COVID-19 and Your Smartphone: BLE-based Smart Contact Tracing
Paper and Code
May 28, 2020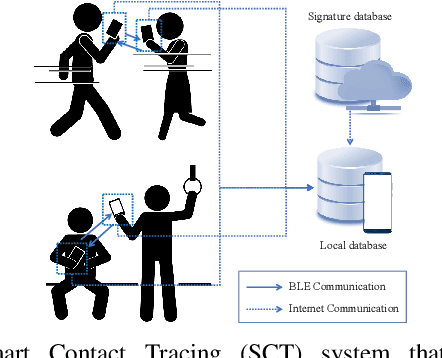
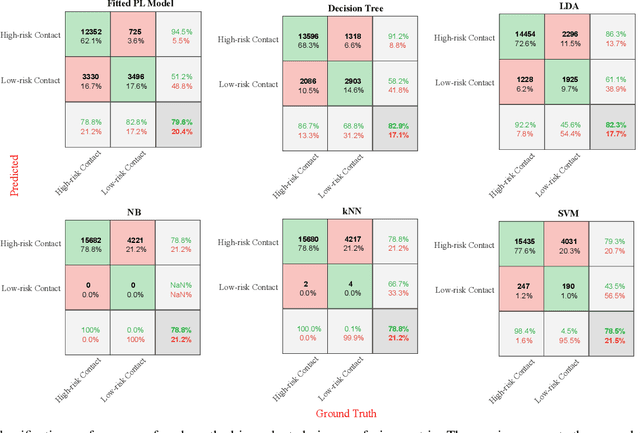
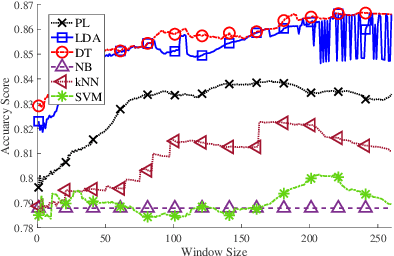
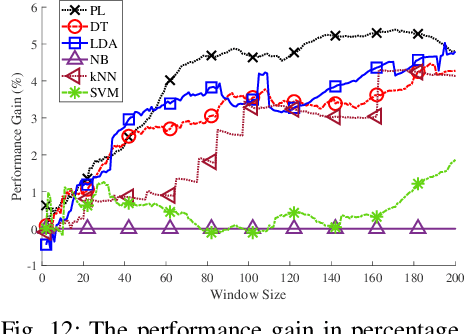
Contact tracing is of paramount importance when it comes to preventing the spreading of infectious diseases. Contact tracing is usually performed manually by authorized personnel. Manual contact tracing is an inefficient, error-prone, time-consuming process of limited utility to the population at large as those in close contact with infected individuals are informed hours, if not days, later. This paper introduces an alternative way to manual contact tracing. The proposed Smart Contact Tracing (SCT) system utilizes the smartphone's Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) signals and machine learning classifier to accurately and quickly determined the contact profile. SCT's contribution is two-fold: a) classification of the user's contact as high/low-risk using precise proximity sensing, and b) user anonymity using a privacy-preserving communications protocol. SCT leverages BLE's non-connectable advertising feature to broadcast a signature packet when the user is in the public space. Both broadcasted and observed signatures are stored in the user's smartphone and they are only uploaded to a secure signature database when a user is confirmed by public health authorities to be infected. Using received signal strength (RSS) each smartphone estimates its distance from other user's phones and issues real-time alerts when social distancing rules are violated. The paper includes extensive experimentation utilizing real-life smartphone positions and a comparative evaluation of five machine learning classifiers. Reported results indicate that a decision tree classifier outperforms other states of the art classification methods in terms of accuracy. Lastly, to facilitate research in this area, and to contribute to the timely development of advanced solutions the entire data set of six experiments with about 123,000 data points is made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge