Mingchen Zou
Establishing Truly Causal Relationship Between Whole Slide Image Predictions and Diagnostic Evidence Subregions in Deep Learning
Jul 24, 2024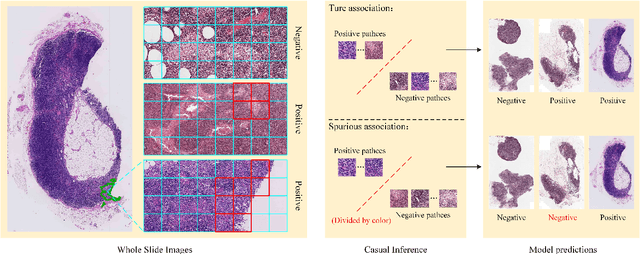

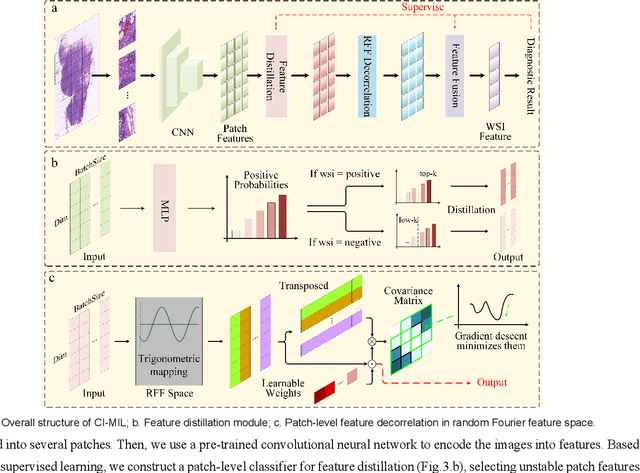
Abstract:In the field of deep learning-driven Whole Slide Image (WSI) classification, Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) has gained significant attention due to its ability to be trained using only slide-level diagnostic labels. Previous MIL researches have primarily focused on enhancing feature aggregators for globally analyzing WSIs, but overlook a causal relationship in diagnosis: model's prediction should ideally stem solely from regions of the image that contain diagnostic evidence (such as tumor cells), which usually occupy relatively small areas. To address this limitation and establish the truly causal relationship between model predictions and diagnostic evidence regions, we propose Causal Inference Multiple Instance Learning (CI-MIL). CI-MIL integrates feature distillation with a novel patch decorrelation mechanism, employing a two-stage causal inference approach to distill and process patches with high diagnostic value. Initially, CI-MIL leverages feature distillation to identify patches likely containing tumor cells and extracts their corresponding feature representations. These features are then mapped to random Fourier feature space, where a learnable weighting scheme is employed to minimize inter-feature correlations, effectively reducing redundancy from homogenous patches and mitigating data bias. These processes strengthen the causal relationship between model predictions and diagnostically relevant regions, making the prediction more direct and reliable. Experimental results demonstrate that CI-MIL outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, CI-MIL exhibits superior interpretability, as its selected regions demonstrate high consistency with ground truth annotations, promising more reliable diagnostic assistance for pathologists.
Global Contrast Masked Autoencoders Are Powerful Pathological Representation Learners
May 21, 2022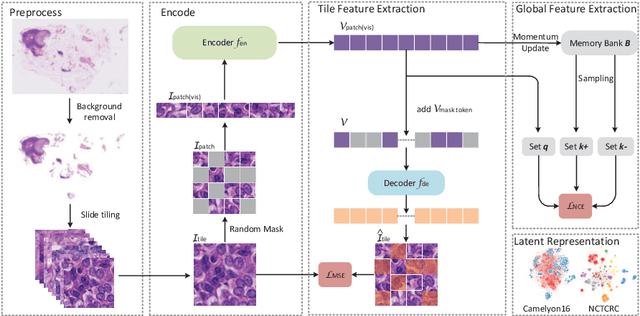
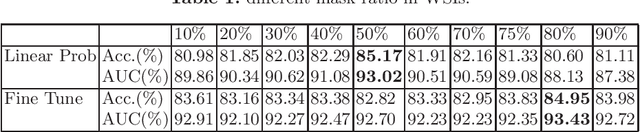
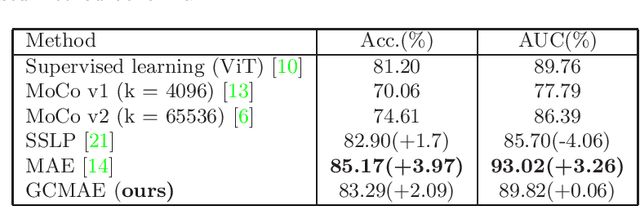
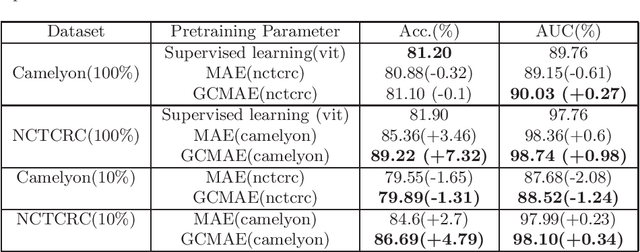
Abstract:Based on digital whole slide scanning technique, artificial intelligence algorithms represented by deep learning have achieved remarkable results in the field of computational pathology. Compared with other medical images such as Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), pathological images are more difficult to annotate, thus there is an extreme lack of data sets that can be used for supervised learning. In this study, a self-supervised learning (SSL) model, Global Contrast Masked Autoencoders (GCMAE), is proposed, which has the ability to represent both global and local domain-specific features of whole slide image (WSI), as well as excellent cross-data transfer ability. The Camelyon16 and NCTCRC datasets are used to evaluate the performance of our model. When dealing with transfer learning tasks with different data sets, the experimental results show that GCMAE has better linear classification accuracy than MAE, which can reach 81.10% and 89.22% respectively. Our method outperforms the previous state-of-the-art algorithm and even surpass supervised learning (improved by 3.86% on NCTCRC data sets). The source code of this paper is publicly available at https://github.com/StarUniversus/gcmae
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge