Moye Chen
Investigating Inference-time Scaling for Chain of Multi-modal Thought: A Preliminary Study
Feb 17, 2025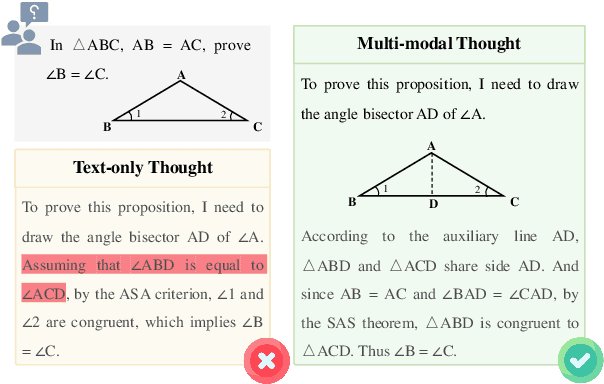
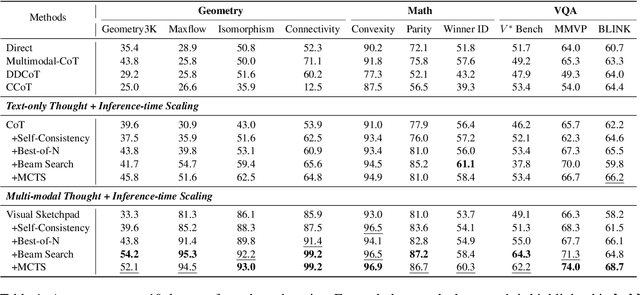
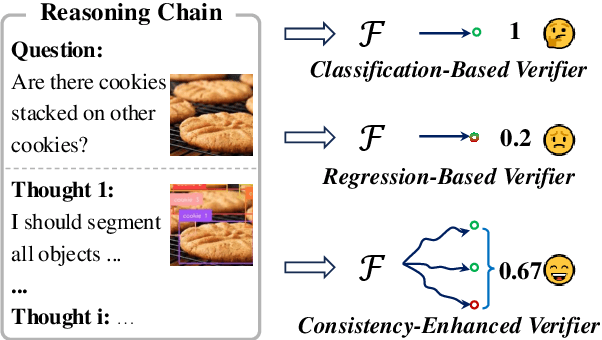
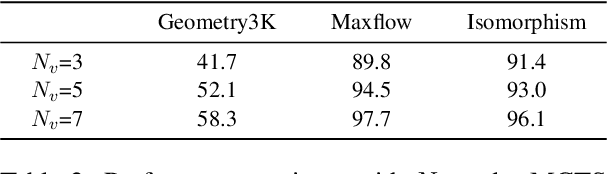
Abstract:Recently, inference-time scaling of chain-of-thought (CoT) has been demonstrated as a promising approach for addressing multi-modal reasoning tasks. While existing studies have predominantly centered on text-based thinking, the integration of both visual and textual modalities within the reasoning process remains unexplored. In this study, we pioneer the exploration of inference-time scaling with multi-modal thought, aiming to bridge this gap. To provide a comprehensive analysis, we systematically investigate popular sampling-based and tree search-based inference-time scaling methods on 10 challenging tasks spanning various domains. Besides, we uniformly adopt a consistency-enhanced verifier to ensure effective guidance for both methods across different thought paradigms. Results show that multi-modal thought promotes better performance against conventional text-only thought, and blending the two types of thought fosters more diverse thinking. Despite these advantages, multi-modal thoughts necessitate higher token consumption for processing richer visual inputs, which raises concerns in practical applications. We hope that our findings on the merits and drawbacks of this research line will inspire future works in the field.
Faithfulness in Natural Language Generation: A Systematic Survey of Analysis, Evaluation and Optimization Methods
Mar 10, 2022
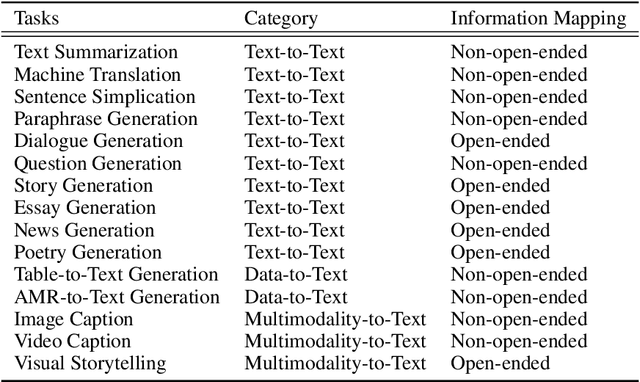


Abstract:Natural Language Generation (NLG) has made great progress in recent years due to the development of deep learning techniques such as pre-trained language models. This advancement has resulted in more fluent, coherent and even properties controllable (e.g. stylistic, sentiment, length etc.) generation, naturally leading to development in downstream tasks such as abstractive summarization, dialogue generation, machine translation, and data-to-text generation. However, the faithfulness problem that the generated text usually contains unfaithful or non-factual information has become the biggest challenge, which makes the performance of text generation unsatisfactory for practical applications in many real-world scenarios. Many studies on analysis, evaluation, and optimization methods for faithfulness problems have been proposed for various tasks, but have not been organized, compared and discussed in a combined manner. In this survey, we provide a systematic overview of the research progress on the faithfulness problem of NLG, including problem analysis, evaluation metrics and optimization methods. We organize the evaluation and optimization methods for different tasks into a unified taxonomy to facilitate comparison and learning across tasks. Several research trends are discussed further.
SgSum: Transforming Multi-document Summarization into Sub-graph Selection
Oct 25, 2021



Abstract:Most of existing extractive multi-document summarization (MDS) methods score each sentence individually and extract salient sentences one by one to compose a summary, which have two main drawbacks: (1) neglecting both the intra and cross-document relations between sentences; (2) neglecting the coherence and conciseness of the whole summary. In this paper, we propose a novel MDS framework (SgSum) to formulate the MDS task as a sub-graph selection problem, in which source documents are regarded as a relation graph of sentences (e.g., similarity graph or discourse graph) and the candidate summaries are its sub-graphs. Instead of selecting salient sentences, SgSum selects a salient sub-graph from the relation graph as the summary. Comparing with traditional methods, our method has two main advantages: (1) the relations between sentences are captured by modeling both the graph structure of the whole document set and the candidate sub-graphs; (2) directly outputs an integrate summary in the form of sub-graph which is more informative and coherent. Extensive experiments on MultiNews and DUC datasets show that our proposed method brings substantial improvements over several strong baselines. Human evaluation results also demonstrate that our model can produce significantly more coherent and informative summaries compared with traditional MDS methods. Moreover, the proposed architecture has strong transfer ability from single to multi-document input, which can reduce the resource bottleneck in MDS tasks. Our code and results are available at: \url{https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Research/tree/master/NLP/EMNLP2021-SgSum}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge