Najeeb Jebreel
DP2Unlearning: An Efficient and Guaranteed Unlearning Framework for LLMs
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently revolutionized language processing tasks but have also brought ethical and legal issues. LLMs have a tendency to memorize potentially private or copyrighted information present in the training data, which might then be delivered to end users at inference time. When this happens, a naive solution is to retrain the model from scratch after excluding the undesired data. Although this guarantees that the target data have been forgotten, it is also prohibitively expensive for LLMs. Approximate unlearning offers a more efficient alternative, as it consists of ex post modifications of the trained model itself to prevent undesirable results, but it lacks forgetting guarantees because it relies solely on empirical evidence. In this work, we present DP2Unlearning, a novel LLM unlearning framework that offers formal forgetting guarantees at a significantly lower cost than retraining from scratch on the data to be retained. DP2Unlearning involves training LLMs on textual data protected using {\epsilon}-differential privacy (DP), which later enables efficient unlearning with the guarantees against disclosure associated with the chosen {\epsilon}. Our experiments demonstrate that DP2Unlearning achieves similar model performance post-unlearning, compared to an LLM retraining from scratch on retained data -- the gold standard exact unlearning -- but at approximately half the unlearning cost. In addition, with a reasonable computational cost, it outperforms approximate unlearning methods at both preserving the utility of the model post-unlearning and effectively forgetting the targeted information.
Digital Forgetting in Large Language Models: A Survey of Unlearning Methods
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:The objective of digital forgetting is, given a model with undesirable knowledge or behavior, obtain a new model where the detected issues are no longer present. The motivations for forgetting include privacy protection, copyright protection, elimination of biases and discrimination, and prevention of harmful content generation. Effective digital forgetting has to be effective (meaning how well the new model has forgotten the undesired knowledge/behavior), retain the performance of the original model on the desirable tasks, and be scalable (in particular forgetting has to be more efficient than retraining from scratch on just the tasks/data to be retained). This survey focuses on forgetting in large language models (LLMs). We first provide background on LLMs, including their components, the types of LLMs, and their usual training pipeline. Second, we describe the motivations, types, and desired properties of digital forgetting. Third, we introduce the approaches to digital forgetting in LLMs, among which unlearning methodologies stand out as the state of the art. Fourth, we provide a detailed taxonomy of machine unlearning methods for LLMs, and we survey and compare current approaches. Fifth, we detail datasets, models and metrics used for the evaluation of forgetting, retaining and runtime. Sixth, we discuss challenges in the area. Finally, we provide some concluding remarks.
An Examination of the Alleged Privacy Threats of Confidence-Ranked Reconstruction of Census Microdata
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:The alleged threat of reconstruction attacks has led the U.S. Census Bureau (USCB) to replace in the Decennial Census 2020 the traditional statistical disclosure limitation based on rank swapping with one based on differential privacy (DP). This has resulted in substantial accuracy loss of the released statistics. Worse yet, it has been shown that the reconstruction attacks used as an argument to move to DP are very far from allowing unequivocal reidentification of the respondents, because in general there are a lot of reconstructions compatible with the released statistics. In a very recent paper, a new reconstruction attack has been proposed, whose goal is to indicate the confidence that a reconstructed record was in the original respondent data. The alleged risk of serious disclosure entailed by such confidence-ranked reconstruction has renewed the interest of the USCB to use DP-based solutions. To forestall the potential accuracy loss in future data releases resulting from adoption of these solutions, we show in this paper that the proposed confidence-ranked reconstruction does not threaten privacy. Specifically, we report empirical results showing that the proposed ranking cannot guide reidentification or attribute disclosure attacks, and hence it fails to warrant the USCB's move towards DP. Further, we also demonstrate that, due to the way the Census data are compiled, processed and released, it is not possible to reconstruct original and complete records through any methodology, and the confidence-ranked reconstruction not only is completely ineffective at accurately reconstructing Census records but is trivially outperformed by an adequate interpretation of the released aggregate statistics.
FL-Defender: Combating Targeted Attacks in Federated Learning
Jul 02, 2022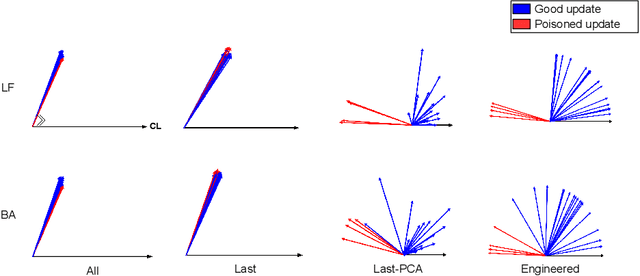
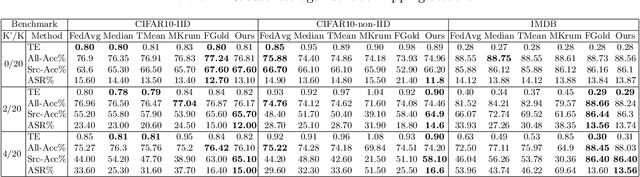

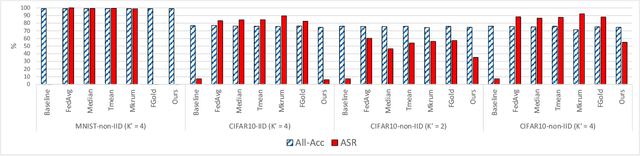
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enables learning a global machine learning model from local data distributed among a set of participating workers. This makes it possible i) to train more accurate models due to learning from rich joint training data, and ii) to improve privacy by not sharing the workers' local private data with others. However, the distributed nature of FL makes it vulnerable to targeted poisoning attacks that negatively impact the integrity of the learned model while, unfortunately, being difficult to detect. Existing defenses against those attacks are limited by assumptions on the workers' data distribution, may degrade the global model performance on the main task and/or are ill-suited to high-dimensional models. In this paper, we analyze targeted attacks against FL and find that the neurons in the last layer of a deep learning (DL) model that are related to the attacks exhibit a different behavior from the unrelated neurons, making the last-layer gradients valuable features for attack detection. Accordingly, we propose \textit{FL-Defender} as a method to combat FL targeted attacks. It consists of i) engineering more robust discriminative features by calculating the worker-wise angle similarity for the workers' last-layer gradients, ii) compressing the resulting similarity vectors using PCA to reduce redundant information, and iii) re-weighting the workers' updates based on their deviation from the centroid of the compressed similarity vectors. Experiments on three data sets with different DL model sizes and data distributions show the effectiveness of our method at defending against label-flipping and backdoor attacks. Compared to several state-of-the-art defenses, FL-Defender achieves the lowest attack success rates, maintains the performance of the global model on the main task and causes minimal computational overhead on the server.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge