Nithin Anchuri
A Short Study on Compressing Decoder-Based Language Models
Oct 16, 2021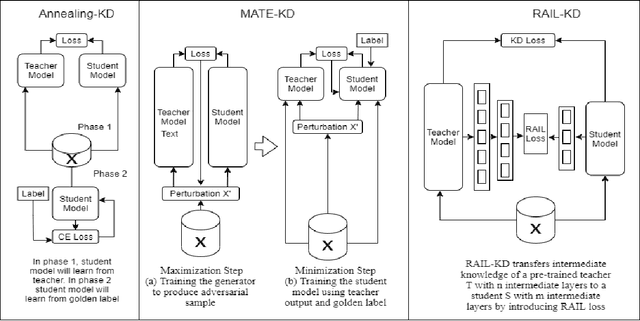
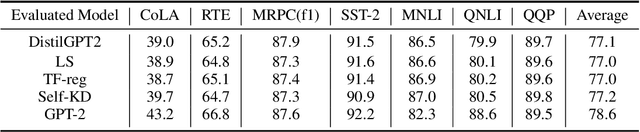
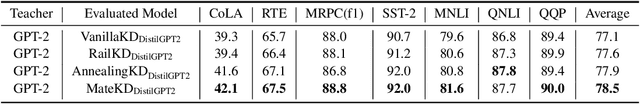
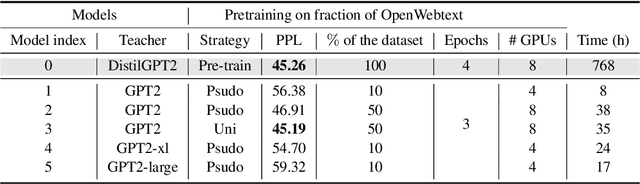
Abstract:Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) have been successful for a wide range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks. The state-of-the-art of PLMs, however, are extremely large to be used on edge devices. As a result, the topic of model compression has attracted increasing attention in the NLP community. Most of the existing works focus on compressing encoder-based models (tiny-BERT, distilBERT, distilRoBERTa, etc), however, to the best of our knowledge, the compression of decoder-based models (such as GPT-2) has not been investigated much. Our paper aims to fill this gap. Specifically, we explore two directions: 1) we employ current state-of-the-art knowledge distillation techniques to improve fine-tuning of DistilGPT-2. 2) we pre-train a compressed GPT-2 model using layer truncation and compare it against the distillation-based method (DistilGPT2). The training time of our compressed model is significantly less than DistilGPT-2, but it can achieve better performance when fine-tuned on downstream tasks. We also demonstrate the impact of data cleaning on model performance.
RAIL-KD: RAndom Intermediate Layer Mapping for Knowledge Distillation
Oct 01, 2021
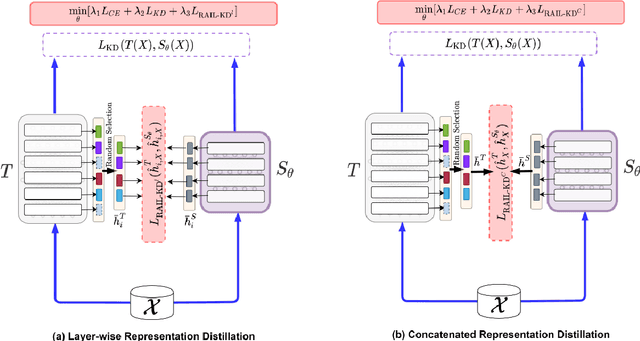
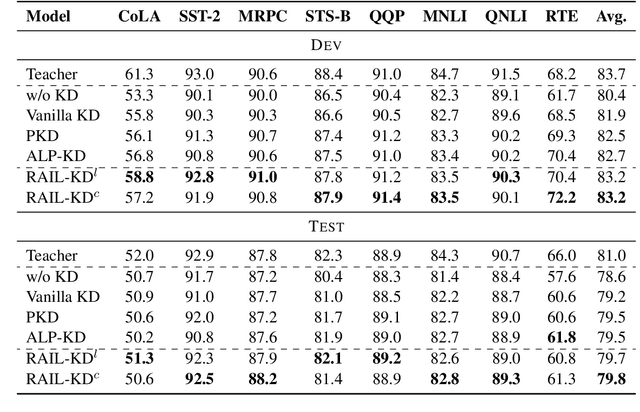
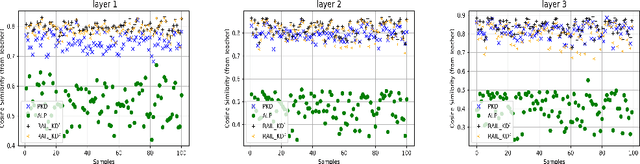
Abstract:Intermediate layer knowledge distillation (KD) can improve the standard KD technique (which only targets the output of teacher and student models) especially over large pre-trained language models. However, intermediate layer distillation suffers from excessive computational burdens and engineering efforts required for setting up a proper layer mapping. To address these problems, we propose a RAndom Intermediate Layer Knowledge Distillation (RAIL-KD) approach in which, intermediate layers from the teacher model are selected randomly to be distilled into the intermediate layers of the student model. This randomized selection enforce that: all teacher layers are taken into account in the training process, while reducing the computational cost of intermediate layer distillation. Also, we show that it act as a regularizer for improving the generalizability of the student model. We perform extensive experiments on GLUE tasks as well as on out-of-domain test sets. We show that our proposed RAIL-KD approach outperforms other state-of-the-art intermediate layer KD methods considerably in both performance and training-time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge