Nicolò Navarin
Unveiling the Actual Performance of Neural-based Models for Equation Discovery on Graph Dynamical Systems
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:The ``black-box'' nature of deep learning models presents a significant barrier to their adoption for scientific discovery, where interpretability is paramount. This challenge is especially pronounced in discovering the governing equations of dynamical processes on networks or graphs, since even their topological structure further affects the processes' behavior. This paper provides a rigorous, comparative assessment of state-of-the-art symbolic regression techniques for this task. We evaluate established methods, including sparse regression and MLP-based architectures, and introduce a novel adaptation of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) for graphs, designed to exploit their inherent interpretability. Across a suite of synthetic and real-world dynamical systems, our results demonstrate that both MLP and KAN-based architectures can successfully identify the underlying symbolic equations, significantly surpassing existing baselines. Critically, we show that KANs achieve this performance with greater parsimony and transparency, as their learnable activation functions provide a clearer mapping to the true physical dynamics. This study offers a practical guide for researchers, clarifying the trade-offs between model expressivity and interpretability, and establishes the viability of neural-based architectures for robust scientific discovery on complex systems.
Economic Recommender Systems -- A Systematic Review
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:Many of today's online services provide personalized recommendations to their users. Such recommendations are typically designed to serve certain user needs, e.g., to quickly find relevant content in situations of information overload. Correspondingly, the academic literature in the field largely focuses on the value of recommender systems for the end user. In this context, one underlying assumption is that the improved service that is achieved through the recommendations will in turn positively impact the organization's goals, e.g., in the form of higher customer retention or loyalty. However, in reality, recommender systems can be used to target organizational economic goals more directly by incorporating monetary considerations such as price awareness and profitability aspects into the underlying recommendation models. In this work, we survey the existing literature on what we call Economic Recommender Systems based on a systematic review approach that helped us identify 133 relevant papers. We first categorize existing works along different dimensions and then review the most important technical approaches from the literature. Furthermore, we discuss common methodologies to evaluate such systems and finally outline the limitations of today's research and future directions.
RGCVAE: Relational Graph Conditioned Variational Autoencoder for Molecule Design
May 19, 2023
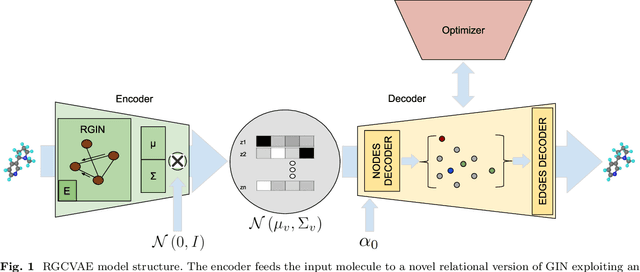
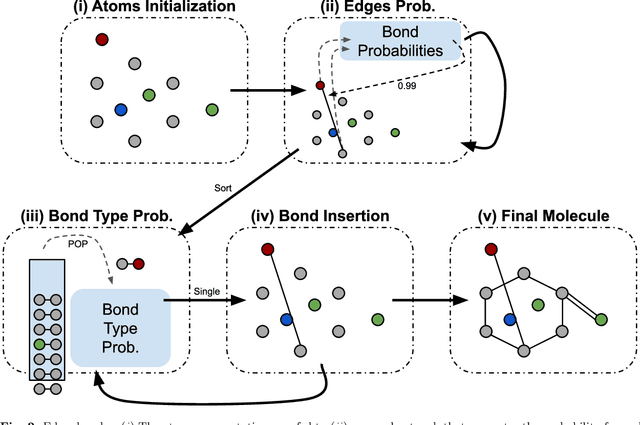
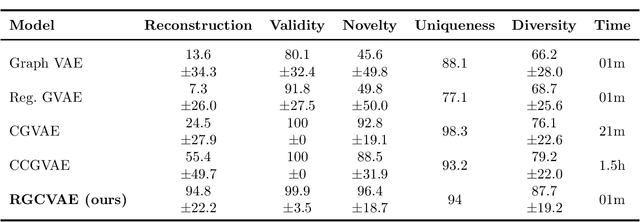
Abstract:Identifying molecules that exhibit some pre-specified properties is a difficult problem to solve. In the last few years, deep generative models have been used for molecule generation. Deep Graph Variational Autoencoders are among the most powerful machine learning tools with which it is possible to address this problem. However, existing methods struggle in capturing the true data distribution and tend to be computationally expensive. In this work, we propose RGCVAE, an efficient and effective Graph Variational Autoencoder based on: (i) an encoding network exploiting a new powerful Relational Graph Isomorphism Network; (ii) a novel probabilistic decoding component. Compared to several state-of-the-art VAE methods on two widely adopted datasets, RGCVAE shows state-of-the-art molecule generation performance while being significantly faster to train.
An Explainable Decision Support System for Predictive Process Analytics
Jul 26, 2022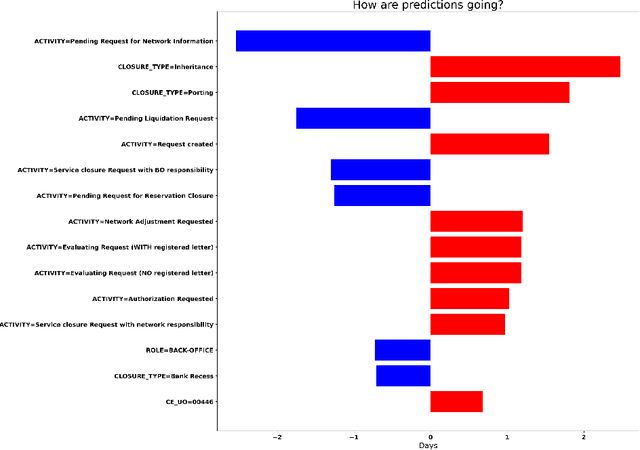
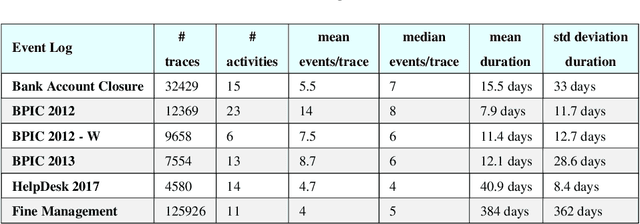
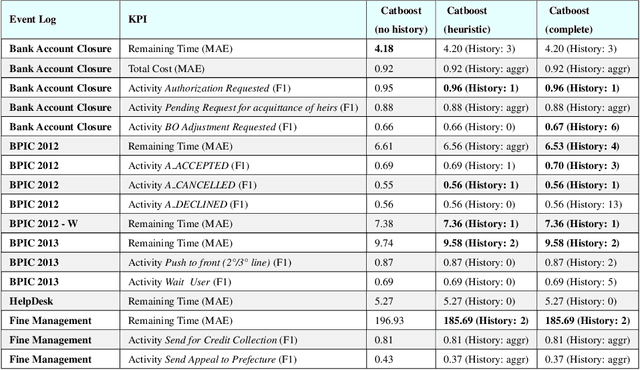
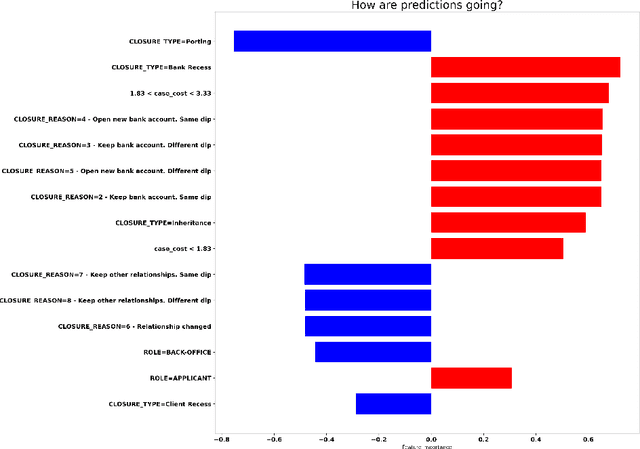
Abstract:Predictive Process Analytics is becoming an essential aid for organizations, providing online operational support of their processes. However, process stakeholders need to be provided with an explanation of the reasons why a given process execution is predicted to behave in a certain way. Otherwise, they will be unlikely to trust the predictive monitoring technology and, hence, adopt it. This paper proposes a predictive analytics framework that is also equipped with explanation capabilities based on the game theory of Shapley Values. The framework has been implemented in the IBM Process Mining suite and commercialized for business users. The framework has been tested on real-life event data to assess the quality of the predictions and the corresponding evaluations. In particular, a user evaluation has been performed in order to understand if the explanations provided by the system were intelligible to process stakeholders.
Object-centric Process Predictive Analytics
Mar 05, 2022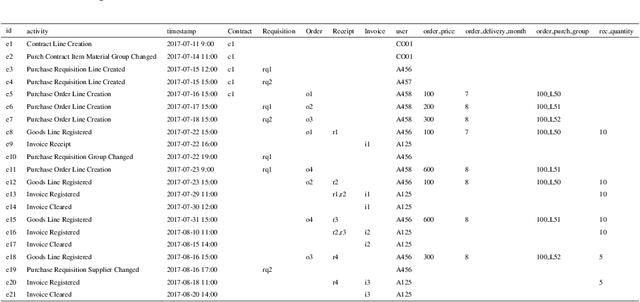
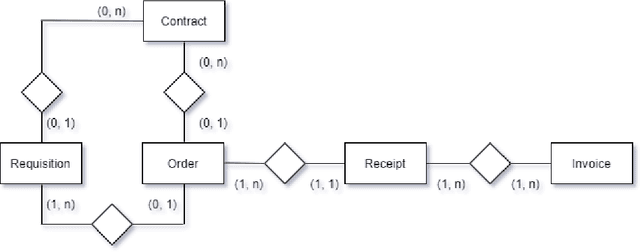
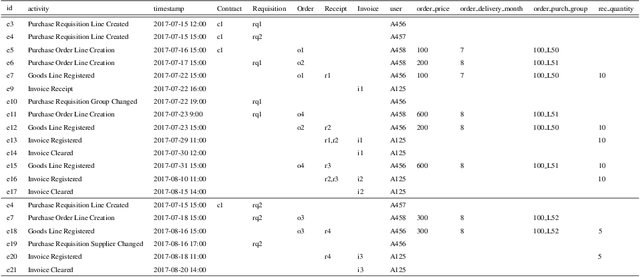
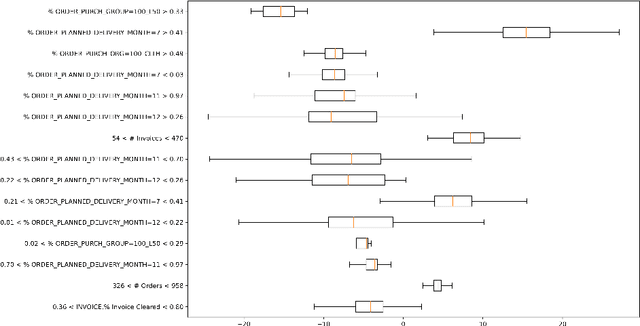
Abstract:Object-centric processes (a.k.a. Artifact-centric processes) are implementations of a paradigm where an instance of one process is not executed in isolation but interacts with other instances of the same or other processes. Interactions take place through bridging events where instances exchange data. Object-centric processes are recently gaining popularity in academia and industry, because their nature is observed in many application scenarios. This poses significant challenges in predictive analytics due to the complex intricacy of the process instances that relate to each other via many-to-many associations. Existing research is unable to directly exploit the benefits of these interactions, thus limiting the prediction quality. This paper proposes an approach to incorporate the information about the object interactions into the predictive models. The approach is assessed on real-life object-centric process event data, using different KPIs. The results are compared with a naive approach that overlooks the object interactions, thus illustrating the benefits of their use on the prediction quality.
Simple Graph Convolutional Networks
Jun 10, 2021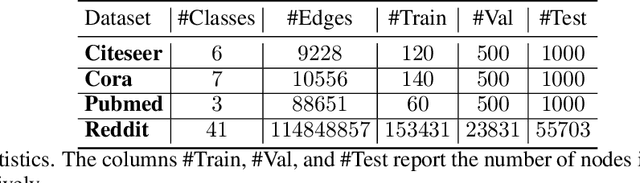
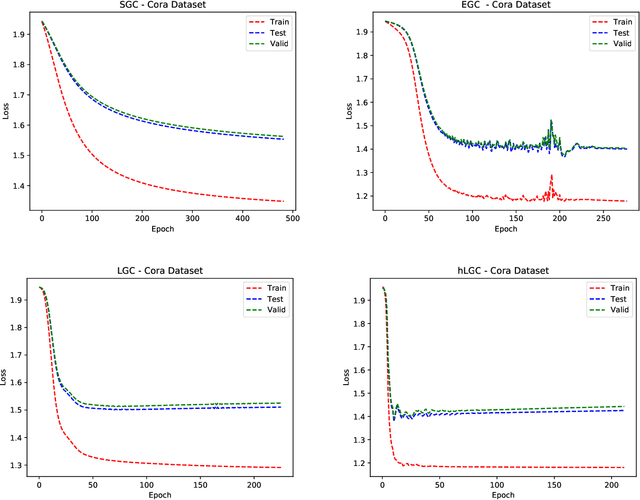
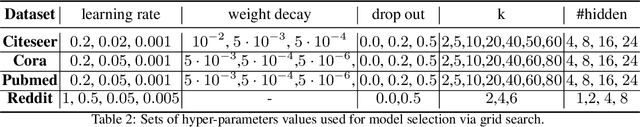
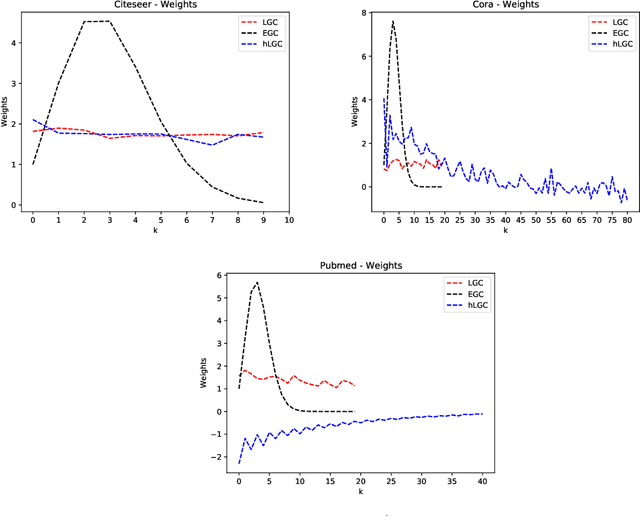
Abstract:Many neural networks for graphs are based on the graph convolution operator, proposed more than a decade ago. Since then, many alternative definitions have been proposed, that tend to add complexity (and non-linearity) to the model. In this paper, we follow the opposite direction by proposing simple graph convolution operators, that can be implemented in single-layer graph convolutional networks. We show that our convolution operators are more theoretically grounded than many proposals in literature, and exhibit state-of-the-art predictive performance on the considered benchmark datasets.
Explainable Predictive Process Monitoring
Sep 16, 2020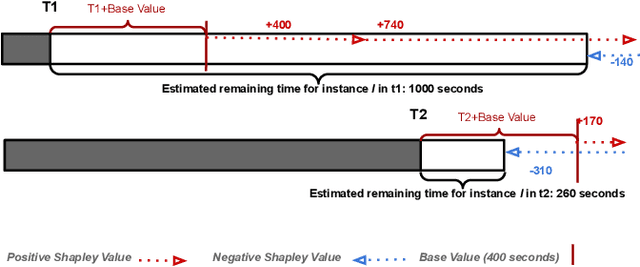
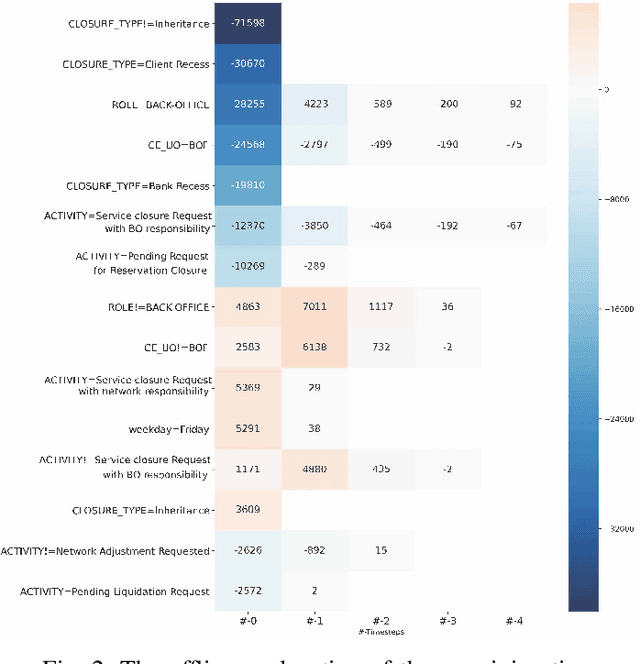
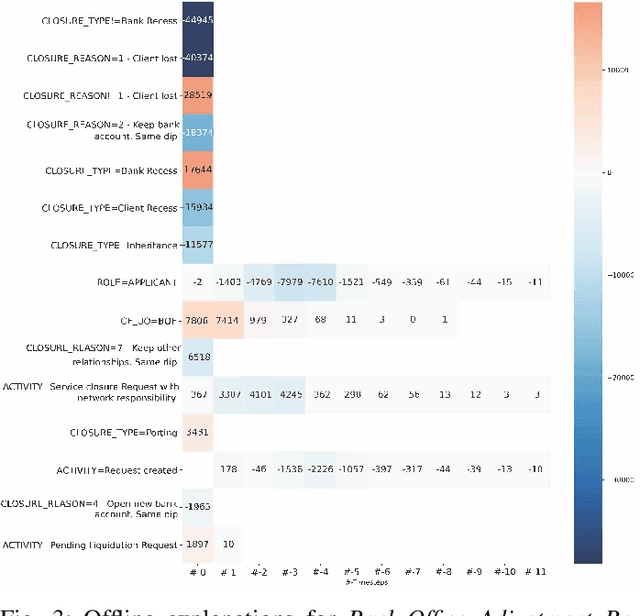
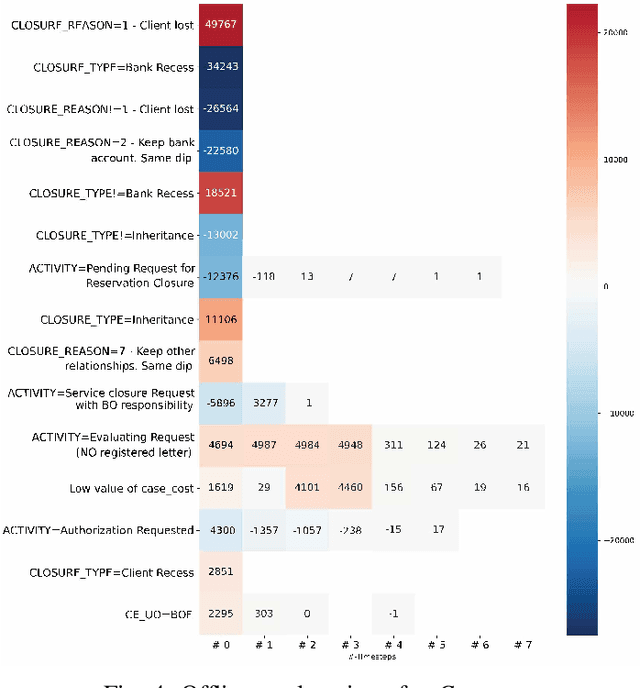
Abstract:Predictive Business Process Monitoring is becoming an essential aid for organizations, providing online operational support of their processes. This paper tackles the fundamental problem of equipping predictive business process monitoring with explanation capabilities, so that not only the what but also the why is reported when predicting generic KPIs like remaining time, or activity execution. We use the game theory of Shapley Values to obtain robust explanations of the predictions. The approach has been implemented and tested on real-life benchmarks, showing for the first time how explanations can be given in the field of predictive business process monitoring.
Conditional Constrained Graph Variational Autoencoders for Molecule Design
Sep 01, 2020



Abstract:In recent years, deep generative models for graphs have been used to generate new molecules. These models have produced good results, leading to several proposals in the literature. However, these models may have troubles learning some of the complex laws governing the chemical world. In this work, we explore the usage of the histogram of atom valences to drive the generation of molecules in such models. We present Conditional Constrained Graph Variational Autoencoder (CCGVAE), a model that implements this key-idea in a state-of-the-art model, and shows improved results on several evaluation metrics on two commonly adopted datasets for molecule generation.
A Systematic Assessment of Deep Learning Models for Molecule Generation
Aug 20, 2020
Abstract:In recent years the scientific community has devoted much effort in the development of deep learning models for the generation of new molecules with desirable properties (i.e. drugs). This has produced many proposals in literature. However, a systematic comparison among the different VAE methods is still missing. For this reason, we propose an extensive testbed for the evaluation of generative models for drug discovery, and we present the results obtained by many of the models proposed in literature.
On Filter Size in Graph Convolutional Networks
Nov 23, 2018



Abstract:Recently, many researchers have been focusing on the definition of neural networks for graphs. The basic component for many of these approaches remains the graph convolution idea proposed almost a decade ago. In this paper, we extend this basic component, following an intuition derived from the well-known convolutional filters over multi-dimensional tensors. In particular, we derive a simple, efficient and effective way to introduce a hyper-parameter on graph convolutions that influences the filter size, i.e. its receptive field over the considered graph. We show with experimental results on real-world graph datasets that the proposed graph convolutional filter improves the predictive performance of Deep Graph Convolutional Networks.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:1811.06930
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge