Oleh Dzyubachyk
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Hierarchical stochastic neighbor embedding as a tool for visualizing the encoding capability of magnetic resonance fingerprinting dictionaries
Oct 07, 2019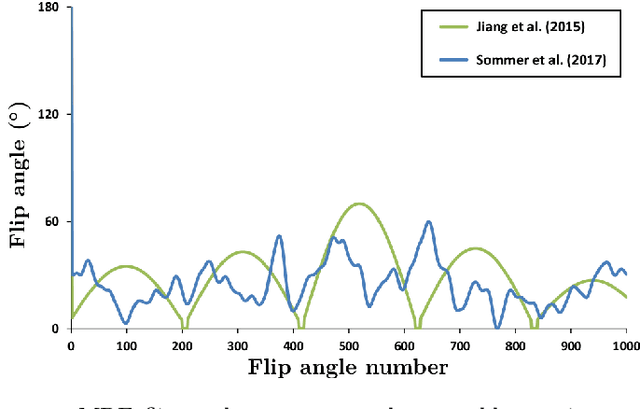
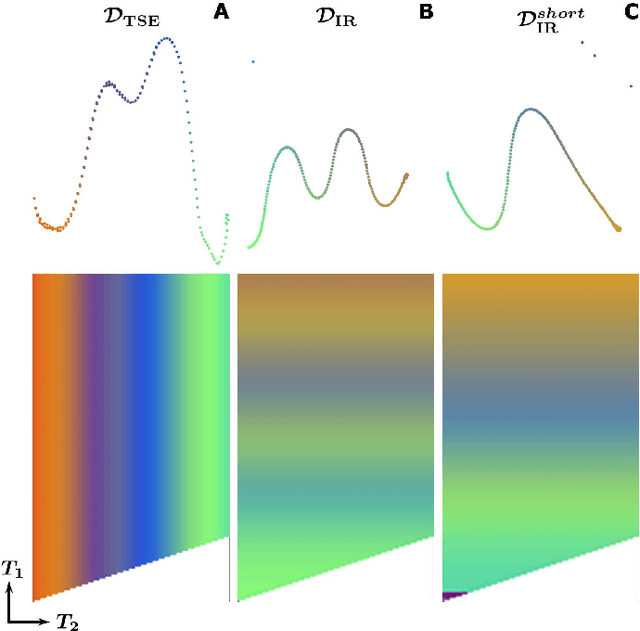
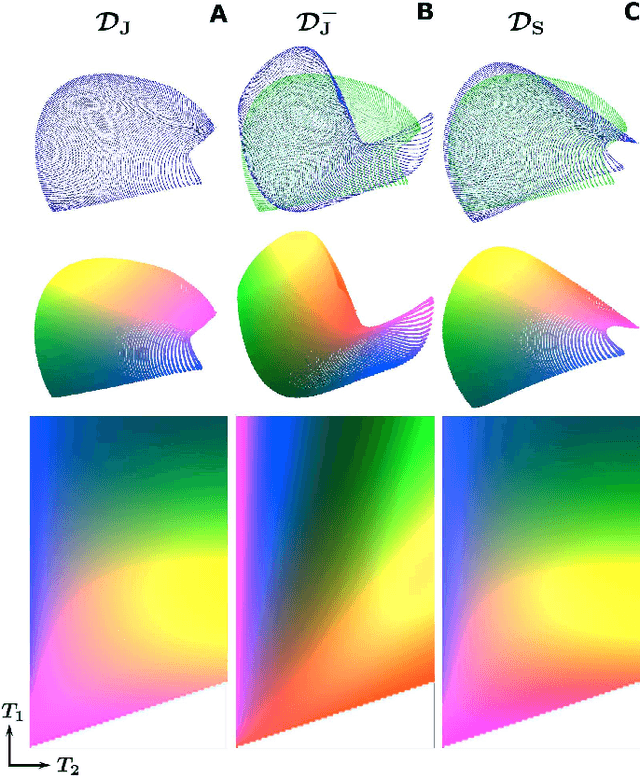
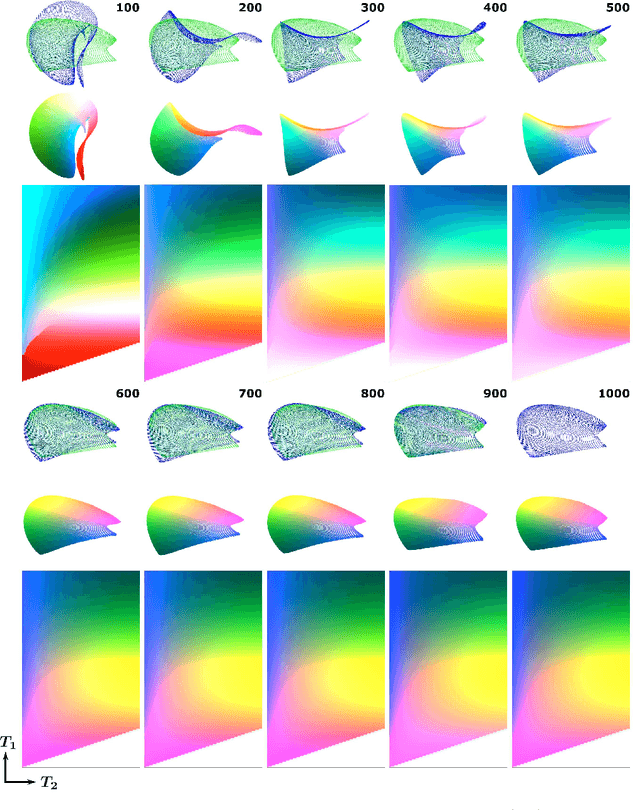
Abstract:In Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting (MRF) the quality of the estimated parameter maps depends on the encoding capability of the variable flip angle train. In this work we show how the dimensionality reduction technique Hierarchical Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (HSNE) can be used to obtain insight into the encoding capability of different MRF sequences. Embedding high-dimensional MRF dictionaries into a lower-dimensional space and visualizing them with colors, being a surrogate for location in low-dimensional space, provides a comprehensive overview of particular dictionaries and, in addition, enables comparison of different sequences. Dictionaries for various sequences and sequence lengths were compared to each other, and the effect of transmit field variations on the encoding capability was assessed. Clear differences in encoding capability were observed between different sequences, and HSNE results accurately reflect those obtained from an MRF matching simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge