Muyao Zhong
Calibrating Agent-Based Financial Markets Simulators with Pretrainable Automatic Posterior Transformation-Based Surrogates
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Calibrating Agent-Based Models (ABMs) is an important optimization problem for simulating the complex social systems, where the goal is to identify the optimal parameter of a given ABM by minimizing the discrepancy between the simulated data and the real-world observations. Unfortunately, it suffers from the extensive computational costs of iterative evaluations, which involves the expensive simulation with the candidate parameter. While Surrogate-Assisted Evolutionary Algorithms (SAEAs) have been widely adopted to alleviate the computational burden, existing methods face two key limitations: 1) surrogating the original evaluation function is hard due the nonlinear yet multi-modal nature of the ABMs, and 2) the commonly used surrogates cannot share the optimization experience among multiple calibration tasks, making the batched calibration less effective. To address these issues, this work proposes Automatic posterior transformation with Negatively Correlated Search and Adaptive Trust-Region (ANTR). ANTR first replaces the traditional surrogates with a pretrainable neural density estimator that directly models the posterior distribution of the parameters given observed data, thereby aligning the optimization objective with parameter-space accuracy. Furthermore, we incorporate a diversity-preserving search strategy to prevent premature convergence and an adaptive trust-region method to efficiently allocate computational resources. We take two representative ABM-based financial market simulators as the test bench as due to the high non-linearity. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed ANTR significantly outperforms conventional metaheuristics and state-of-the-art SAEAs in both calibration accuracy and computational efficiency, particularly in batch calibration scenarios across multiple market conditions.
Representation Learning of Limit Order Book: A Comprehensive Study and Benchmarking
May 04, 2025



Abstract:The Limit Order Book (LOB), the mostly fundamental data of the financial market, provides a fine-grained view of market dynamics while poses significant challenges in dealing with the esteemed deep models due to its strong autocorrelation, cross-feature constrains, and feature scale disparity. Existing approaches often tightly couple representation learning with specific downstream tasks in an end-to-end manner, failed to analyze the learned representations individually and explicitly, limiting their reusability and generalization. This paper conducts the first systematic comparative study of LOB representation learning, aiming to identify the effective way of extracting transferable, compact features that capture essential LOB properties. We introduce LOBench, a standardized benchmark with real China A-share market data, offering curated datasets, unified preprocessing, consistent evaluation metrics, and strong baselines. Extensive experiments validate the sufficiency and necessity of LOB representations for various downstream tasks and highlight their advantages over both the traditional task-specific end-to-end models and the advanced representation learning models for general time series. Our work establishes a reproducible framework and provides clear guidelines for future research. Datasets and code will be publicly available at https://github.com/financial-simulation-lab/LOBench.
Pointer Networks Trained Better via Evolutionary Algorithms
Dec 06, 2023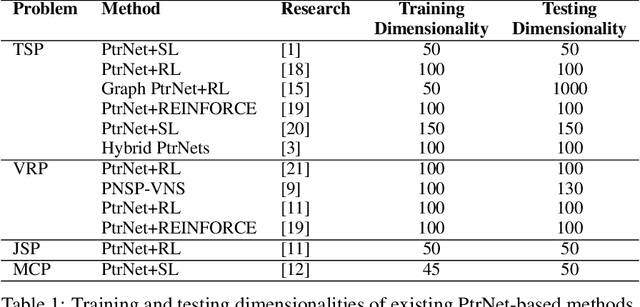



Abstract:Pointer Network (PtrNet) is a specific neural network for solving Combinatorial Optimization Problems (COPs). While PtrNets offer real-time feed-forward inference for complex COPs instances, its quality of the results tends to be less satisfactory. One possible reason is that such issue suffers from the lack of global search ability of the gradient descent, which is frequently employed in traditional PtrNet training methods including both supervised learning and reinforcement learning. To improve the performance of PtrNet, this paper delves deeply into the advantages of training PtrNet with Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs), which have been widely acknowledged for not easily getting trapped by local optima. Extensive empirical studies based on the Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) have been conducted. Results demonstrate that PtrNet trained with EA can consistently perform much better inference results than eight state-of-the-art methods on various problem scales. Compared with gradient descent based PtrNet training methods, EA achieves up to 30.21\% improvement in quality of the solution with the same computational time. With this advantage, this paper is able to at the first time report the results of solving 1000-dimensional TSPs by training a PtrNet on the same dimensionality, which strongly suggests that scaling up the training instances is in need to improve the performance of PtrNet on solving higher-dimensional COPs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge