Mohamed A. Naser
DASS Good: Explainable Data Mining of Spatial Cohort Data
Apr 10, 2023Abstract:Developing applicable clinical machine learning models is a difficult task when the data includes spatial information, for example, radiation dose distributions across adjacent organs at risk. We describe the co-design of a modeling system, DASS, to support the hybrid human-machine development and validation of predictive models for estimating long-term toxicities related to radiotherapy doses in head and neck cancer patients. Developed in collaboration with domain experts in oncology and data mining, DASS incorporates human-in-the-loop visual steering, spatial data, and explainable AI to augment domain knowledge with automatic data mining. We demonstrate DASS with the development of two practical clinical stratification models and report feedback from domain experts. Finally, we describe the design lessons learned from this collaborative experience.
Why is the winner the best?
Mar 30, 2023
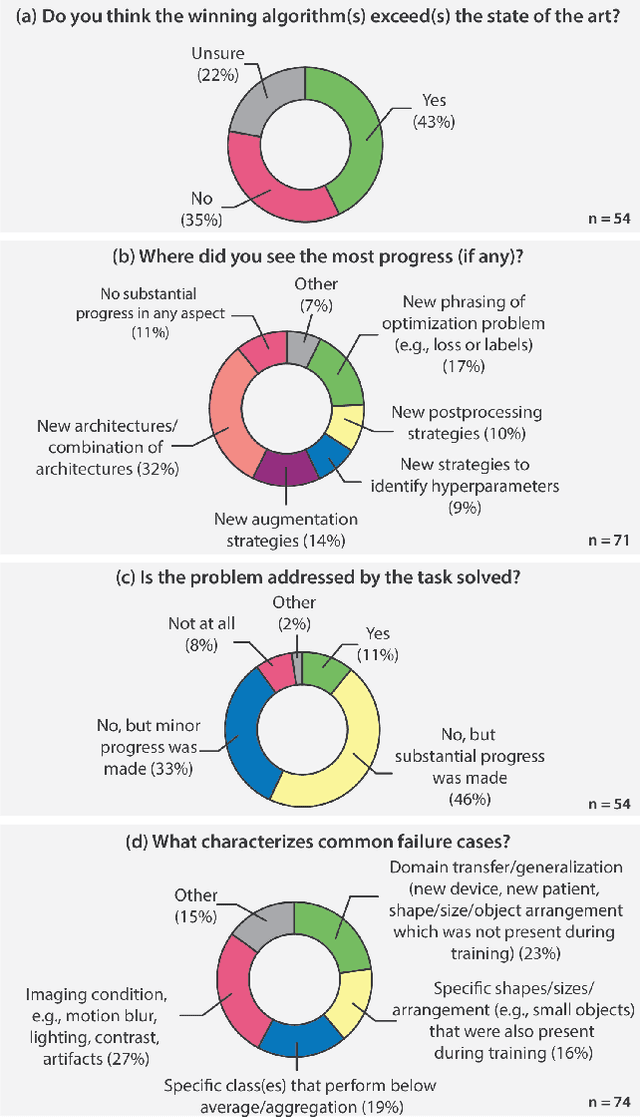
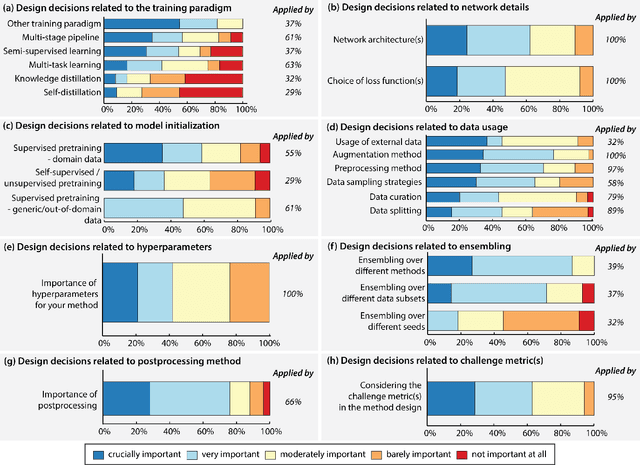
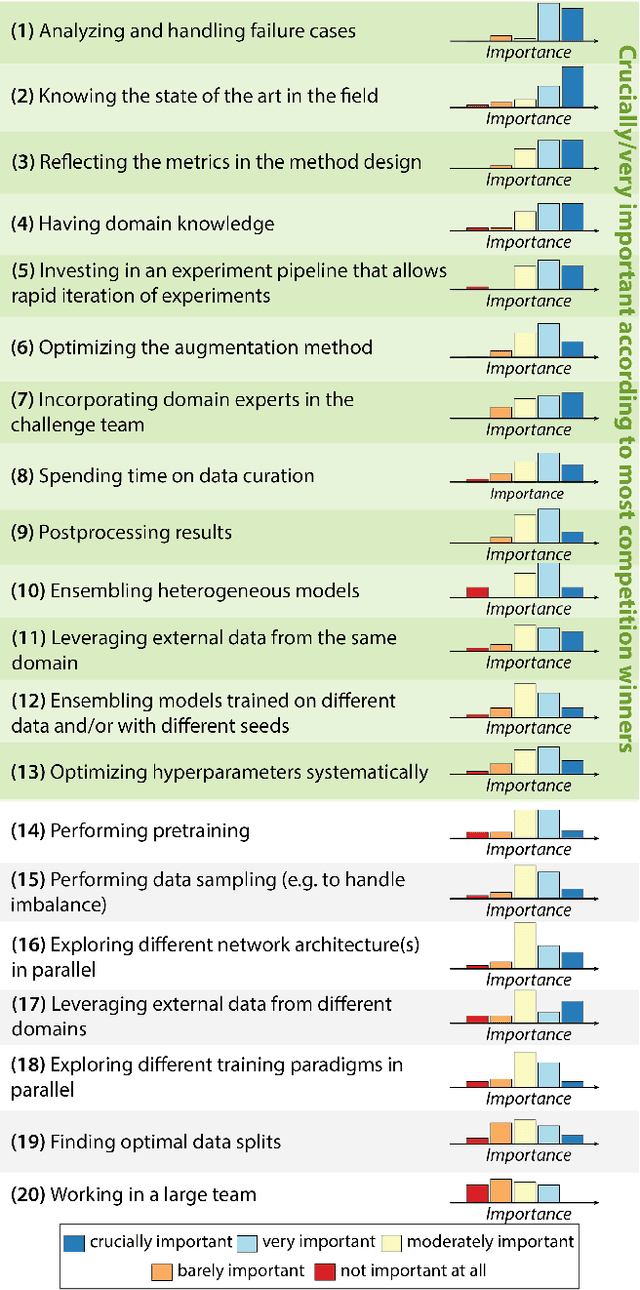
Abstract:International benchmarking competitions have become fundamental for the comparative performance assessment of image analysis methods. However, little attention has been given to investigating what can be learnt from these competitions. Do they really generate scientific progress? What are common and successful participation strategies? What makes a solution superior to a competing method? To address this gap in the literature, we performed a multi-center study with all 80 competitions that were conducted in the scope of IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021. Statistical analyses performed based on comprehensive descriptions of the submitted algorithms linked to their rank as well as the underlying participation strategies revealed common characteristics of winning solutions. These typically include the use of multi-task learning (63%) and/or multi-stage pipelines (61%), and a focus on augmentation (100%), image preprocessing (97%), data curation (79%), and postprocessing (66%). The "typical" lead of a winning team is a computer scientist with a doctoral degree, five years of experience in biomedical image analysis, and four years of experience in deep learning. Two core general development strategies stood out for highly-ranked teams: the reflection of the metrics in the method design and the focus on analyzing and handling failure cases. According to the organizers, 43% of the winning algorithms exceeded the state of the art but only 11% completely solved the respective domain problem. The insights of our study could help researchers (1) improve algorithm development strategies when approaching new problems, and (2) focus on open research questions revealed by this work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge