Muhammad Salman Pathan
Integration of Agentic AI with 6G Networks for Mission-Critical Applications: Use-case and Challenges
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:We are in a transformative era, and advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI), especially the foundational models, are constantly in the news. AI has been an integral part of many applications that rely on automation for service delivery, and one of them is mission-critical public safety applications. The problem with AI-oriented mission-critical applications is the humanin-the-loop system and the lack of adaptability to dynamic conditions while maintaining situational awareness. Agentic AI (AAI) has gained a lot of attention recently due to its ability to analyze textual data through a contextual lens while quickly adapting to conditions. In this context, this paper proposes an AAI framework for mission-critical applications. We propose a novel framework with a multi-layer architecture to realize the AAI. We also present a detailed implementation of AAI layer that bridges the gap between network infrastructure and missioncritical applications. Our preliminary analysis shows that the AAI reduces initial response time by 5.6 minutes on average, while alert generation time is reduced by 15.6 seconds on average and resource allocation is improved by up to 13.4%. We also show that the AAI methods improve the number of concurrent operations by 40, which reduces the recovery time by up to 5.2 minutes. Finally, we highlight some of the issues and challenges that need to be considered when implementing AAI frameworks.
UCloudNet: A Residual U-Net with Deep Supervision for Cloud Image Segmentation
Jan 11, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in meteorology involve the use of ground-based sky cameras for cloud observation. Analyzing images from these cameras helps in calculating cloud coverage and understanding atmospheric phenomena. Traditionally, cloud image segmentation relied on conventional computer vision techniques. However, with the advent of deep learning, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are increasingly applied for this purpose. Despite their effectiveness, CNNs often require many epochs to converge, posing challenges for real-time processing in sky camera systems. In this paper, we introduce a residual U-Net with deep supervision for cloud segmentation which provides better accuracy than previous approaches, and with less training consumption. By utilizing residual connection in encoders of UCloudNet, the feature extraction ability is further improved.
* 6 pages, 4 figures
Analyzing the impact of feature selection on the accuracy of heart disease prediction
Jun 07, 2022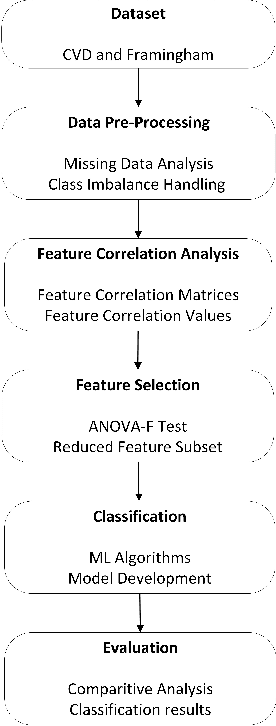
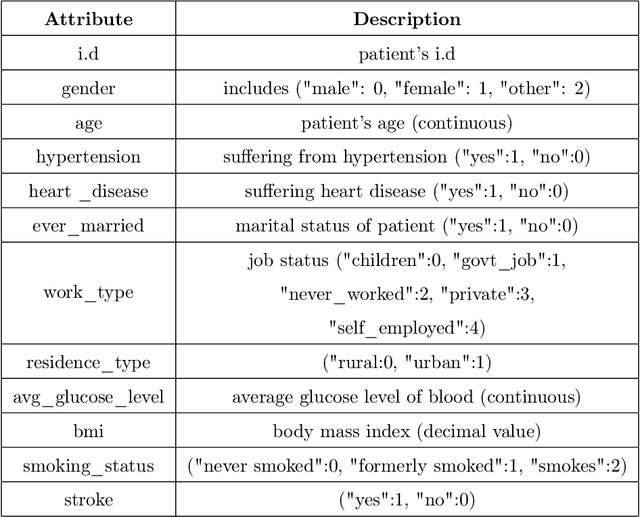
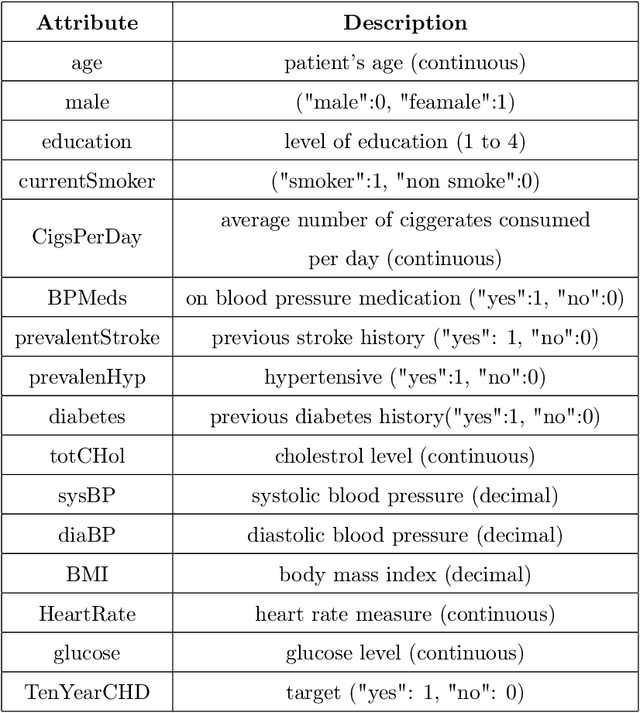
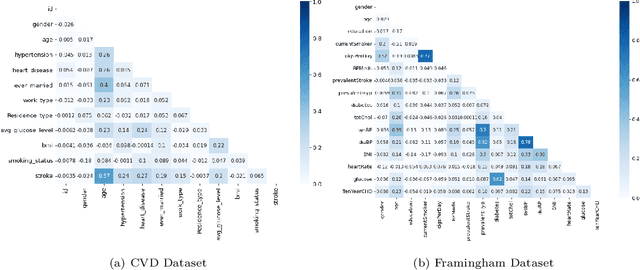
Abstract:Heart Disease has become one of the most serious diseases that has a significant impact on human life. It has emerged as one of the leading causes of mortality among the people across the globe during the last decade. In order to prevent patients from further damage, an accurate diagnosis of heart disease on time is an essential factor. Recently we have seen the usage of non-invasive medical procedures, such as artificial intelligence-based techniques in the field of medical. Specially machine learning employs several algorithms and techniques that are widely used and are highly useful in accurately diagnosing the heart disease with less amount of time. However, the prediction of heart disease is not an easy task. The increasing size of medical datasets has made it a complicated task for practitioners to understand the complex feature relations and make disease predictions. Accordingly, the aim of this research is to identify the most important risk-factors from a highly dimensional dataset which helps in the accurate classification of heart disease with less complications. For a broader analysis, we have used two heart disease datasets with various medical features. The classification results of the benchmarked models proved that there is a high impact of relevant features on the classification accuracy. Even with a reduced number of features, the performance of the classification models improved significantly with a reduced training time as compared with models trained on full feature set.
Identifying Stroke Indicators Using Rough Sets
Oct 19, 2021
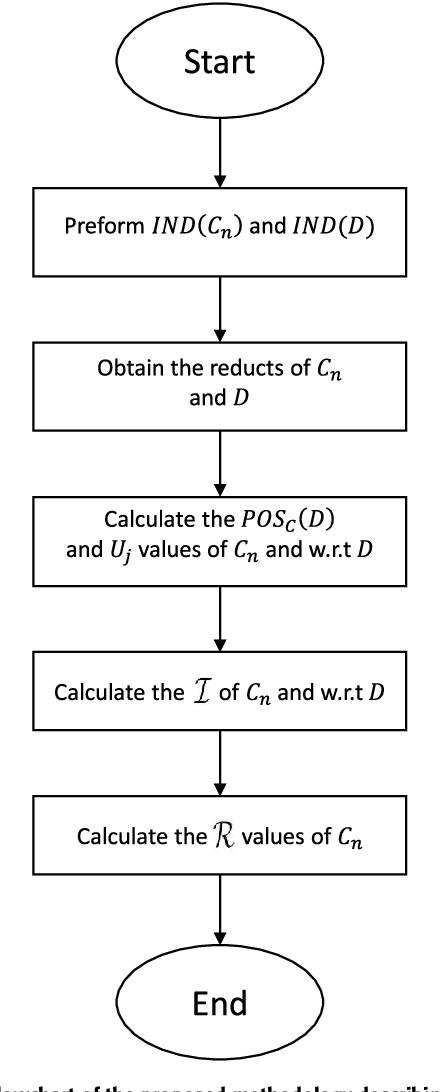

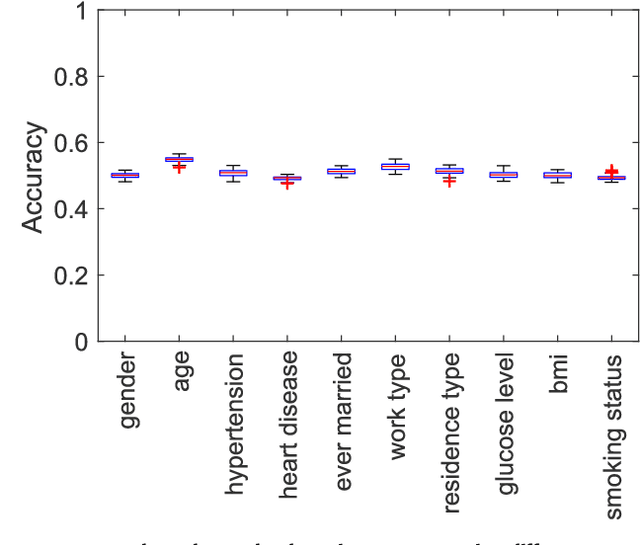
Abstract:Stroke is widely considered as the second most common cause of mortality. The adverse consequences of stroke have led to global interest and work for improving the management and diagnosis of stroke. Various techniques for data mining have been used globally for accurate prediction of occurrence of stroke based on the risk factors that are associated with the electronic health care records (EHRs) of the patients. In particular, EHRs routinely contain several thousands of features and most of them are redundant and irrelevant that need to be discarded to enhance the prediction accuracy. The choice of feature-selection methods can help in improving the prediction accuracy of the model and efficient data management of the archived input features. In this paper, we systematically analyze the various features in EHR records for the detection of stroke. We propose a novel rough-set based technique for ranking the importance of the various EHR records in detecting stroke. Unlike the conventional rough-set techniques, our proposed technique can be applied on any dataset that comprises binary feature sets. We evaluated our proposed method in a publicly available dataset of EHR, and concluded that age, average glucose level, heart disease, and hypertension were the most essential attributes for detecting stroke in patients. Furthermore, we benchmarked the proposed technique with other popular feature-selection techniques. We obtained the best performance in ranking the importance of individual features in detecting stroke.
Stereo Matching Based on Visual Sensitive Information
May 23, 2021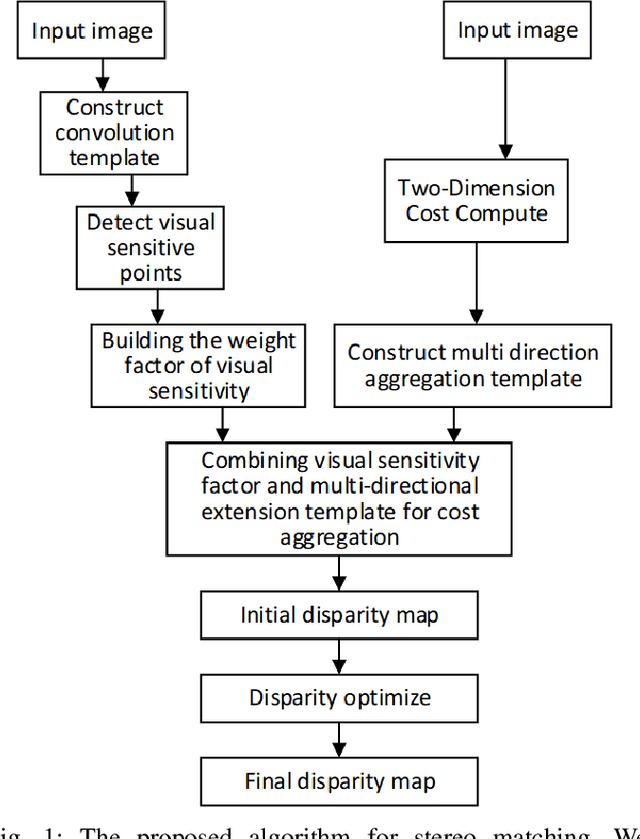
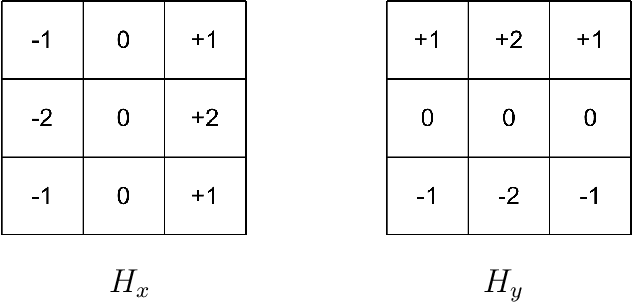

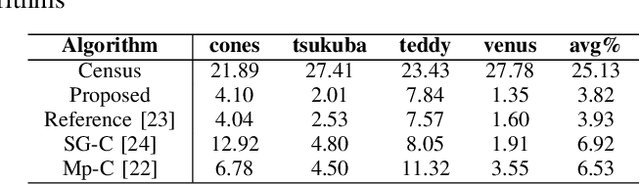
Abstract:The area of computer vision is one of the most discussed topics amongst many scholars, and stereo matching is its most important sub fields. After the parallax map is transformed into a depth map, it can be applied to many intelligent fields. In this paper, a stereo matching algorithm based on visual sensitive information is proposed by using standard images from Middlebury dataset. Aiming at the limitation of traditional stereo matching algorithms regarding the cost window, a cost aggregation algorithm based on the dynamic window is proposed, and the disparity image is optimized by using left and right consistency detection to further reduce the error matching rate. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively enhance the stereo matching effect of the image providing significant improvement in accuracy as compared with the classical census algorithm. The proposed model code, dataset, and experimental results are available at https://github.com/WangHewei16/Stereo-Matching.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge