Mostafa Salem
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Synthesis in MRI using an encoder-decoder U-NET
Jan 17, 2019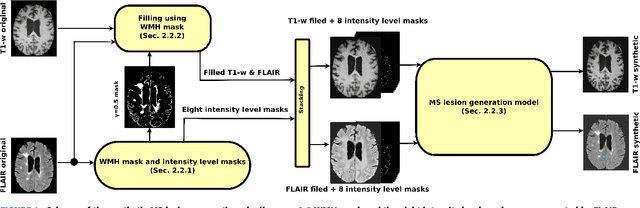

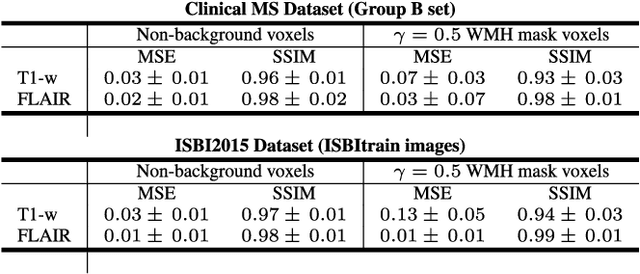
Abstract:In this paper, we propose generating synthetic multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions on MRI images with the final aim to improve the performance of supervised machine learning algorithms, therefore avoiding the problem of the lack of available ground truth. We propose a two-input two-output fully convolutional neural network model for MS lesion synthesis in MRI images. The lesion information is encoded as discrete binary intensity level masks passed to the model and stacked with the input images. The model is trained end-to-end without the need for manually annotating the lesions in the training set. We then perform the generation of synthetic lesions on healthy images via registration of patient images, which are subsequently used for data augmentation to increase the performance for supervised MS lesion detection algorithms. Our pipeline is evaluated on MS patient data from an in-house clinical dataset and the public ISBI2015 challenge dataset. The evaluation is based on measuring the similarities between the real and the synthetic images as well as in terms of lesion detection performance by segmenting both the original and synthetic images individually using a state-of-the-art segmentation framework. We also demonstrate the usage of synthetic MS lesions generated on healthy images as data augmentation. We analyze a scenario of limited training data (one-image training) to demonstrate the effect of the data augmentation on both datasets. Our results significantly show the effectiveness of the usage of synthetic MS lesion images. For the ISBI2015 challenge, our one-image model trained using only a single image plus the synthetic data augmentation strategy showed a performance similar to that of other CNN methods that were fully trained using the entire training set, yielding a comparable human expert rater performance
One-shot domain adaptation in multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation using convolutional neural networks
May 31, 2018
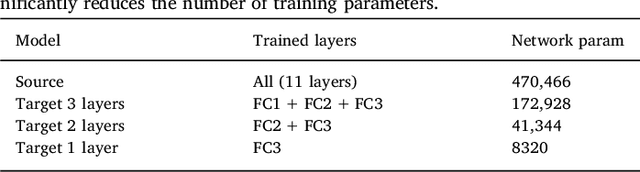
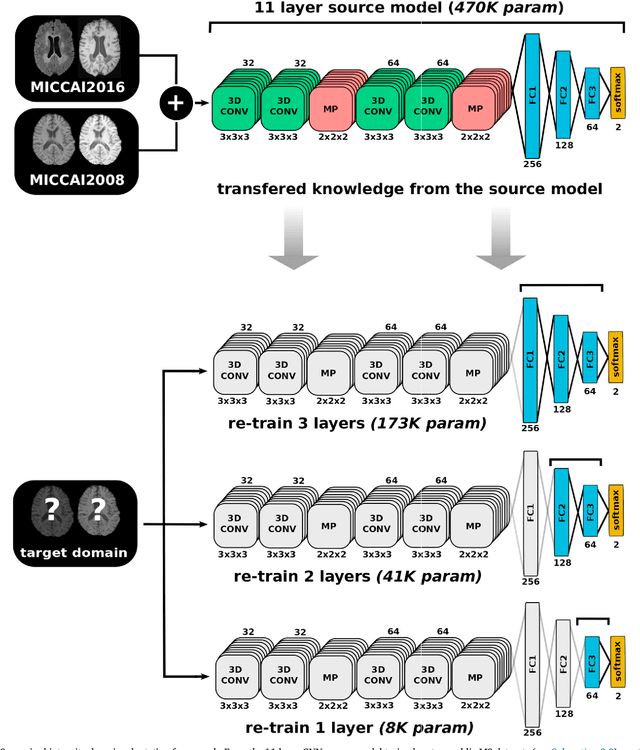
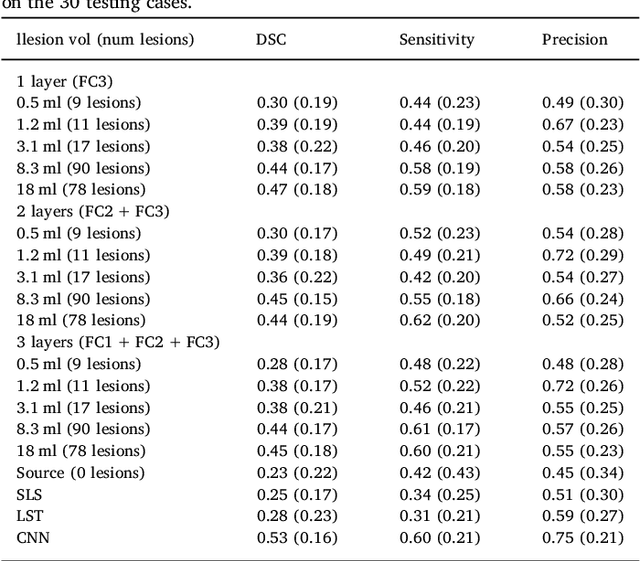
Abstract:In recent years, several convolutional neural network (CNN) methods have been proposed for the automated white matter lesion segmentation of multiple sclerosis (MS) patient images, due to their superior performance compared with those of other state-of-the-art methods. However, the accuracies of CNN methods tend to decrease significantly when evaluated on different image domains compared with those used for training, which demonstrates the lack of adaptability of CNNs to unseen imaging data. In this study, we analyzed the effect of intensity domain adaptation on our recently proposed CNN-based MS lesion segmentation method. Given a source model trained on two public MS datasets, we investigated the transferability of the CNN model when applied to other MRI scanners and protocols, evaluating the minimum number of annotated images needed from the new domain and the minimum number of layers needed to re-train to obtain comparable accuracy. Our analysis comprised MS patient data from both a clinical center and the public ISBI2015 challenge database, which permitted us to compare the domain adaptation capability of our model to that of other state-of-the-art methods. For the ISBI2015 challenge, our one-shot domain adaptation model trained using only a single image showed a performance similar to that of other CNN methods that were fully trained using the entire available training set, yielding a comparable human expert rater performance. We believe that our experiments will encourage the MS community to incorporate its use in different clinical settings with reduced amounts of annotated data. This approach could be meaningful not only in terms of the accuracy in delineating MS lesions but also in the related reductions in time and economic costs derived from manual lesion labeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge