Mingjie Wu
WalnutData: A UAV Remote Sensing Dataset of Green Walnuts and Model Evaluation
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:The UAV technology is gradually maturing and can provide extremely powerful support for smart agriculture and precise monitoring. Currently, there is no dataset related to green walnuts in the field of agricultural computer vision. Thus, in order to promote the algorithm design in the field of agricultural computer vision, we used UAV to collect remote-sensing data from 8 walnut sample plots. Considering that green walnuts are subject to various lighting conditions and occlusion, we constructed a large-scale dataset with a higher-granularity of target features - WalnutData. This dataset contains a total of 30,240 images and 706,208 instances, and there are 4 target categories: being illuminated by frontal light and unoccluded (A1), being backlit and unoccluded (A2), being illuminated by frontal light and occluded (B1), and being backlit and occluded (B2). Subsequently, we evaluated many mainstream algorithms on WalnutData and used these evaluation results as the baseline standard. The dataset and all evaluation results can be obtained at https://github.com/1wuming/WalnutData.
Background Segmentation for Vehicle Re-Identification
Oct 15, 2019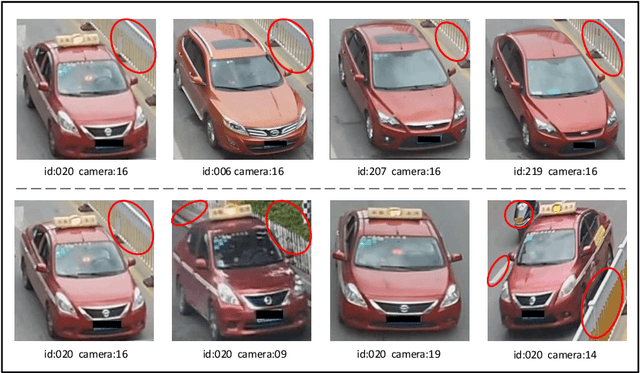
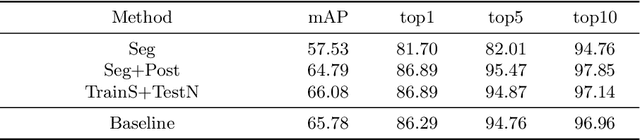
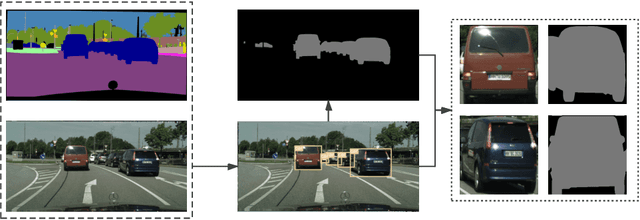
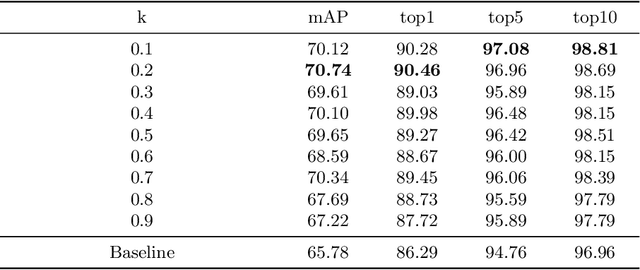
Abstract:Vehicle re-identification (Re-ID) is very important in intelligent transportation and video surveillance.Prior works focus on extracting discriminative features from visual appearance of vehicles or using visual-spatio-temporal information.However, background interference in vehicle re-identification have not been explored.In the actual large-scale spatio-temporal scenes, the same vehicle usually appears in different backgrounds while different vehicles might appear in the same background, which will seriously affect the re-identification performance. To the best of our knowledge, this paper is the first to consider the background interference problem in vehicle re-identification. We construct a vehicle segmentation dataset and develop a vehicle Re-ID framework with a background interference removal (BIR) mechanism to improve the vehicle Re-ID performance as well as robustness against complex background in large-scale spatio-temporal scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework, with an average 9% gain on mAP over state-of-the-art vehicle Re-ID algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge