Ning Niu
Boosting Sclera Segmentation through Semi-supervised Learning with Fewer Labels
Jan 13, 2025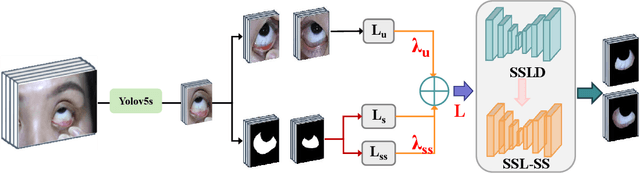
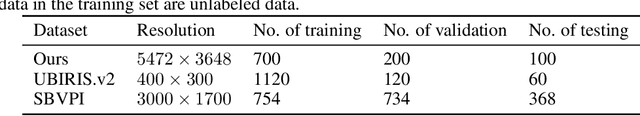
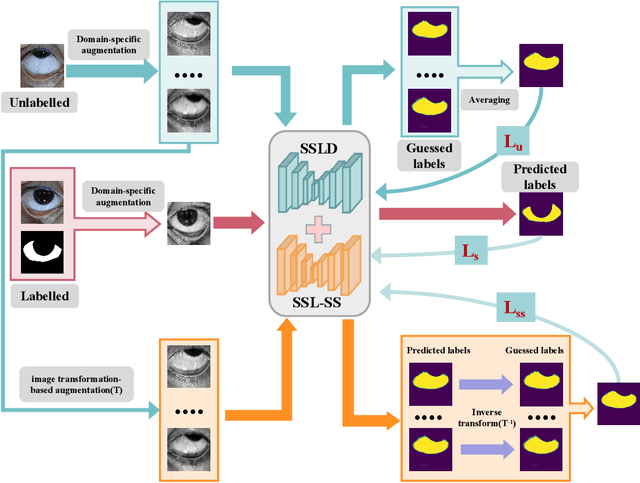
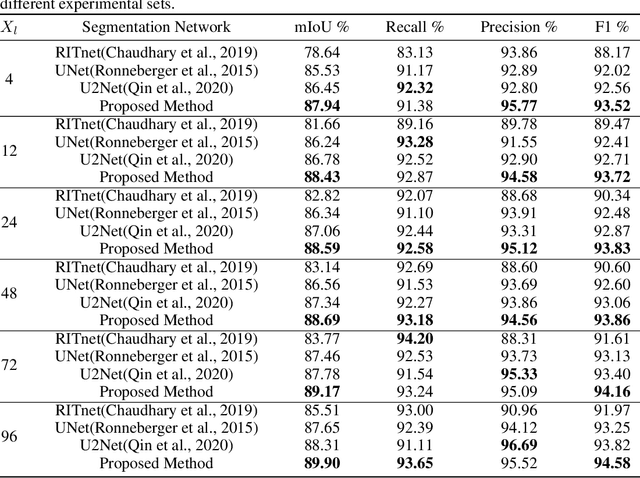
Abstract:Sclera segmentation is crucial for developing automatic eye-related medical computer-aided diagnostic systems, as well as for personal identification and verification, because the sclera contains distinct personal features. Deep learning-based sclera segmentation has achieved significant success compared to traditional methods that rely on hand-crafted features, primarily because it can autonomously extract critical output-related features without the need to consider potential physical constraints. However, achieving accurate sclera segmentation using these methods is challenging due to the scarcity of high-quality, fully labeled datasets, which depend on costly, labor-intensive medical acquisition and expertise. To address this challenge, this paper introduces a novel sclera segmentation framework that excels with limited labeled samples. Specifically, we employ a semi-supervised learning method that integrates domain-specific improvements and image-based spatial transformations to enhance segmentation performance. Additionally, we have developed a real-world eye diagnosis dataset to enrich the evaluation process. Extensive experiments on our dataset and two additional public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed method, especially with significantly fewer labeled samples.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge