Na Jiang
Object-aware Feature Aggregation for Video Object Detection
Oct 23, 2020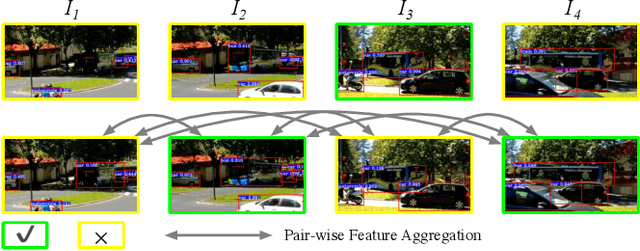

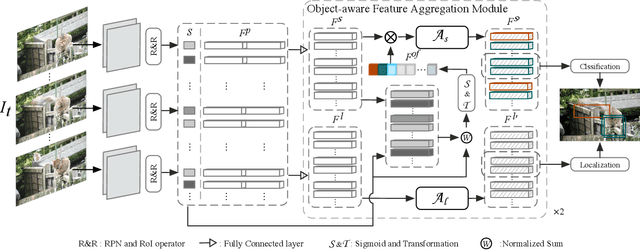
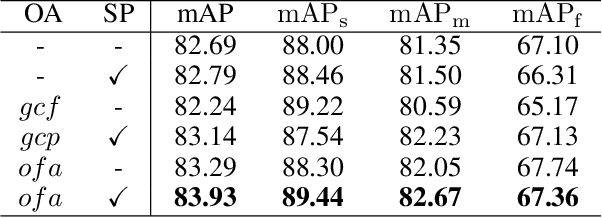
Abstract:We present an Object-aware Feature Aggregation (OFA) module for video object detection (VID). Our approach is motivated by the intriguing property that video-level object-aware knowledge can be employed as a powerful semantic prior to help object recognition. As a consequence, augmenting features with such prior knowledge can effectively improve the classification and localization performance. To make features get access to more content about the whole video, we first capture the object-aware knowledge of proposals and incorporate such knowledge with the well-established pair-wise contexts. With extensive experimental results on the ImageNet VID dataset, our approach demonstrates the effectiveness of object-aware knowledge with the superior performance of 83.93% and 86.09% mAP with ResNet-101 and ResNeXt-101, respectively. When further equipped with Sequence DIoU NMS, we obtain the best-reported mAP of 85.07% and 86.88% upon the paper submitted. The code to reproduce our results will be released after acceptance.
Co-Saliency Spatio-Temporal Interaction Network for Person Re-Identification in Videos
May 11, 2020



Abstract:Person re-identification aims at identifying a certain pedestrian across non-overlapping camera networks. Video-based re-identification approaches have gained significant attention recently, expanding image-based approaches by learning features from multiple frames. In this work, we propose a novel Co-Saliency Spatio-Temporal Interaction Network (CSTNet) for person re-identification in videos. It captures the common salient foreground regions among video frames and explores the spatial-temporal long-range context interdependency from such regions, towards learning discriminative pedestrian representation. Specifically, multiple co-saliency learning modules within CSTNet are designed to utilize the correlated information across video frames to extract the salient features from the task-relevant regions and suppress background interference. Moreover, multiple spatialtemporal interaction modules within CSTNet are proposed, which exploit the spatial and temporal long-range context interdependencies on such features and spatial-temporal information correlation, to enhance feature representation. Extensive experiments on two benchmarks have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge