Mohi Reza
Co-Writing with AI, on Human Terms: Aligning Research with User Demands Across the Writing Process
Apr 16, 2025



Abstract:As generative AI tools like ChatGPT become integral to everyday writing, critical questions arise about how to preserve writers' sense of agency and ownership when using these tools. Yet, a systematic understanding of how AI assistance affects different aspects of the writing process - and how this shapes writers' agency - remains underexplored. To address this gap, we conducted a systematic review of 109 HCI papers using the PRISMA approach. From this literature, we identify four overarching design strategies for AI writing support: structured guidance, guided exploration, active co-writing, and critical feedback - mapped across the four key cognitive processes in writing: planning, translating, reviewing, and monitoring. We complement this analysis with interviews of 15 writers across diverse domains. Our findings reveal that writers' desired levels of AI intervention vary across the writing process: content-focused writers (e.g., academics) prioritize ownership during planning, while form-focused writers (e.g., creatives) value control over translating and reviewing. Writers' preferences are also shaped by contextual goals, values, and notions of originality and authorship. By examining when ownership matters, what writers want to own, and how AI interactions shape agency, we surface both alignment and gaps between research and user needs. Our findings offer actionable design guidance for developing human-centered writing tools for co-writing with AI, on human terms.
PromptHive: Bringing Subject Matter Experts Back to the Forefront with Collaborative Prompt Engineering for Educational Content Creation
Oct 21, 2024


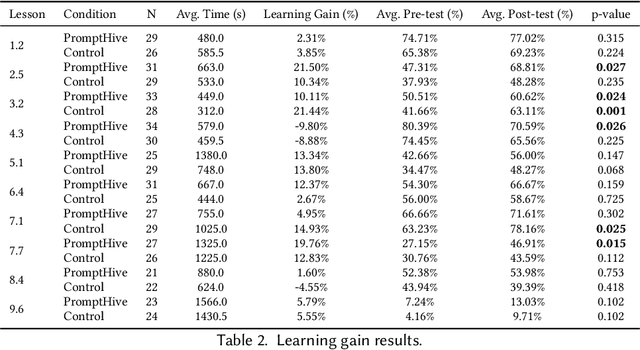
Abstract:Involving subject matter experts in prompt engineering can guide LLM outputs toward more helpful, accurate, and tailored content that meets the diverse needs of different domains. However, iterating towards effective prompts can be challenging without adequate interface support for systematic experimentation within specific task contexts. In this work, we introduce PromptHive, a collaborative interface for prompt authoring, designed to better connect domain knowledge with prompt engineering through features that encourage rapid iteration on prompt variations. We conducted an evaluation study with ten subject matter experts in math and validated our design through two collaborative prompt-writing sessions and a learning gain study with 358 learners. Our results elucidate the prompt iteration process and validate the tool's usability, enabling non-AI experts to craft prompts that generate content comparable to human-authored materials while reducing perceived cognitive load by half and shortening the authoring process from several months to just a few hours.
Understanding Help-Seeking Behavior of Students Using LLMs vs. Web Search for Writing SQL Queries
Aug 15, 2024

Abstract:Growth in the use of large language models (LLMs) in programming education is altering how students write SQL queries. Traditionally, students relied heavily on web search for coding assistance, but this has shifted with the adoption of LLMs like ChatGPT. However, the comparative process and outcomes of using web search versus LLMs for coding help remain underexplored. To address this, we conducted a randomized interview study in a database classroom to compare web search and LLMs, including a publicly available LLM (ChatGPT) and an instructor-tuned LLM, for writing SQL queries. Our findings indicate that using an instructor-tuned LLM required significantly more interactions than both ChatGPT and web search, but resulted in a similar number of edits to the final SQL query. No significant differences were found in the quality of the final SQL queries between conditions, although the LLM conditions directionally showed higher query quality. Furthermore, students using instructor-tuned LLM reported a lower mental demand. These results have implications for learning and productivity in programming education.
Impact of Guidance and Interaction Strategies for LLM Use on Learner Performance and Perception
Oct 13, 2023Abstract:Personalized chatbot-based teaching assistants can be crucial in addressing increasing classroom sizes, especially where direct teacher presence is limited. Large language models (LLMs) offer a promising avenue, with increasing research exploring their educational utility. However, the challenge lies not only in establishing the efficacy of LLMs but also in discerning the nuances of interaction between learners and these models, which impact learners' engagement and results. We conducted a formative study in an undergraduate computer science classroom (N=145) and a controlled experiment on Prolific (N=356) to explore the impact of four pedagogically informed guidance strategies and the interaction between student approaches and LLM responses. Direct LLM answers marginally improved performance, while refining student solutions fostered trust. Our findings suggest a nuanced relationship between the guidance provided and LLM's role in either answering or refining student input. Based on our findings, we provide design recommendations for optimizing learner-LLM interactions.
ABScribe: Rapid Exploration of Multiple Writing Variations in Human-AI Co-Writing Tasks using Large Language Models
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:Exploring alternative ideas by rewriting text is integral to the writing process. State-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) can simplify writing variation generation. However, current interfaces pose challenges for simultaneous consideration of multiple variations: creating new versions without overwriting text can be difficult, and pasting them sequentially can clutter documents, increasing workload and disrupting writers' flow. To tackle this, we present ABScribe, an interface that supports rapid, yet visually structured, exploration of writing variations in human-AI co-writing tasks. With ABScribe, users can swiftly produce multiple variations using LLM prompts, which are auto-converted into reusable buttons. Variations are stored adjacently within text segments for rapid in-place comparisons using mouse-over interactions on a context toolbar. Our user study with 12 writers shows that ABScribe significantly reduces task workload (d = 1.20, p < 0.001), enhances user perceptions of the revision process (d = 2.41, p < 0.001) compared to a popular baseline workflow, and provides insights into how writers explore variations using LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge