Revealing Secrets in SPARQL Session Level
Paper and Code
Sep 13, 2020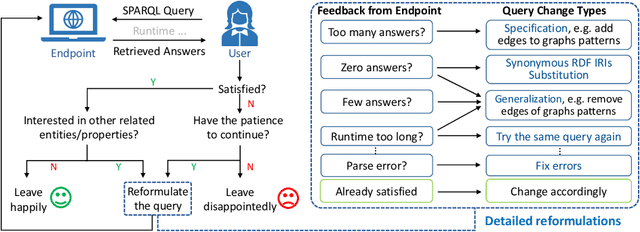
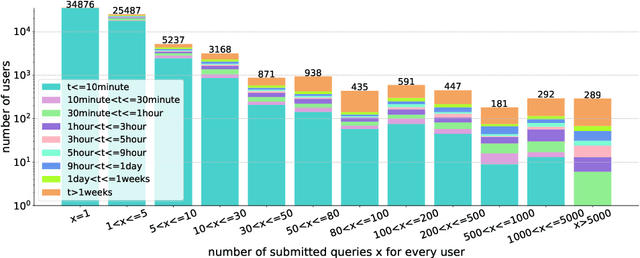
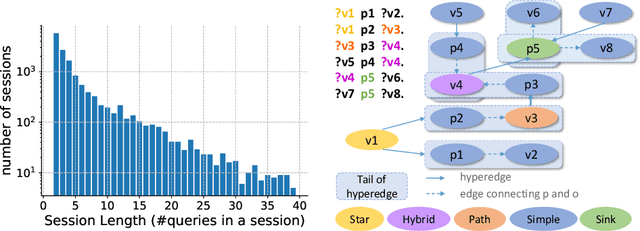
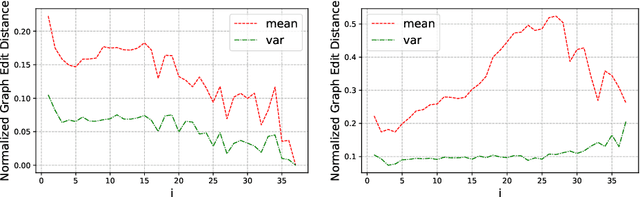
Based on Semantic Web technologies, knowledge graphs help users to discover information of interest by using live SPARQL services. Answer-seekers often examine intermediate results iteratively and modify SPARQL queries repeatedly in a search session. In this context, understanding user behaviors is critical for effective intention prediction and query optimization. However, these behaviors have not yet been researched systematically at the SPARQL session level. This paper reveals the secrets of session-level user search behaviors by conducting a comprehensive investigation over massive real-world SPARQL query logs. In particular, we thoroughly assess query changes made by users w.r.t. structural and data-driven features of SPARQL queries. To illustrate the potentiality of our findings, we employ a proof-of-concept model to predict user intentions, i.e., future directions of the given session, and give reformulation suggestions based on the predicted intention. We hope the results presented here will help to devise efficient SPARQL caching, auto-completion, query suggestion, approximation, and relaxation techniques in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge