Mutlu Cukurova
What Students Ask, How a Generative AI Assistant Responds: Exploring Higher Education Students' Dialogues on Learning Analytics Feedback
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Learning analytics dashboards (LADs) aim to support students' regulation of learning by translating complex data into feedback. Yet students, especially those with lower self-regulated learning (SRL) competence, often struggle to engage with and interpret analytics feedback. Conversational generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) assistants have shown potential to scaffold this process through real-time, personalised, dialogue-based support. Further advancing this potential, we explored authentic dialogues between students and GenAI assistant integrated into LAD during a 10-week semester. The analysis focused on questions students with different SRL levels posed, the relevance and quality of the assistant's answers, and how students perceived the assistant's role in their learning. Findings revealed distinct query patterns. While low SRL students sought clarification and reassurance, high SRL students queried technical aspects and requested personalised strategies. The assistant provided clear and reliable explanations but limited in personalisation, handling emotionally charged queries, and integrating multiple data points for tailored responses. Findings further extend that GenAI interventions can be especially valuable for low SRL students, offering scaffolding that supports engagement with feedback and narrows gaps with their higher SRL peers. At the same time, students' reflections underscored the importance of trust, need for greater adaptivity, context-awareness, and technical refinement in future systems.
Problems With Large Language Models for Learner Modelling: Why LLMs Alone Fall Short for Responsible Tutoring in K--12 Education
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:The rapid rise of large language model (LLM)-based tutors in K--12 education has fostered a misconception that generative models can replace traditional learner modelling for adaptive instruction. This is especially problematic in K--12 settings, which the EU AI Act classifies as high-risk domain requiring responsible design. Motivated by these concerns, this study synthesises evidence on limitations of LLM-based tutors and empirically investigates one critical issue: the accuracy, reliability, and temporal coherence of assessing learners' evolving knowledge over time. We compare a deep knowledge tracing (DKT) model with a widely used LLM, evaluated zero-shot and fine-tuned, using a large open-access dataset. Results show that DKT achieves the highest discrimination performance (AUC = 0.83) on next-step correctness prediction and consistently outperforms the LLM across settings. Although fine-tuning improves the LLM's AUC by approximately 8\% over the zero-shot baseline, it remains 6\% below DKT and produces higher early-sequence errors, where incorrect predictions are most harmful for adaptive support. Temporal analyses further reveal that DKT maintains stable, directionally correct mastery updates, whereas LLM variants exhibit substantial temporal weaknesses, including inconsistent and wrong-direction updates. These limitations persist despite the fine-tuned LLM requiring nearly 198 hours of high-compute training, far exceeding the computational demands of DKT. Our qualitative analysis of multi-skill mastery estimation further shows that, even after fine-tuning, the LLM produced inconsistent mastery trajectories, while DKT maintained smooth and coherent updates. Overall, the findings suggest that LLMs alone are unlikely to match the effectiveness of established intelligent tutoring systems, and that responsible tutoring requires hybrid frameworks that incorporate learner modelling.
Examining Student Interactions with a Pedagogical AI-Assistant for Essay Writing and their Impact on Students Writing Quality
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:The dynamic nature of interactions between students and GenAI, as well as their relationship to writing quality, remains underexplored. While most research has examined how general-purpose GenAI can support writing, fewer studies have investigated how students interact with pedagogically designed systems across different phases of the writing process. To address this gap, we evaluated a GenAI-driven essay-writing assistant (EWA) designed to support higher education students in argumentative writing. Drawing on 1,282 interaction logs from 32 undergraduates during a two-hour writing session, Sequential Pattern Mining and K-Means clustering were used to identify behavioral patterns. Two clusters emerged: Cluster 1 emphasized outline planning and essay structure, while Cluster 2 focused on content development. A Mann-Whitney U test revealed a moderate effect size (r = 0.36) in the essay Organization dimension, with Cluster 1 showing higher scores. Qualitative analysis indicated that students with better performance actively wrote and shared essay sections with EWA for feedback, rather than interacted passively by asking questions. These findings suggest implications for teaching and system design. Teachers can encourage active engagement, while future EWAs may integrate automatic labeling and monitoring to prompt students to move from questioning to writing, enabling fuller benefits from GenAI-supported learning.
Benchmarking Educational LLMs with Analytics: A Case Study on Gender Bias in Feedback
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:As teachers increasingly turn to GenAI in their educational practice, we need robust methods to benchmark large language models (LLMs) for pedagogical purposes. This article presents an embedding-based benchmarking framework to detect bias in LLMs in the context of formative feedback. Using 600 authentic student essays from the AES 2.0 corpus, we constructed controlled counterfactuals along two dimensions: (i) implicit cues via lexicon-based swaps of gendered terms within essays, and (ii) explicit cues via gendered author background in the prompt. We investigated six representative LLMs (i.e. GPT-5 mini, GPT-4o mini, DeepSeek-R1, DeepSeek-R1-Qwen, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Llama-3-8B). We first quantified the response divergence with cosine and Euclidean distances over sentence embeddings, then assessed significance via permutation tests, and finally, visualised structure using dimensionality reduction. In all models, implicit manipulations reliably induced larger semantic shifts for male-female counterfactuals than for female-male. Only the GPT and Llama models showed sensitivity to explicit gender cues. These findings show that even state-of-the-art LLMs exhibit asymmetric semantic responses to gender substitutions, suggesting persistent gender biases in feedback they provide learners. Qualitative analyses further revealed consistent linguistic differences (e.g., more autonomy-supportive feedback under male cues vs. more controlling feedback under female cues). We discuss implications for fairness auditing of pedagogical GenAI, propose reporting standards for counterfactual evaluation in learning analytics, and outline practical guidance for prompt design and deployment to safeguard equitable feedback.
Evaluating Trust in AI, Human, and Co-produced Feedback Among Undergraduate Students
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:As generative AI transforms educational feedback practices, understanding students' perceptions of different feedback providers becomes crucial for effective implementation. This study addresses a critical gap by comparing undergraduate students' trust in AI-generated, human-created, and human-AI co-produced feedback, informing how institutions can adapt feedback practices in this new era. Through a within-subject experiment with 91 participants, we investigated factors predicting students' ability to distinguish between feedback types, perception of feedback quality, and potential biases to AI involvement. Findings revealed that students generally preferred AI and co-produced feedback over human feedback in terms of perceived usefulness and objectivity. Only AI feedback suffered a decline in perceived genuineness when feedback sources were revealed, while co-produced feedback maintained its positive perception. Educational AI experience improved students' ability to identify AI feedback and increased their trust in all feedback types, while general AI experience decreased perceived usefulness and credibility. Male students consistently rated all feedback types as less valuable than their female and non-binary counterparts. These insights inform evidence-based guidelines for integrating AI into higher education feedback systems while addressing trust concerns and fostering AI literacy among students.
A Novel Approach to Scalable and Automatic Topic-Controlled Question Generation in Education
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:The development of Automatic Question Generation (QG) models has the potential to significantly improve educational practices by reducing the teacher workload associated with creating educational content. This paper introduces a novel approach to educational question generation that controls the topical focus of questions. The proposed Topic-Controlled Question Generation (T-CQG) method enhances the relevance and effectiveness of the generated content for educational purposes. Our approach uses fine-tuning on a pre-trained T5-small model, employing specially created datasets tailored to educational needs. The research further explores the impacts of pre-training strategies, quantisation, and data augmentation on the model's performance. We specifically address the challenge of generating semantically aligned questions with paragraph-level contexts, thereby improving the topic specificity of the generated questions. In addition, we introduce and explore novel evaluation methods to assess the topical relatedness of the generated questions. Our results, validated through rigorous offline and human-backed evaluations, demonstrate that the proposed models effectively generate high-quality, topic-focused questions. These models have the potential to reduce teacher workload and support personalised tutoring systems by serving as bespoke question generators. With its relatively small number of parameters, the proposals not only advance the capabilities of question generation models for handling specific educational topics but also offer a scalable solution that reduces infrastructure costs. This scalability makes them feasible for widespread use in education without reliance on proprietary large language models like ChatGPT.
Biometrics and Behavioral Modelling for Detecting Distractions in Online Learning
May 24, 2024


Abstract:In this article, we explore computer vision approaches to detect abnormal head pose during e-learning sessions and we introduce a study on the effects of mobile phone usage during these sessions. We utilize behavioral data collected from 120 learners monitored while participating in a MOOC learning sessions. Our study focuses on the influence of phone-usage events on behavior and physiological responses, specifically attention, heart rate, and meditation, before, during, and after phone usage. Additionally, we propose an approach for estimating head pose events using images taken by the webcam during the MOOC learning sessions to detect phone-usage events. Our hypothesis suggests that head posture undergoes significant changes when learners interact with a mobile phone, contrasting with the typical behavior seen when learners face a computer during e-learning sessions. We propose an approach designed to detect deviations in head posture from the average observed during a learner's session, operating as a semi-supervised method. This system flags events indicating alterations in head posture for subsequent human review and selection of mobile phone usage occurrences with a sensitivity over 90%.
The Interplay of Learning, Analytics, and Artificial Intelligence in Education
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a multi dimensional view of AI's role in learning and education, emphasizing the intricate interplay between AI, analytics, and the learning processes. Here, I challenge the prevalent narrow conceptualization of AI as stochastic tools, as exemplified in generative AI, and argue for the importance of alternative conceptualisations of AI. I highlight the differences between human intelligence and artificial information processing, the cognitive diversity inherent in AI algorithms, and posit that AI can also serve as an instrument for understanding human learning. Early learning sciences and AI in Education research, which saw AI as an analogy for human intelligence, have diverged from this perspective, prompting a need to rekindle this connection. The paper presents three unique conceptualizations of AI in education: the externalization of human cognition, the internalization of AI models to influence human thought processes, and the extension of human cognition via tightly integrated human-AI systems. Examples from current research and practice are examined as instances of the three conceptualisations, highlighting the potential value and limitations of each conceptualisation for education, as well as the perils of overemphasis on externalising human cognition as exemplified in today's hype surrounding generative AI tools. The paper concludes with an advocacy for a broader educational approach that includes educating people about AI and innovating educational systems to remain relevant in an AI enabled world.
Predicting challenge moments from students' discourse: A comparison of GPT-4 to two traditional natural language processing approaches
Jan 03, 2024Abstract:Effective collaboration requires groups to strategically regulate themselves to overcome challenges. Research has shown that groups may fail to regulate due to differences in members' perceptions of challenges which may benefit from external support. In this study, we investigated the potential of leveraging three distinct natural language processing models: an expert knowledge rule-based model, a supervised machine learning (ML) model and a Large Language model (LLM), in challenge detection and challenge dimension identification (cognitive, metacognitive, emotional and technical/other challenges) from student discourse, was investigated. The results show that the supervised ML and the LLM approaches performed considerably well in both tasks, in contrast to the rule-based approach, whose efficacy heavily relies on the engineered features by experts. The paper provides an extensive discussion of the three approaches' performance for automated detection and support of students' challenge moments in collaborative learning activities. It argues that, although LLMs provide many advantages, they are unlikely to be the panacea to issues of the detection and feedback provision of socially shared regulation of learning due to their lack of reliability, as well as issues of validity evaluation, privacy and confabulation. We conclude the paper with a discussion on additional considerations, including model transparency to explore feasible and meaningful analytical feedback for students and educators using LLMs.
M2LADS: A System for Generating MultiModal Learning Analytics Dashboards in Open Education
May 21, 2023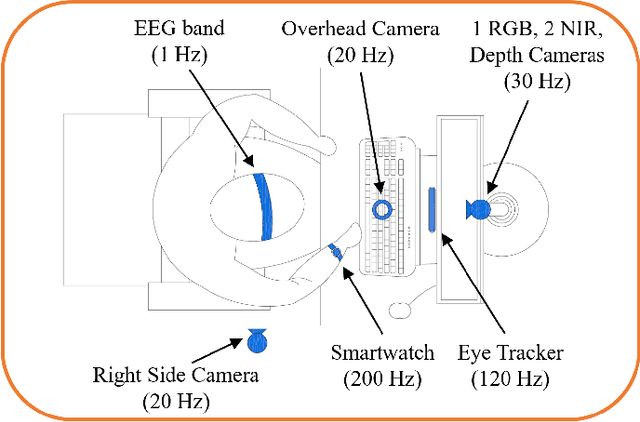


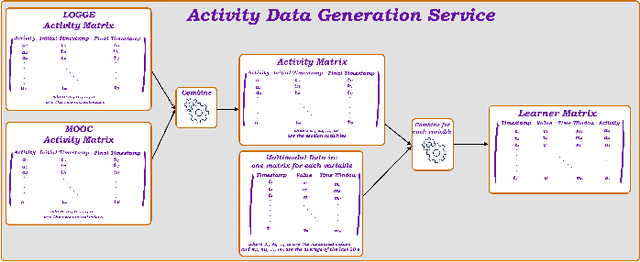
Abstract:In this article, we present a Web-based System called M2LADS, which supports the integration and visualization of multimodal data recorded in learning sessions in a MOOC in the form of Web-based Dashboards. Based on the edBB platform, the multimodal data gathered contains biometric and behavioral signals including electroencephalogram data to measure learners' cognitive attention, heart rate for affective measures, visual attention from the video recordings. Additionally, learners' static background data and their learning performance measures are tracked using LOGCE and MOOC tracking logs respectively, and both are included in the Web-based System. M2LADS provides opportunities to capture learners' holistic experience during their interactions with the MOOC, which can in turn be used to improve their learning outcomes through feedback visualizations and interventions, as well as to enhance learning analytics models and improve the open content of the MOOC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge