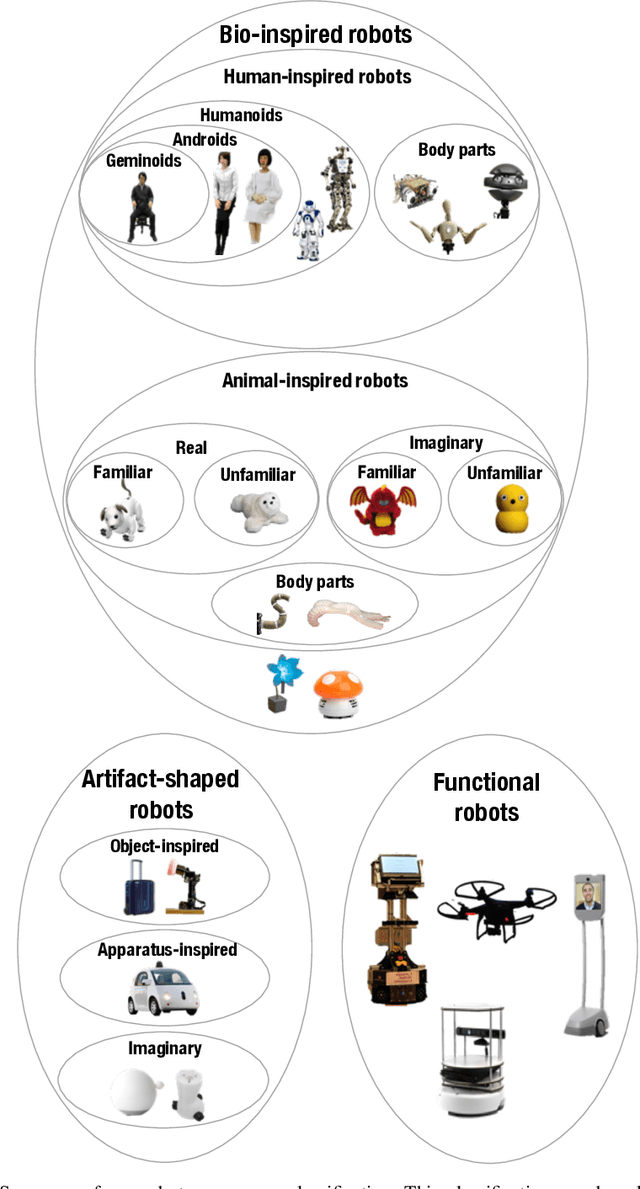
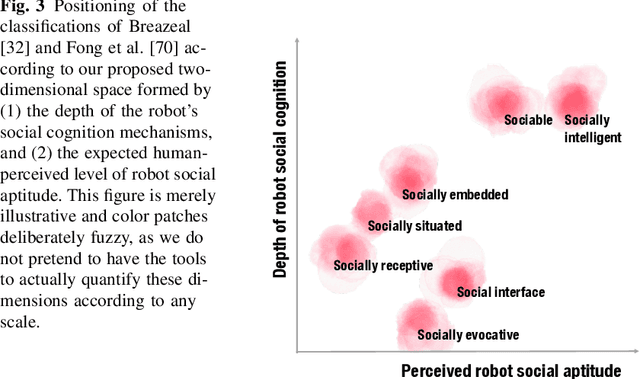

Abstract:Social robots are becoming increasingly diverse in their design, behavior, and usage. In this chapter, we provide a broad-ranging overview of the main characteristics that arise when one considers social robots and their interactions with humans. We specifically contribute a framework for characterizing social robots along 7 dimensions that we found to be most relevant to their design. These dimensions are: appearance, social capabilities, purpose and application area, relational role, autonomy and intelligence, proximity, and temporal profile. Within each dimension, we account for the variety of social robots through a combination of classifications and/or explanations. Our framework builds on and goes beyond existing frameworks, such as classifications and taxonomies found in the literature. More specifically, it contributes to the unification, clarification, and extension of key concepts, drawing from a rich body of relevant literature. This chapter is meant to serve as a resource for researchers, designers, and developers within and outside the field of social robotics. It is intended to provide them with tools to better understand and position existing social robots, as well as to inform their future design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge