Pai Chet Ng
ARMOR: Agentic Reasoning for Methods Orchestration and Reparameterization for Robust Adversarial Attacks
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Existing automated attack suites operate as static ensembles with fixed sequences, lacking strategic adaptation and semantic awareness. This paper introduces the Agentic Reasoning for Methods Orchestration and Reparameterization (ARMOR) framework to address these limitations. ARMOR orchestrates three canonical adversarial primitives, Carlini-Wagner (CW), Jacobian-based Saliency Map Attack (JSMA), and Spatially Transformed Attacks (STA) via Vision Language Models (VLM)-guided agents that collaboratively generate and synthesize perturbations through a shared ``Mixing Desk". Large Language Models (LLMs) adaptively tune and reparameterize parallel attack agents in a real-time, closed-loop system that exploits image-specific semantic vulnerabilities. On standard benchmarks, ARMOR achieves improved cross-architecture transfer and reliably fools both settings, delivering a blended output for blind targets and selecting the best attack or blended attacks for white-box targets using a confidence-and-SSIM score.
Yes FLoReNce, I Will Do Better Next Time! Agentic Feedback Reasoning for Humorous Meme Detection
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Humorous memes blend visual and textual cues to convey irony, satire, or social commentary, posing unique challenges for AI systems that must interpret intent rather than surface correlations. Existing multimodal or prompting-based models generate explanations for humor but operate in an open loop,lacking the ability to critique or refine their reasoning once a prediction is made. We propose FLoReNce, an agentic feedback reasoning framework that treats meme understanding as a closed-loop process during learning and an open-loop process during inference. In the closed loop, a reasoning agent is critiqued by a judge; the error and semantic feedback are converted into control signals and stored in a feedback-informed, non-parametric knowledge base. At inference, the model retrieves similar judged experiences from this KB and uses them to modulate its prompt, enabling better, self-aligned reasoning without finetuning. On the PrideMM dataset, FLoReNce improves both predictive performance and explanation quality over static multimodal baselines, showing that feedback-regulated prompting is a viable path to adaptive meme humor understanding.
CLARITY: Contextual Linguistic Adaptation and Accent Retrieval for Dual-Bias Mitigation in Text-to-Speech Generation
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Instruction-guided text-to-speech (TTS) research has reached a maturity level where excellent speech generation quality is possible on demand, yet two coupled biases persist: accent bias, where models default to dominant phonetic patterns, and linguistic bias, where dialect-specific lexical and cultural cues are ignored. These biases are interdependent, as authentic accent generation requires both accent fidelity and localized text. We present Contextual Linguistic Adaptation and Retrieval for Inclusive TTS sYnthesis (CLARITY), a backbone-agnostic framework that addresses these biases through dual-signal optimization: (i) contextual linguistic adaptation that localizes input text to the target dialect, and (ii) retrieval-augmented accent prompting (RAAP) that supplies accent-consistent speech prompts. Across twelve English accents, CLARITY improves accent accuracy and fairness while maintaining strong perceptual quality.
MS-GAGA: Metric-Selective Guided Adversarial Generation Attack
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:We present MS-GAGA (Metric-Selective Guided Adversarial Generation Attack), a two-stage framework for crafting transferable and visually imperceptible adversarial examples against deepfake detectors in black-box settings. In Stage 1, a dual-stream attack module generates adversarial candidates: MNTD-PGD applies enhanced gradient calculations optimized for small perturbation budgets, while SG-PGD focuses perturbations on visually salient regions. This complementary design expands the adversarial search space and improves transferability across unseen models. In Stage 2, a metric-aware selection module evaluates candidates based on both their success against black-box models and their structural similarity (SSIM) to the original image. By jointly optimizing transferability and imperceptibility, MS-GAGA achieves up to 27% higher misclassification rates on unseen detectors compared to state-of-the-art attacks.
Exploring Machine Learning and Language Models for Multimodal Depression Detection
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:This paper presents our approach to the first Multimodal Personality-Aware Depression Detection Challenge, focusing on multimodal depression detection using machine learning and deep learning models. We explore and compare the performance of XGBoost, transformer-based architectures, and large language models (LLMs) on audio, video, and text features. Our results highlight the strengths and limitations of each type of model in capturing depression-related signals across modalities, offering insights into effective multimodal representation strategies for mental health prediction.
On-Device LLMs for SMEs: Challenges and Opportunities
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a systematic review of the infrastructure requirements for deploying Large Language Models (LLMs) on-device within the context of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), focusing on both hardware and software perspectives. From the hardware viewpoint, we discuss the utilization of processing units like GPUs and TPUs, efficient memory and storage solutions, and strategies for effective deployment, addressing the challenges of limited computational resources typical in SME settings. From the software perspective, we explore framework compatibility, operating system optimization, and the use of specialized libraries tailored for resource-constrained environments. The review is structured to first identify the unique challenges faced by SMEs in deploying LLMs on-device, followed by an exploration of the opportunities that both hardware innovations and software adaptations offer to overcome these obstacles. Such a structured review provides practical insights, contributing significantly to the community by enhancing the technological resilience of SMEs in integrating LLMs.
Hyper-Skin: A Hyperspectral Dataset for Reconstructing Facial Skin-Spectra from RGB Images
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:We introduce Hyper-Skin, a hyperspectral dataset covering wide range of wavelengths from visible (VIS) spectrum (400nm - 700nm) to near-infrared (NIR) spectrum (700nm - 1000nm), uniquely designed to facilitate research on facial skin-spectra reconstruction. By reconstructing skin spectra from RGB images, our dataset enables the study of hyperspectral skin analysis, such as melanin and hemoglobin concentrations, directly on the consumer device. Overcoming limitations of existing datasets, Hyper-Skin consists of diverse facial skin data collected with a pushbroom hyperspectral camera. With 330 hyperspectral cubes from 51 subjects, the dataset covers the facial skin from different angles and facial poses. Each hyperspectral cube has dimensions of 1024$\times$1024$\times$448, resulting in millions of spectra vectors per image. The dataset, carefully curated in adherence to ethical guidelines, includes paired hyperspectral images and synthetic RGB images generated using real camera responses. We demonstrate the efficacy of our dataset by showcasing skin spectra reconstruction using state-of-the-art models on 31 bands of hyperspectral data resampled in the VIS and NIR spectrum. This Hyper-Skin dataset would be a valuable resource to NeurIPS community, encouraging the development of novel algorithms for skin spectral reconstruction while fostering interdisciplinary collaboration in hyperspectral skin analysis related to cosmetology and skin's well-being. Instructions to request the data and the related benchmarking codes are publicly available at: \url{https://github.com/hyperspectral-skin/Hyper-Skin-2023}.
A Kernel Method to Nonlinear Location Estimation with RSS-based Fingerprint
Apr 07, 2022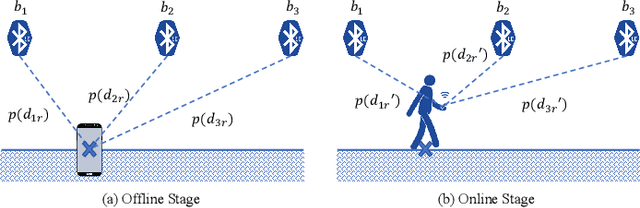
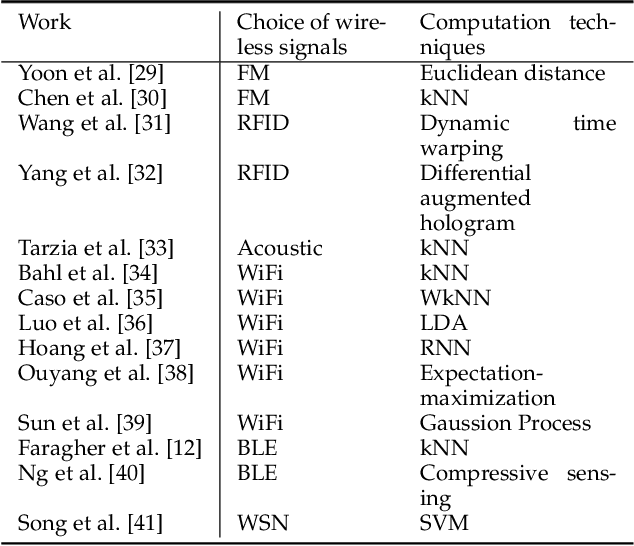
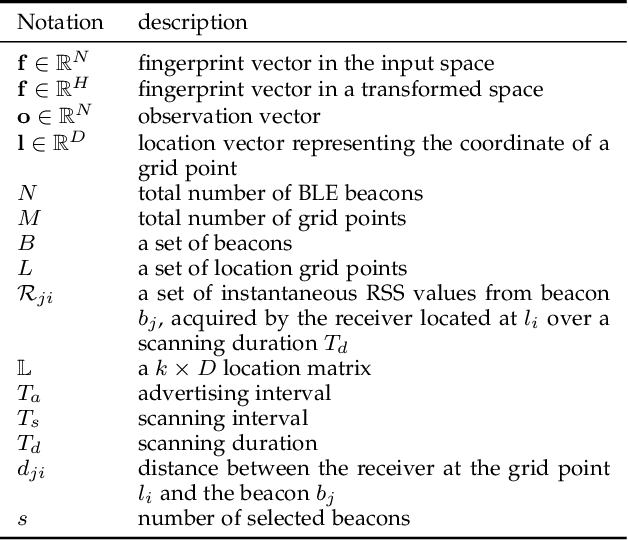
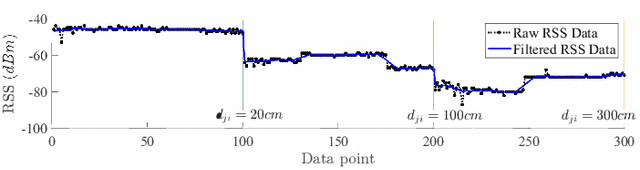
Abstract:This paper presents a nonlinear location estimation to infer the position of a user holding a smartphone. We consider a large location with $M$ number of grid points, each grid point is labeled with a unique fingerprint consisting of the received signal strength (RSS) values measured from $N$ number of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons. Given the fingerprint observed by the smartphone, the user's current location can be estimated by finding the top-k similar fingerprints from the list of fingerprints registered in the database. Besides the environmental factors, the dynamicity in holding the smartphone is another source to the variation in fingerprint measurements, yet there are not many studies addressing the fingerprint variability due to dynamic smartphone positions held by human hands during online detection. To this end, we propose a nonlinear location estimation using the kernel method. Specifically, our proposed method comprises of two steps: 1) a beacon selection strategy to select a subset of beacons that is insensitive to the subtle change of holding positions, and 2) a kernel method to compute the similarity between this subset of observed signals and all the fingerprints registered in the database. The experimental results based on large-scale data collected in a complex building indicate a substantial performance gain of our proposed approach in comparison to state-of-the-art methods. The dataset consisting of the signal information collected from the beacons is available online.
Personal Devices for Contact Tracing: Smartphones and Wearables to Fight Covid-19
Aug 02, 2021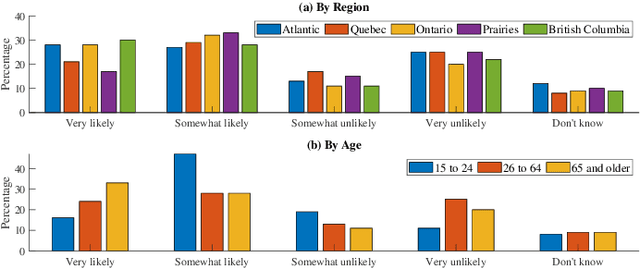
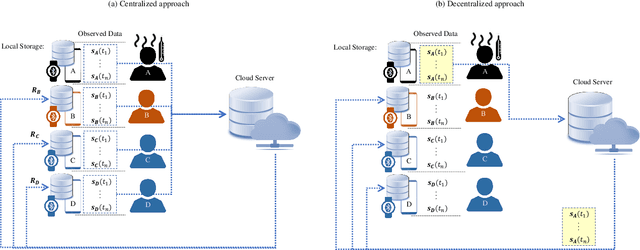
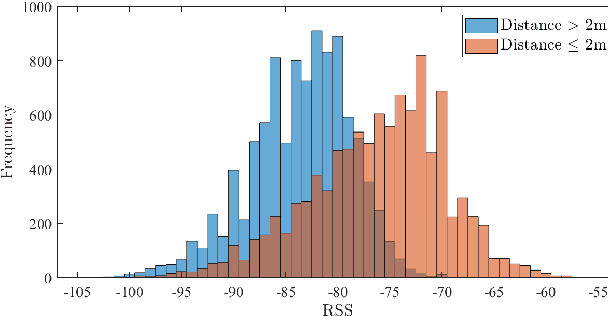
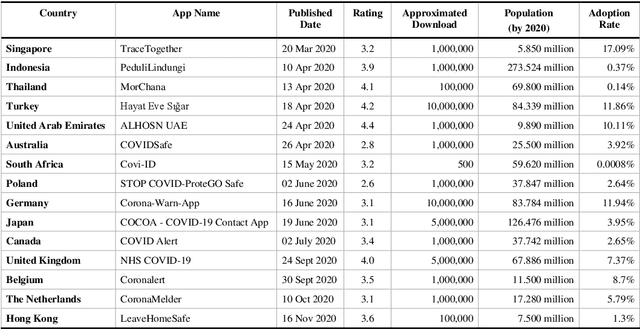
Abstract:Digital contact tracing has emerged as a viable tool supplementing manual contact tracing. To date, more than 100 contact tracing applications have been published to slow down the spread of highly contagious Covid-19. Despite subtle variabilities among these applications, all of them achieve contact tracing by manipulating the following three components: a) use a personal device to identify the user while designing a secure protocol to anonymize the user's identity; b) leverage networking technologies to analyze and store the data; c) exploit rich sensing features on the user device to detect the interaction among users and thus estimate the exposure risk. This paper reviews the current digital contact tracing based on these three components. We focus on two personal devices that are intimate to the user: smartphones and wearables. We discuss the centralized and decentralized networking approaches that use to facilitate the data flow. Lastly, we investigate the sensing feature available on smartphones and wearables to detect the proximity between any two users and present experiments comparing the proximity sensing performance between these two personal devices.
Epidemic Exposure Notification with Smartwatch: A Proximity-Based Privacy-Preserving Approach
Jul 08, 2020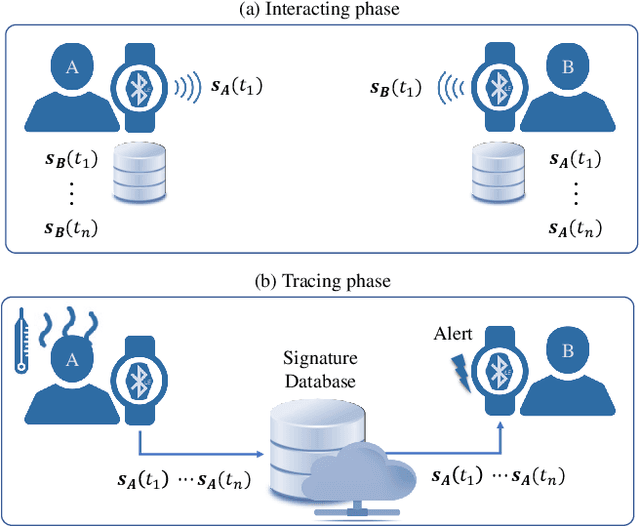
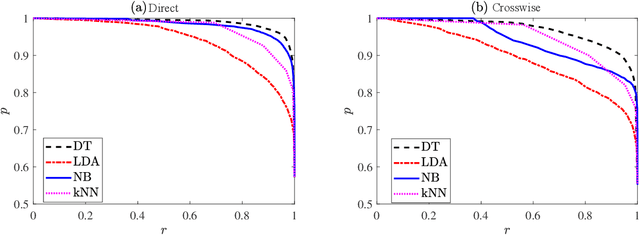
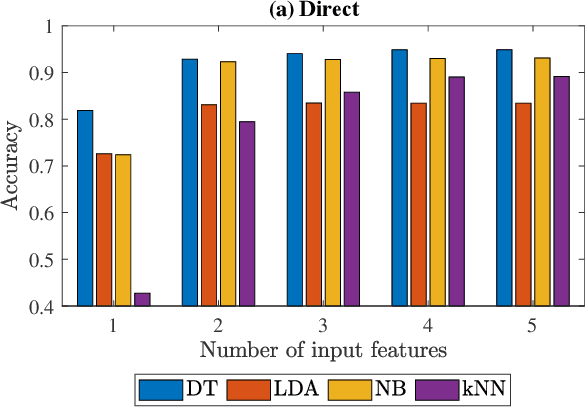
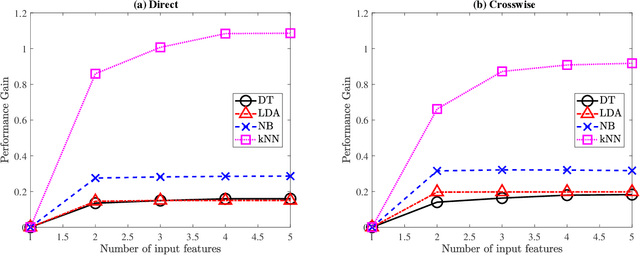
Abstract:Businesses planning for the post-pandemic world are looking for innovative ways to protect the health and welfare of their employees and customers. Wireless technologies can play a key role in assisting contact tracing to quickly halt a local infection outbreak and prevent further spread. In this work, we present a wearable proximity and exposure notification solution based on a smartwatch that also promotes safe physical distancing in business, hospitality, or recreational facilities. Our proximity-based privacy-preserving contact tracing (P$^3$CT) leverages the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology for reliable proximity sensing, and an ambient signature protocol for preserving identity. Proximity sensing exploits the received signal strength (RSS) to detect the user's interaction and thus classifying them into low- or high-risk with respect to a patient diagnosed with an infectious disease. More precisely, a user is notified of their exposure based on their interactions, in terms of distance and time, with a patient. Our privacy-preserving protocol uses the ambient signatures to ensure that users' identities be anonymized. We demonstrate the feasibility of our proposed solution through extensive experimentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge