Muhammad Saleem
HybridFC: A Hybrid Fact-Checking Approach for Knowledge Graphs
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:We consider fact-checking approaches that aim to predict the veracity of assertions in knowledge graphs. Five main categories of fact-checking approaches for knowledge graphs have been proposed in the recent literature, of which each is subject to partially overlapping limitations. In particular, current text-based approaches are limited by manual feature engineering. Path-based and rule-based approaches are limited by their exclusive use of knowledge graphs as background knowledge, and embedding-based approaches suffer from low accuracy scores on current fact-checking tasks. We propose a hybrid approach -- dubbed HybridFC -- that exploits the diversity of existing categories of fact-checking approaches within an ensemble learning setting to achieve a significantly better prediction performance. In particular, our approach outperforms the state of the art by 0.14 to 0.27 in terms of Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve on the FactBench dataset. Our code is open-source and can be found at https://github.com/dice-group/HybridFC.
An Empirical Evaluation of Cost-based Federated SPARQL Query Processing Engines
Apr 02, 2021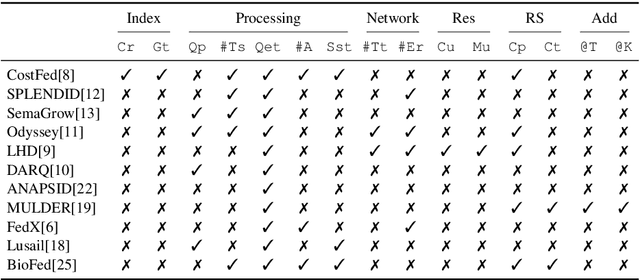
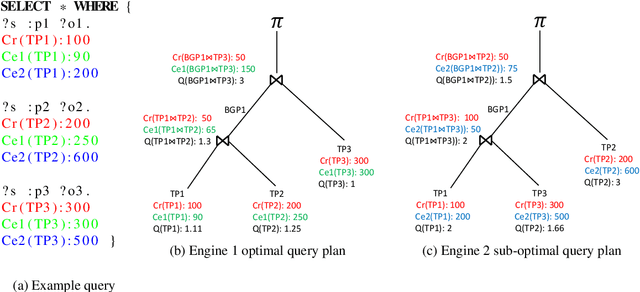
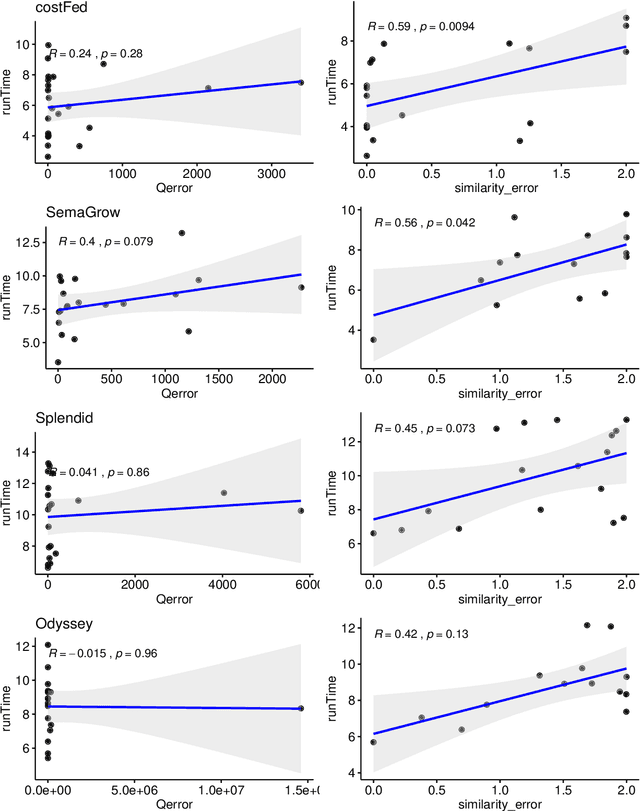
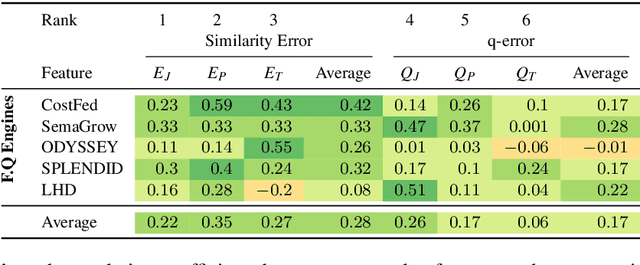
Abstract:Finding a good query plan is key to the optimization of query runtime. This holds in particular for cost-based federation engines, which make use of cardinality estimations to achieve this goal. A number of studies compare SPARQL federation engines across different performance metrics, including query runtime, result set completeness and correctness, number of sources selected and number of requests sent. Albeit informative, these metrics are generic and unable to quantify and evaluate the accuracy of the cardinality estimators of cost-based federation engines. To thoroughly evaluate cost-based federation engines, the effect of estimated cardinality errors on the overall query runtime performance must be measured. In this paper, we address this challenge by presenting novel evaluation metrics targeted at a fine-grained benchmarking of cost-based federated SPARQL query engines. We evaluate five cost-based federated SPARQL query engines using existing as well as novel evaluation metrics by using LargeRDFBench queries. Our results provide a detailed analysis of the experimental outcomes that reveal novel insights, useful for the development of future cost-based federated SPARQL query processing engines.
* 24 pages, Semantic Web, 2020, #article
Revealing Secrets in SPARQL Session Level
Sep 13, 2020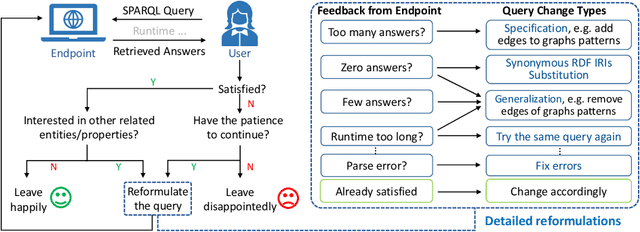
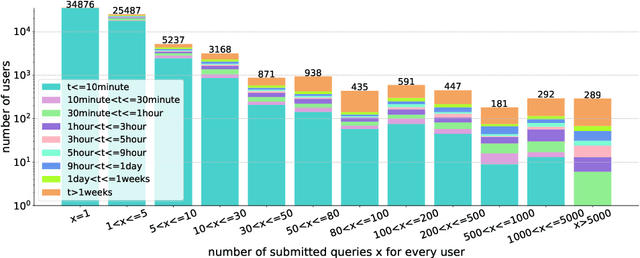
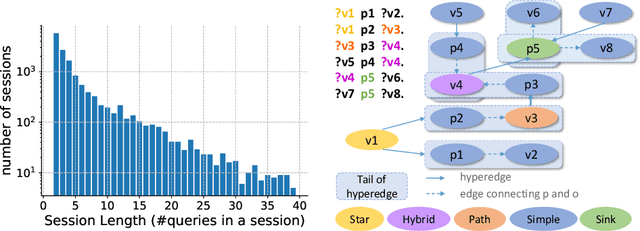
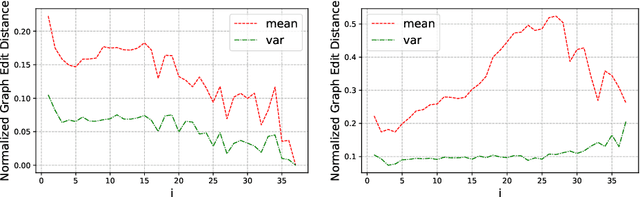
Abstract:Based on Semantic Web technologies, knowledge graphs help users to discover information of interest by using live SPARQL services. Answer-seekers often examine intermediate results iteratively and modify SPARQL queries repeatedly in a search session. In this context, understanding user behaviors is critical for effective intention prediction and query optimization. However, these behaviors have not yet been researched systematically at the SPARQL session level. This paper reveals the secrets of session-level user search behaviors by conducting a comprehensive investigation over massive real-world SPARQL query logs. In particular, we thoroughly assess query changes made by users w.r.t. structural and data-driven features of SPARQL queries. To illustrate the potentiality of our findings, we employ a proof-of-concept model to predict user intentions, i.e., future directions of the given session, and give reformulation suggestions based on the predicted intention. We hope the results presented here will help to devise efficient SPARQL caching, auto-completion, query suggestion, approximation, and relaxation techniques in the future.
Where is Linked Data in Question Answering over Linked Data?
May 07, 2020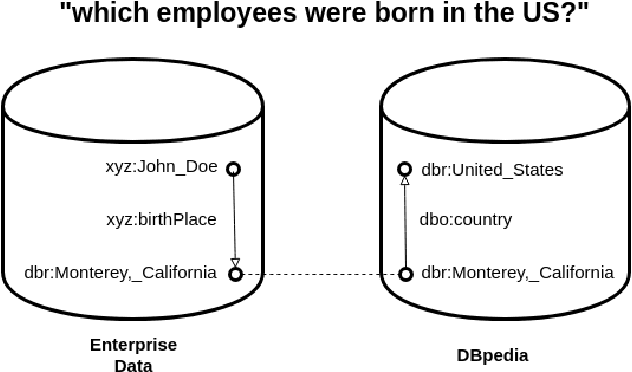
Abstract:We argue that "Question Answering with Knowledge Base" and "Question Answering over Linked Data" are currently two instances of the same problem, despite one explicitly declares to deal with Linked Data. We point out the lack of existing methods to evaluate question answering on datasets which exploit external links to the rest of the cloud or share common schema. To this end, we propose the creation of new evaluation settings to leverage the advantages of the Semantic Web to achieve AI-complete question answering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge