Niels Lobo
Improving Replay Sample Selection and Storage for Less Forgetting in Continual Learning
Aug 03, 2023



Abstract:Continual learning seeks to enable deep learners to train on a series of tasks of unknown length without suffering from the catastrophic forgetting of previous tasks. One effective solution is replay, which involves storing few previous experiences in memory and replaying them when learning the current task. However, there is still room for improvement when it comes to selecting the most informative samples for storage and determining the optimal number of samples to be stored. This study aims to address these issues with a novel comparison of the commonly used reservoir sampling to various alternative population strategies and providing a novel detailed analysis of how to find the optimal number of stored samples.
Learning Situation Hyper-Graphs for Video Question Answering
Apr 18, 2023



Abstract:Answering questions about complex situations in videos requires not only capturing the presence of actors, objects, and their relations but also the evolution of these relationships over time. A situation hyper-graph is a representation that describes situations as scene sub-graphs for video frames and hyper-edges for connected sub-graphs and has been proposed to capture all such information in a compact structured form. In this work, we propose an architecture for Video Question Answering (VQA) that enables answering questions related to video content by predicting situation hyper-graphs, coined Situation Hyper-Graph based Video Question Answering (SHG-VQA). To this end, we train a situation hyper-graph decoder to implicitly identify graph representations with actions and object/human-object relationships from the input video clip. and to use cross-attention between the predicted situation hyper-graphs and the question embedding to predict the correct answer. The proposed method is trained in an end-to-end manner and optimized by a VQA loss with the cross-entropy function and a Hungarian matching loss for the situation graph prediction. The effectiveness of the proposed architecture is extensively evaluated on two challenging benchmarks: AGQA and STAR. Our results show that learning the underlying situation hyper-graphs helps the system to significantly improve its performance for novel challenges of video question-answering tasks.
Found a Reason for me? Weakly-supervised Grounded Visual Question Answering using Capsules
May 11, 2021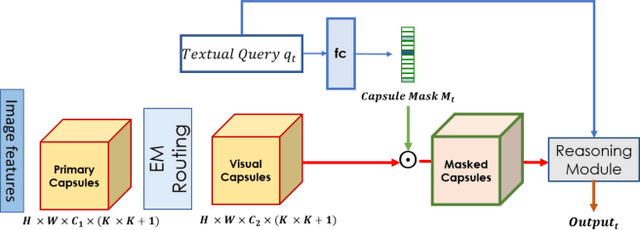
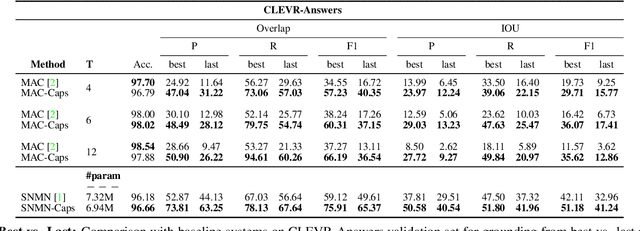
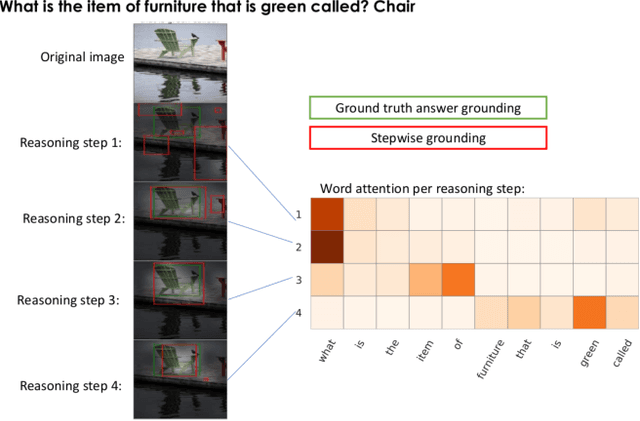
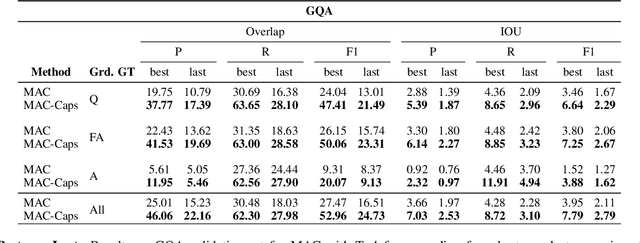
Abstract:The problem of grounding VQA tasks has seen an increased attention in the research community recently, with most attempts usually focusing on solving this task by using pretrained object detectors. However, pre-trained object detectors require bounding box annotations for detecting relevant objects in the vocabulary, which may not always be feasible for real-life large-scale applications. In this paper, we focus on a more relaxed setting: the grounding of relevant visual entities in a weakly supervised manner by training on the VQA task alone. To address this problem, we propose a visual capsule module with a query-based selection mechanism of capsule features, that allows the model to focus on relevant regions based on the textual cues about visual information in the question. We show that integrating the proposed capsule module in existing VQA systems significantly improves their performance on the weakly supervised grounding task. Overall, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on two state-of-the-art VQA systems, stacked NMN and MAC, on the CLEVR-Answers benchmark, our new evaluation set based on CLEVR scenes with ground truth bounding boxes for objects that are relevant for the correct answer, as well as on GQA, a real world VQA dataset with compositional questions. We show that the systems with the proposed capsule module consistently outperform the respective baseline systems in terms of answer grounding, while achieving comparable performance on VQA task.
Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning with Increasing Object Shape Bias
Nov 24, 2019


Abstract:(Very early draft)Traditional supervised learning keeps pushing convolution neural network(CNN) achieving state-of-art performance. However, lack of large-scale annotation data is always a big problem due to the high cost of it, even ImageNet dataset is over-fitted by complex models now. The success of unsupervised learning method represented by the Bert model in natural language processing(NLP) field shows its great potential. And it makes that unlimited training samples becomes possible and the great universal generalization ability changes NLP research direction directly. In this article, we purpose a novel unsupervised learning method based on contrastive predictive coding. Under that, we are able to train model with any non-annotation images and improve model's performance to reach state-of-art performance at the same level of model complexity. Beside that, since the number of training images could be unlimited amplification, an universal large-scale pre-trained computer vision model is possible in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge