Pamela Guevara
Federated Learning Enables Big Data for Rare Cancer Boundary Detection
Apr 25, 2022Abstract:Although machine learning (ML) has shown promise in numerous domains, there are concerns about generalizability to out-of-sample data. This is currently addressed by centrally sharing ample, and importantly diverse, data from multiple sites. However, such centralization is challenging to scale (or even not feasible) due to various limitations. Federated ML (FL) provides an alternative to train accurate and generalizable ML models, by only sharing numerical model updates. Here we present findings from the largest FL study to-date, involving data from 71 healthcare institutions across 6 continents, to generate an automatic tumor boundary detector for the rare disease of glioblastoma, utilizing the largest dataset of such patients ever used in the literature (25,256 MRI scans from 6,314 patients). We demonstrate a 33% improvement over a publicly trained model to delineate the surgically targetable tumor, and 23% improvement over the tumor's entire extent. We anticipate our study to: 1) enable more studies in healthcare informed by large and diverse data, ensuring meaningful results for rare diseases and underrepresented populations, 2) facilitate further quantitative analyses for glioblastoma via performance optimization of our consensus model for eventual public release, and 3) demonstrate the effectiveness of FL at such scale and task complexity as a paradigm shift for multi-site collaborations, alleviating the need for data sharing.
GeoSP: A parallel method for a cortical surface parcellation based on geodesic distance
Mar 26, 2021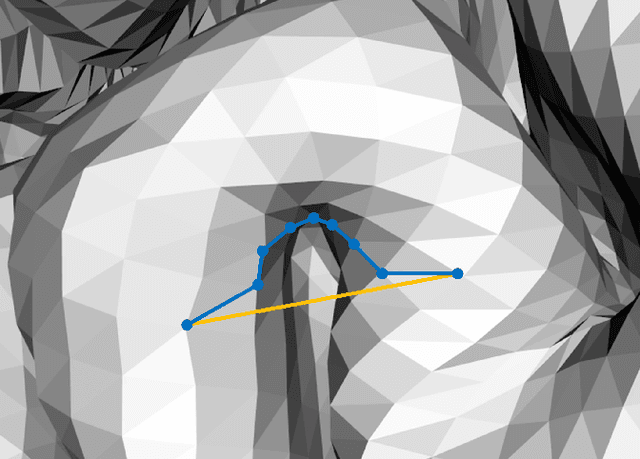
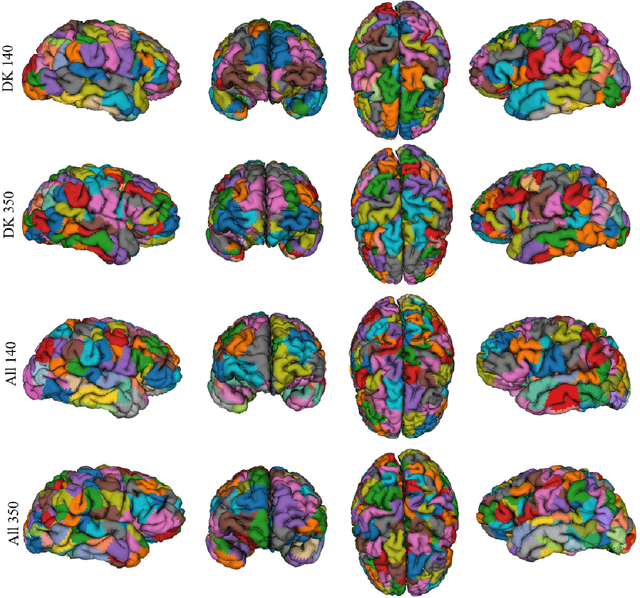
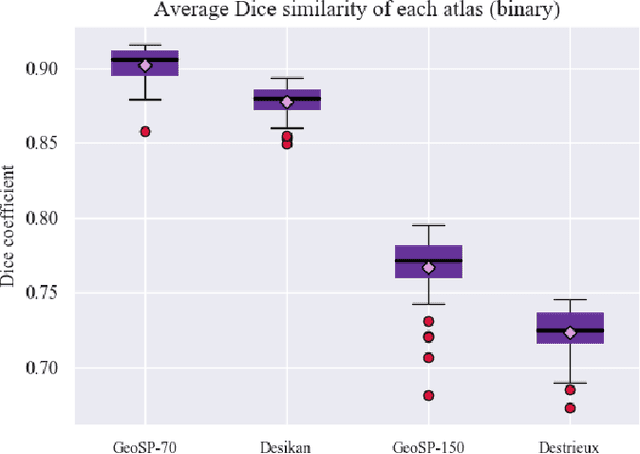
Abstract:We present GeoSP, a parallel method that creates a parcellation of the cortical mesh based on a geodesic distance, in order to consider gyri and sulci topology. The method represents the mesh with a graph and performs a K-means clustering in parallel. It has two modes of use, by default, it performs the geodesic cortical parcellation based on the boundaries of the anatomical parcels provided by the Desikan-Killiany atlas. The other mode performs the complete parcellation of the cortex. Results for both modes and with different values for the total number of sub-parcels show homogeneous sub-parcels. Furthermore, the execution time is 82 s for the whole cortex mode and 18 s for the Desikan-Killiany atlas subdivision, for a parcellation into 350 sub-parcels. The proposed method will be available to the community to perform the evaluation of data-driven cortical parcellations. As an example, we compared GeoSP parcellation with Desikan-Killiany and Destrieux atlases in 50 subjects, obtaining more homogeneous parcels for GeoSP and minor differences in structural connectivity reproducibility across subjects.
Cortical surface parcellation based on intra-subject white matter fiber clustering
Feb 16, 2020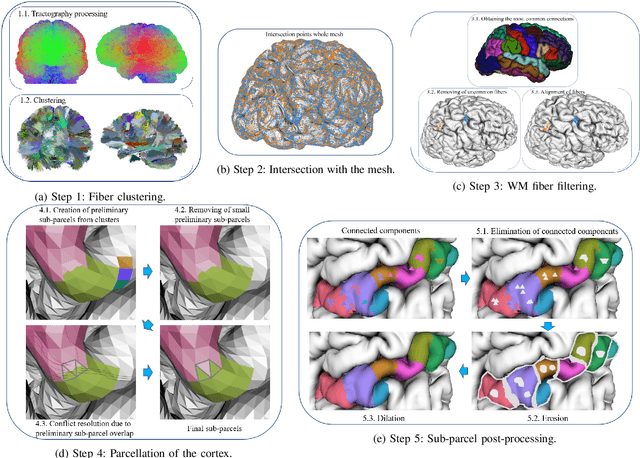
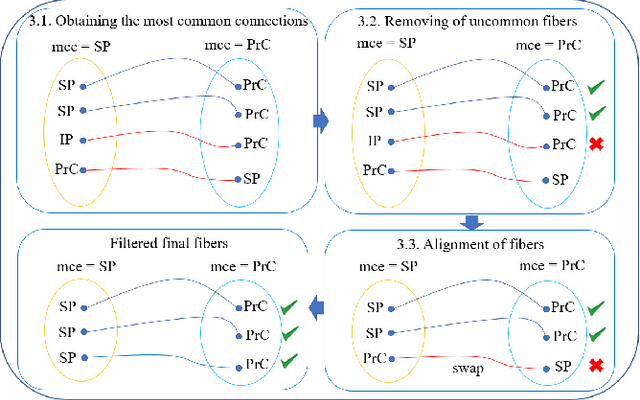
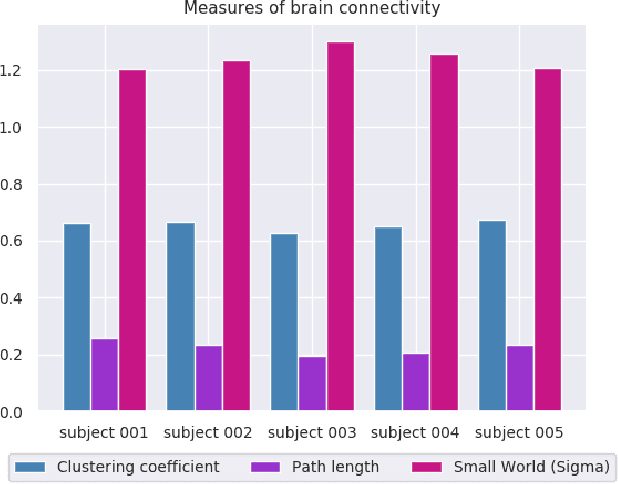
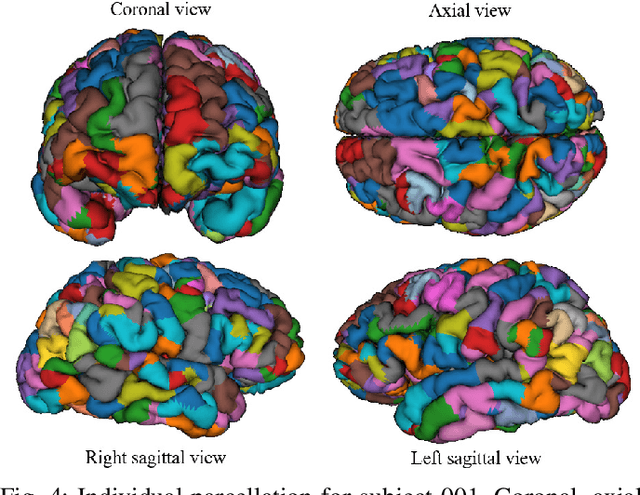
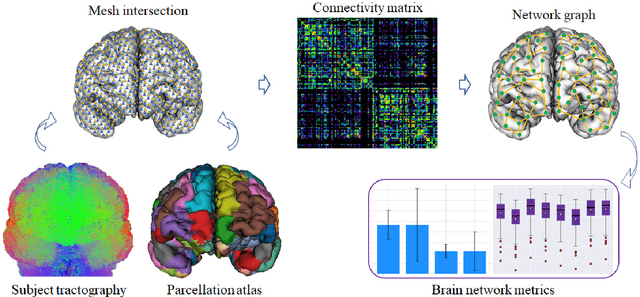
Abstract:We present a hybrid method that performs the complete parcellation of the cerebral cortex of an individual, based on the connectivity information of the white matter fibers from a whole-brain tractography dataset. The method consists of five steps, first intra-subject clustering is performed on the brain tractography. The fibers that make up each cluster are then intersected with the cortical mesh and then filtered to discard outliers. In addition, the method resolves the overlapping between the different intersection regions (sub-parcels) throughout the cortex efficiently. Finally, a post-processing is done to achieve more uniform sub-parcels. The output is the complete labeling of cortical mesh vertices, representing the different cortex sub-parcels, with strong connections to other sub-parcels. We evaluated our method with measures of brain connectivity such as functional segregation (clustering coefficient), functional integration (characteristic path length) and small-world. Results in five subjects from ARCHI database show a good individual cortical parcellation for each one, composed of about 200 subparcels per hemisphere and complying with these connectivity measures.
Parallel optimization of fiber bundle segmentation for massive tractography datasets
Dec 24, 2019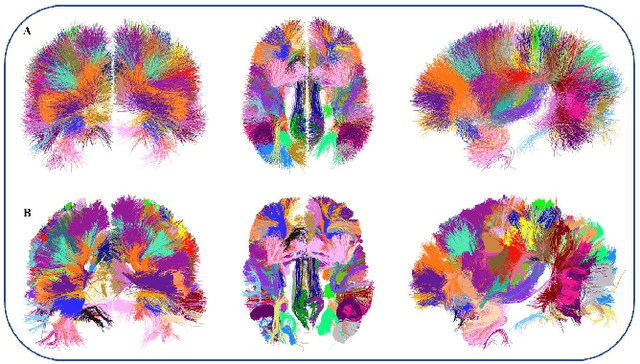
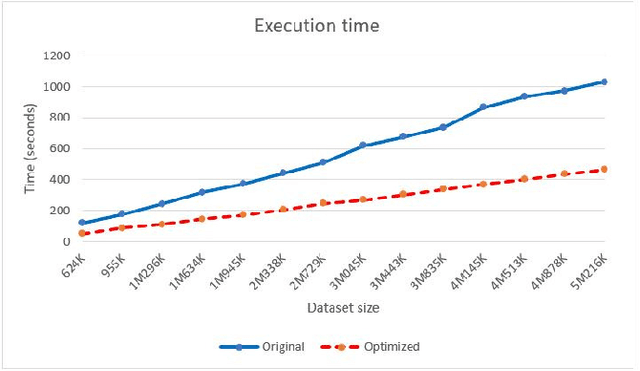
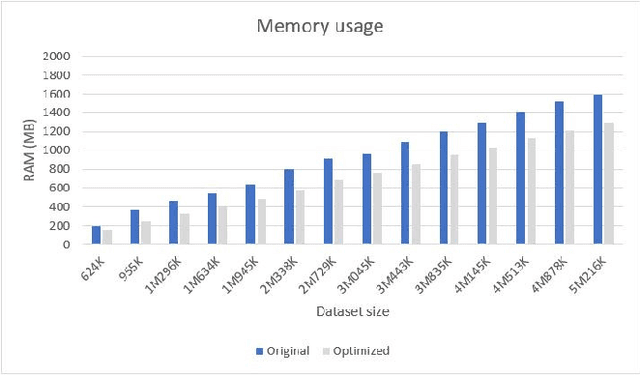
Abstract:We present an optimized algorithm that performs automatic classification of white matter fibers based on a multi-subject bundle atlas. We implemented a parallel algorithm that improves upon its previous version in both execution time and memory usage. Our new version uses the local memory of each processor, which leads to a reduction in execution time. Hence, it allows the analysis of bigger subject and/or atlas datasets. As a result, the segmentation of a subject of 4,145,000 fibers is reduced from about 14 minutes in the previous version to about 6 minutes, yielding an acceleration of 2.34. In addition, the new algorithm reduces the memory consumption of the previous version by a factor of 0.79.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge