Muhammad Adil
Neuro-Symbolic AI for Cybersecurity: State of the Art, Challenges, and Opportunities
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:Traditional Artificial Intelligence (AI) approaches in cybersecurity exhibit fundamental limitations: inadequate conceptual grounding leading to non-robustness against novel attacks; limited instructibility impeding analyst-guided adaptation; and misalignment with cybersecurity objectives. Neuro-Symbolic (NeSy) AI has emerged with the potential to revolutionize cybersecurity AI. However, there is no systematic understanding of this emerging approach. These hybrid systems address critical cybersecurity challenges by combining neural pattern recognition with symbolic reasoning, enabling enhanced threat understanding while introducing concerning autonomous offensive capabilities that reshape threat landscapes. In this survey, we systematically characterize this field by analyzing 127 publications spanning 2019-July 2025. We introduce a Grounding-Instructibility-Alignment (G-I-A) framework to evaluate these systems, focusing on both cyber defense and cyber offense across network security, malware analysis, and cyber operations. Our analysis shows advantages of multi-agent NeSy architectures and identifies critical implementation challenges including standardization gaps, computational complexity, and human-AI collaboration requirements that constrain deployment. We show that causal reasoning integration is the most transformative advancement, enabling proactive defense beyond correlation-based approaches. Our findings highlight dual-use implications where autonomous systems demonstrate substantial capabilities in zero-day exploitation while achieving significant cost reductions, altering threat dynamics. We provide insights and future research directions, emphasizing the urgent need for community-driven standardization frameworks and responsible development practices that ensure advancement serves defensive cybersecurity objectives while maintaining societal alignment.
Efficient Neuro-Symbolic Retrieval-Augmented Generation through Adaptive Query Routing
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems address factual inconsistencies in Large Language Models by grounding generation in external knowledge, yet they face a fundamental efficiency problem: simple queries consume computational resources equivalent to complex multi-hop reasoning tasks. We present SymRAG, a neuro-symbolic framework that introduces adaptive query routing based on real-time complexity and system load assessments. SymRAG dynamically selects symbolic, neural, or hybrid processing paths to align resource use with query demands. Evaluated on 2,000 queries from HotpotQA and DROP using Llama-3.2-3B and Mistral-7B models, SymRAG achieves 97.6--100.0% exact match accuracy with significantly lower CPU utilization (3.6--6.2%) and processing time (0.985--3.165s). Disabling adaptive logic results in 169--1151% increase in processing time, highlighting the framework's impact. These results underscore the potential of adaptive neuro-symbolic routing for scalable, sustainable AI systems.
Using Vision Language Models for Safety Hazard Identification in Construction
Apr 12, 2025



Abstract:Safety hazard identification and prevention are the key elements of proactive safety management. Previous research has extensively explored the applications of computer vision to automatically identify hazards from image clips collected from construction sites. However, these methods struggle to identify context-specific hazards, as they focus on detecting predefined individual entities without understanding their spatial relationships and interactions. Furthermore, their limited adaptability to varying construction site guidelines and conditions hinders their generalization across different projects. These limitations reduce their ability to assess hazards in complex construction environments and adaptability to unseen risks, leading to potential safety gaps. To address these challenges, we proposed and experimentally validated a Vision Language Model (VLM)-based framework for the identification of construction hazards. The framework incorporates a prompt engineering module that structures safety guidelines into contextual queries, allowing VLM to process visual information and generate hazard assessments aligned with the regulation guide. Within this framework, we evaluated state-of-the-art VLMs, including GPT-4o, Gemini, Llama 3.2, and InternVL2, using a custom dataset of 1100 construction site images. Experimental results show that GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro outperformed alternatives and displayed promising BERTScore of 0.906 and 0.888 respectively, highlighting their ability to identify both general and context-specific hazards. However, processing times remain a significant challenge, impacting real-time feasibility. These findings offer insights into the practical deployment of VLMs for construction site hazard detection, thereby contributing to the enhancement of proactive safety management.
ANSR-DT: An Adaptive Neuro-Symbolic Learning and Reasoning Framework for Digital Twins
Jan 15, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose an Adaptive Neuro-Symbolic Learning Framework for digital twin technology called ``ANSR-DT." Our approach combines pattern recognition algorithms with reinforcement learning and symbolic reasoning to enable real-time learning and adaptive intelligence. This integration enhances the understanding of the environment and promotes continuous learning, leading to better and more effective decision-making in real-time for applications that require human-machine collaboration. We evaluated the \textit{ANSR-DT} framework for its ability to learn and adapt to dynamic patterns, observing significant improvements in decision accuracy, reliability, and interpretability when compared to existing state-of-the-art methods. However, challenges still exist in extracting and integrating symbolic rules in complex environments, which limits the full potential of our framework in heterogeneous settings. Moreover, our ongoing research aims to address this issue in the future by ensuring seamless integration of neural models at large. In addition, our open-source implementation promotes reproducibility and encourages future research to build on our foundational work.
Decoding Android Malware with a Fraction of Features: An Attention-Enhanced MLP-SVM Approach
Sep 28, 2024Abstract:The escalating sophistication of Android malware poses significant challenges to traditional detection methods, necessitating innovative approaches that can efficiently identify and classify threats with high precision. This paper introduces a novel framework that synergistically integrates an attention-enhanced Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) with a Support Vector Machine (SVM) to make Android malware detection and classification more effective. By carefully analyzing a mere 47 features out of over 9,760 available in the comprehensive CCCS-CIC-AndMal-2020 dataset, our MLP-SVM model achieves an impressive accuracy over 99% in identifying malicious applications. The MLP, enhanced with an attention mechanism, focuses on the most discriminative features and further reduces the 47 features to only 14 components using Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA). Despite this significant reduction in dimensionality, the SVM component, equipped with an RBF kernel, excels in mapping these components to a high-dimensional space, facilitating precise classification of malware into their respective families. Rigorous evaluations, encompassing accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score metrics, confirm the superiority of our approach compared to existing state-of-the-art techniques. The proposed framework not only significantly reduces the computational complexity by leveraging a compact feature set but also exhibits resilience against the evolving Android malware landscape.
Machine Learning Based Relative Orbit Transfer for Swarm Spacecraft Motion Planning
Jan 28, 2022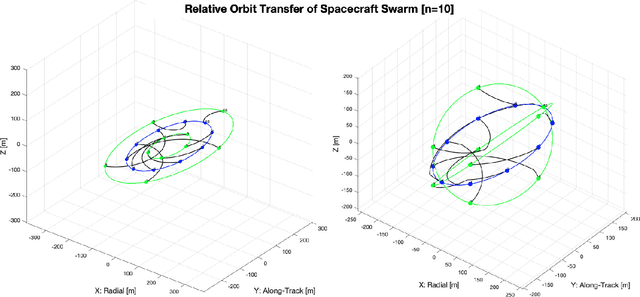
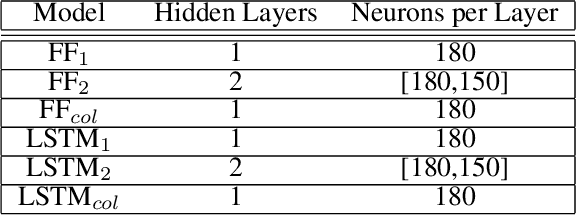
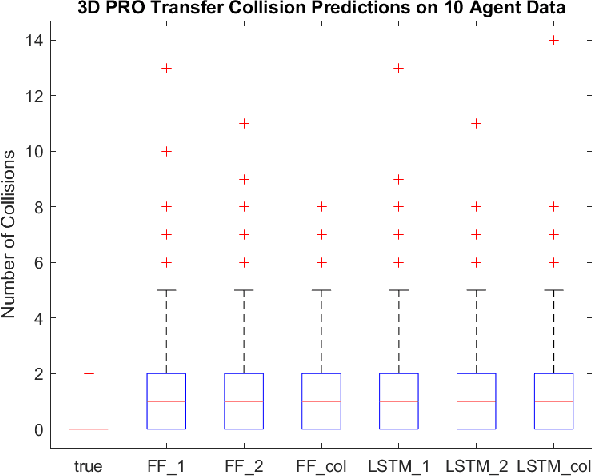
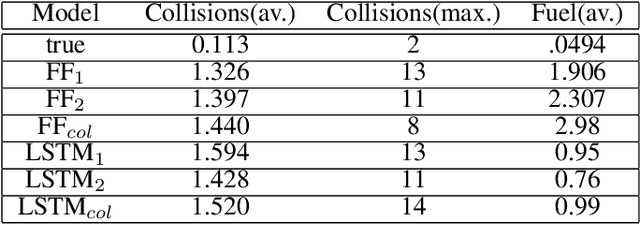
Abstract:In this paper we describe a machine learning based framework for spacecraft swarm trajectory planning. In particular, we focus on coordinating motions of multi-spacecraft in formation flying through passive relative orbit(PRO) transfers. Accounting for spacecraft dynamics while avoiding collisions between the agents makes spacecraft swarm trajectory planning difficult. Centralized approaches can be used to solve this problem, but are computationally demanding and scale poorly with the number of agents in the swarm. As a result, centralized algorithms are ill-suited for real time trajectory planning on board small spacecraft (e.g. CubeSats) comprising the swarm. In our approach a neural network is used to approximate solutions of a centralized method. The necessary training data is generated using a centralized convex optimization framework through which several instances of the n=10 spacecraft swarm trajectory planning problem are solved. We are interested in answering the following questions which will give insight on the potential utility of deep learning-based approaches to the multi-spacecraft motion planning problem: 1) Can neural networks produce feasible trajectories that satisfy safety constraints (e.g. collision avoidance) and low in fuel cost? 2) Can a neural network trained using n spacecraft data be used to solve problems for spacecraft swarms of differing size?
Optimal Multi-Robot Motion Planning via Parabolic Relaxation
Nov 28, 2021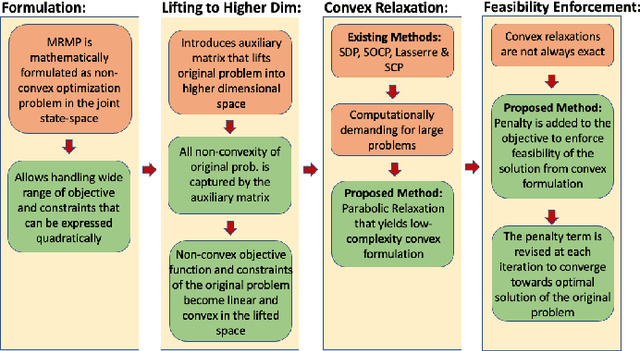
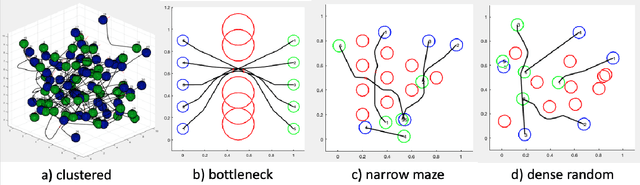
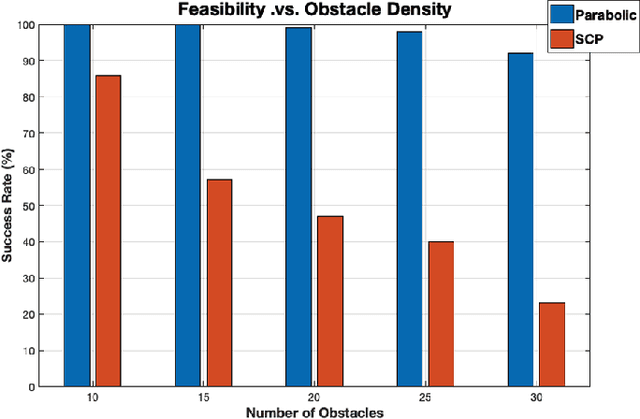
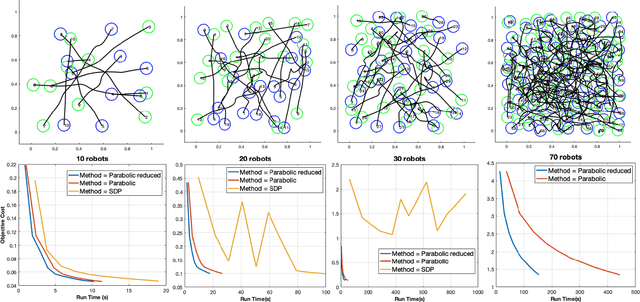
Abstract:Multi-robot systems offer enhanced capability over their monolithic counterparts, but they come at a cost of increased complexity in coordination. To reduce complexity and to make the problem tractable, multi-robot motion planning (MRMP) methods in the literature adopt de-coupled approaches that sacrifice either optimality or dynamic feasibility. In this paper, we present a convexification method, namely "parabolic relaxation", to generate optimal and dynamically feasible trajectories for MRMP in the coupled joint-space of all robots. We leverage upon the proposed relaxation to tackle the problem complexity and to attain computational tractability for planning over one hundred robots in extremely clustered environments. We take a multi-stage optimization approach that consists of i) mathematically formulating MRMP as a non-convex optimization, ii) lifting the problem into a higher dimensional space, iii) convexifying the problem through the proposed computationally efficient parabolic relaxation, and iv) penalizing with iterative search to ensure feasibility and recovery of feasible and near-optimal solutions to the original problem. Our numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach is capable of generating optimal and dynamically feasible trajectories for challenging motion planning problems with higher success rate than the state-of-the-art, yet remain computationally tractable for over one hundred robots in a highly dense environment.
Rapid Detection of Aircrafts in Satellite Imagery based on Deep Neural Networks
Apr 21, 2021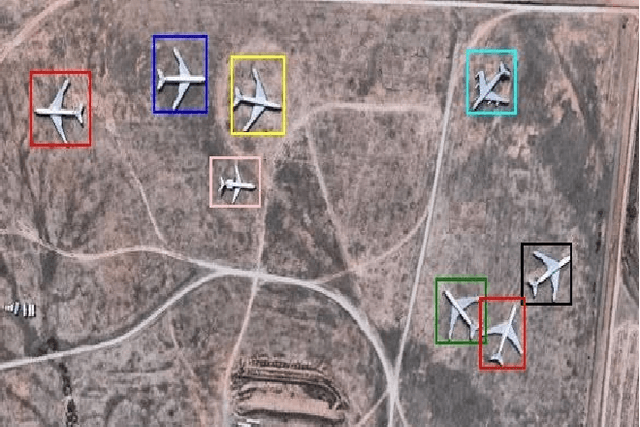
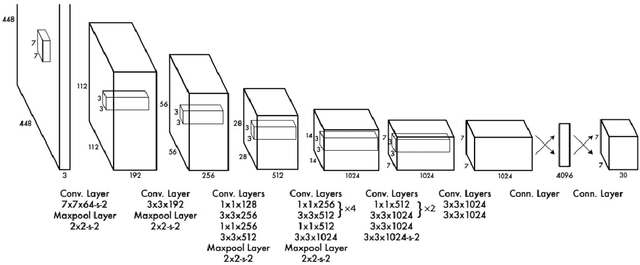
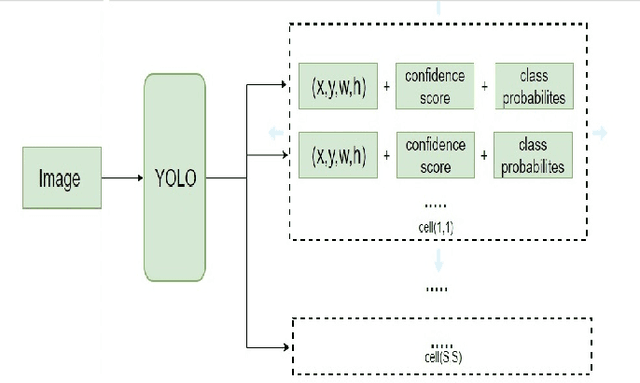
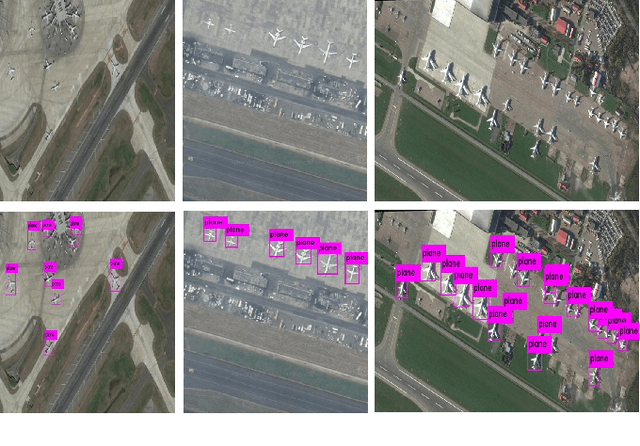
Abstract:Object detection is one of the fundamental objectives in Applied Computer Vision. In some of the applications, object detection becomes very challenging such as in the case of satellite image processing. Satellite image processing has remained the focus of researchers in domains of Precision Agriculture, Climate Change, Disaster Management, etc. Therefore, object detection in satellite imagery is one of the most researched problems in this domain. This paper focuses on aircraft detection. in satellite imagery using deep learning techniques. In this paper, we used YOLO deep learning framework for aircraft detection. This method uses satellite images collected by different sources as learning for the model to perform detection. Object detection in satellite images is mostly complex because objects have many variations, types, poses, sizes, complex and dense background. YOLO has some limitations for small size objects (less than$\sim$32 pixels per object), therefore we upsample the prediction grid to reduce the coarseness of the model and to accurately detect the densely clustered objects. The improved model shows good accuracy and performance on different unknown images having small, rotating, and dense objects to meet the requirements in real-time.
Multi-Agent Motion Planning using Deep Learning for Space Applications
Oct 15, 2020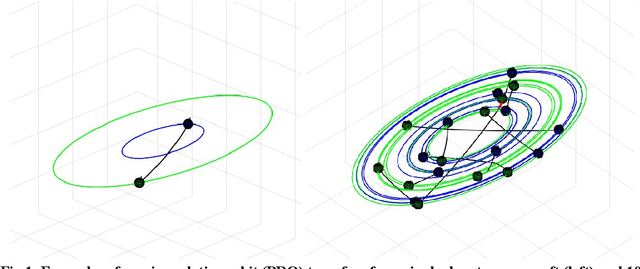
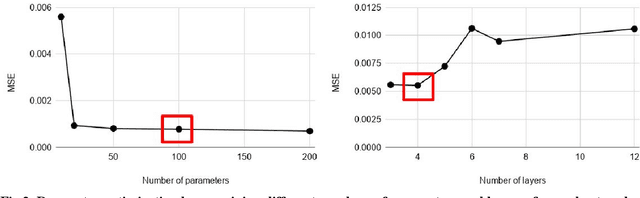
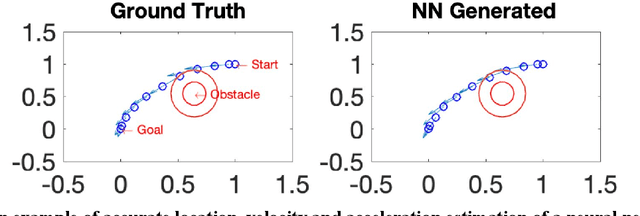
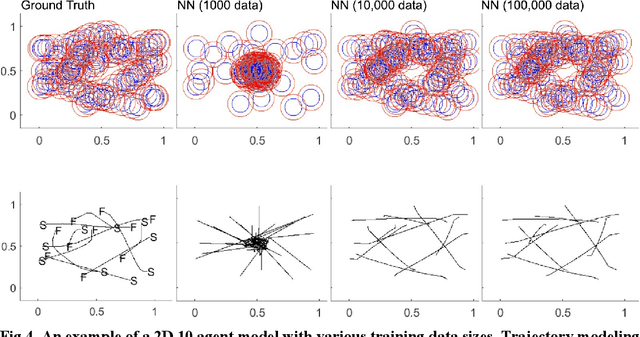
Abstract:State-of-the-art motion planners cannot scale to a large number of systems. Motion planning for multiple agents is an NP (non-deterministic polynomial-time) hard problem, so the computation time increases exponentially with each addition of agents. This computational demand is a major stumbling block to the motion planner's application to future NASA missions involving the swarm of space vehicles. We applied a deep neural network to transform computationally demanding mathematical motion planning problems into deep learning-based numerical problems. We showed optimal motion trajectories can be accurately replicated using deep learning-based numerical models in several 2D and 3D systems with multiple agents. The deep learning-based numerical model demonstrates superior computational efficiency with plans generated 1000 times faster than the mathematical model counterpart.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge