Nicholas Vincent
WikiGap: Promoting Epistemic Equity by Surfacing Knowledge Gaps Between English Wikipedia and other Language Editions
May 30, 2025Abstract:With more than 11 times as many pageviews as the next, English Wikipedia dominates global knowledge access relative to other language editions. Readers are prone to assuming English Wikipedia as a superset of all language editions, leading many to prefer it even when their primary language is not English. Other language editions, however, comprise complementary facts rooted in their respective cultures and media environments, which are marginalized in English Wikipedia. While Wikipedia's user interface enables switching between language editions through its Interlanguage Link (ILL) system, it does not reveal to readers that other language editions contain valuable, complementary information. We present WikiGap, a system that surfaces complementary facts sourced from other Wikipedias within the English Wikipedia interface. Specifically, by combining a recent multilingual information-gap discovery method with a user-centered design, WikiGap enables access to complementary information from French, Russian, and Chinese Wikipedia. In a mixed-methods study (n=21), WikiGap significantly improved fact-finding accuracy, reduced task time, and received a 32-point higher usability score relative to Wikipedia's current ILL-based navigation system. Participants reported increased awareness of the availability of complementary information in non-English editions and reconsidered the completeness of English Wikipedia. WikiGap thus paves the way for improved epistemic equity across language editions.
Algorithmic Collective Action with Two Collectives
Apr 30, 2025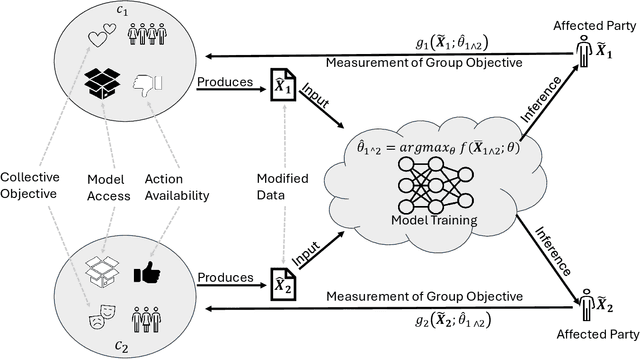
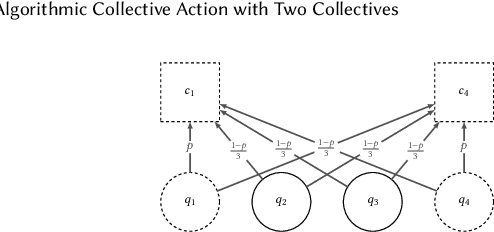
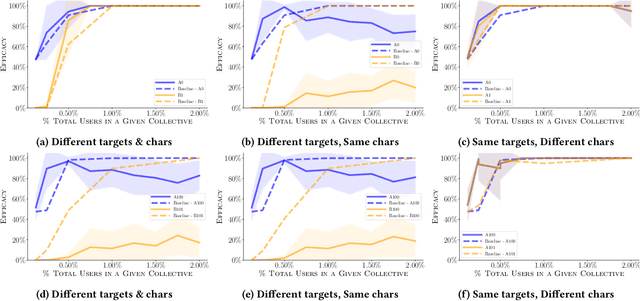
Abstract:Given that data-dependent algorithmic systems have become impactful in more domains of life, the need for individuals to promote their own interests and hold algorithms accountable has grown. To have meaningful influence, individuals must band together to engage in collective action. Groups that engage in such algorithmic collective action are likely to vary in size, membership characteristics, and crucially, objectives. In this work, we introduce a first of a kind framework for studying collective action with two or more collectives that strategically behave to manipulate data-driven systems. With more than one collective acting on a system, unexpected interactions may occur. We use this framework to conduct experiments with language model-based classifiers and recommender systems where two collectives each attempt to achieve their own individual objectives. We examine how differing objectives, strategies, sizes, and homogeneity can impact a collective's efficacy. We find that the unintentional interactions between collectives can be quite significant; a collective acting in isolation may be able to achieve their objective (e.g., improve classification outcomes for themselves or promote a particular item), but when a second collective acts simultaneously, the efficacy of the first group drops by as much as $75\%$. We find that, in the recommender system context, neither fully heterogeneous nor fully homogeneous collectives stand out as most efficacious and that heterogeneity's impact is secondary compared to collective size. Our results signal the need for more transparency in both the underlying algorithmic models and the different behaviors individuals or collectives may take on these systems. This approach also allows collectives to hold algorithmic system developers accountable and provides a framework for people to actively use their own data to promote their own interests.
Responsible AI in Open Ecosystems: Reconciling Innovation with Risk Assessment and Disclosure
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:The rapid scaling of AI has spurred a growing emphasis on ethical considerations in both development and practice. This has led to the formulation of increasingly sophisticated model auditing and reporting requirements, as well as governance frameworks to mitigate potential risks to individuals and society. At this critical juncture, we review the practical challenges of promoting responsible AI and transparency in informal sectors like OSS that support vital infrastructure and see widespread use. We focus on how model performance evaluation may inform or inhibit probing of model limitations, biases, and other risks. Our controlled analysis of 7903 Hugging Face projects found that risk documentation is strongly associated with evaluation practices. Yet, submissions (N=789) from the platform's most popular competitive leaderboard showed less accountability among high performers. Our findings can inform AI providers and legal scholars in designing interventions and policies that preserve open-source innovation while incentivizing ethical uptake.
Push and Pull: A Framework for Measuring Attentional Agency
May 23, 2024

Abstract:We propose a framework for measuring attentional agency - the ability to allocate one's attention according to personal desires, goals, and intentions - on digital platforms. Platforms extend people's limited powers of attention by extrapolating their preferences to large collections of previously unconsidered informational objects. However, platforms typically also allow people to influence one another's attention. We introduce a formal framework for measuring how much a given platform empowers people to both pull information into their own attentional field and push information into the attentional fields of others. We also use these definitions to shed light on the implications of generative foundation models, which enable users to bypass the implicit "attentional bargain" that underlies embedded advertising and other methods for capturing economic value from informational goods. We conclude with a set of policy strategies that can be used to understand and reshape the distribution of attentional agency online.
Addressing "Documentation Debt" in Machine Learning Research: A Retrospective Datasheet for BookCorpus
May 11, 2021


Abstract:Recent literature has underscored the importance of dataset documentation work for machine learning, and part of this work involves addressing "documentation debt" for datasets that have been used widely but documented sparsely. This paper aims to help address documentation debt for BookCorpus, a popular text dataset for training large language models. Notably, researchers have used BookCorpus to train OpenAI's GPT-N models and Google's BERT models, even though little to no documentation exists about the dataset's motivation, composition, collection process, etc. We offer a preliminary datasheet that provides key context and information about BookCorpus, highlighting several notable deficiencies. In particular, we find evidence that (1) BookCorpus likely violates copyright restrictions for many books, (2) BookCorpus contains thousands of duplicated books, and (3) BookCorpus exhibits significant skews in genre representation. We also find hints of other potential deficiencies that call for future research, including problematic content, potential skews in religious representation, and lopsided author contributions. While more work remains, this initial effort to provide a datasheet for BookCorpus adds to growing literature that urges more careful and systematic documentation for machine learning datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge