Mikel L. Forcada
Estimating post-editing effort: a study on human judgements, task-based and reference-based metrics of MT quality
Oct 14, 2019
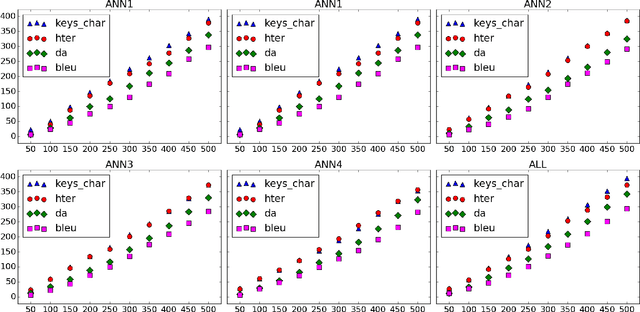
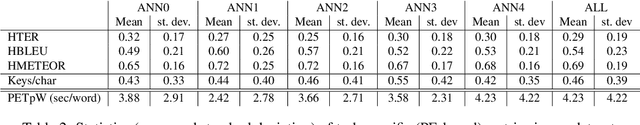
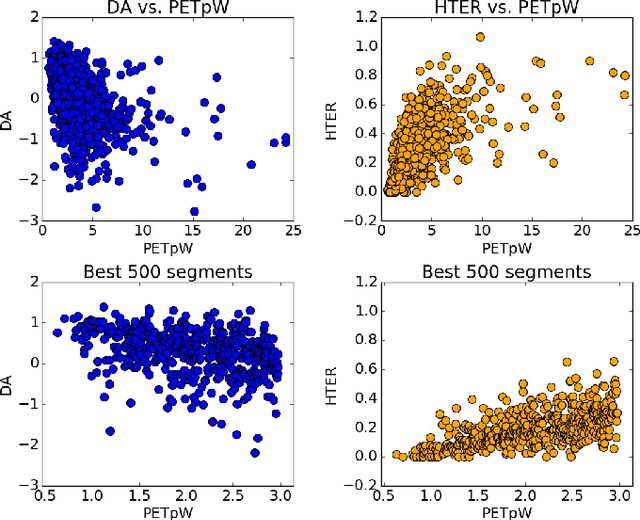
Abstract:Devising metrics to assess translation quality has always been at the core of machine translation (MT) research. Traditional automatic reference-based metrics, such as BLEU, have shown correlations with human judgements of adequacy and fluency and have been paramount for the advancement of MT system development. Crowd-sourcing has popularised and enabled the scalability of metrics based on human judgements, such as subjective direct assessments (DA) of adequacy, that are believed to be more reliable than reference-based automatic metrics. Finally, task-based measurements, such as post-editing time, are expected to provide a more detailed evaluation of the usefulness of translations for a specific task. Therefore, while DA averages adequacy judgements to obtain an appraisal of (perceived) quality independently of the task, and reference-based automatic metrics try to objectively estimate quality also in a task-independent way, task-based metrics are measurements obtained either during or after performing a specific task. In this paper we argue that, although expensive, task-based measurements are the most reliable when estimating MT quality in a specific task; in our case, this task is post-editing. To that end, we report experiments on a dataset with newly-collected post-editing indicators and show their usefulness when estimating post-editing effort. Our results show that task-based metrics comparing machine-translated and post-edited versions are the best at tracking post-editing effort, as expected. These metrics are followed by DA, and then by metrics comparing the machine-translated version and independent references. We suggest that MT practitioners should be aware of these differences and acknowledge their implications when deciding how to evaluate MT for post-editing purposes.
UAlacant machine translation quality estimation at WMT 2018: a simple approach using phrase tables and feed-forward neural networks
Nov 06, 2018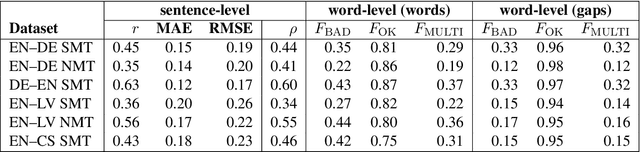
Abstract:We describe the Universitat d'Alacant submissions to the word- and sentence-level machine translation (MT) quality estimation (QE) shared task at WMT 2018. Our approach to word-level MT QE builds on previous work to mark the words in the machine-translated sentence as \textit{OK} or \textit{BAD}, and is extended to determine if a word or sequence of words need to be inserted in the gap after each word. Our sentence-level submission simply uses the edit operations predicted by the word-level approach to approximate TER. The method presented ranked first in the sub-task of identifying insertions in gaps for three out of the six datasets, and second in the rest of them.
Exploring Gap Filling as a Cheaper Alternative to Reading Comprehension Questionnaires when Evaluating Machine Translation for Gisting
Sep 02, 2018
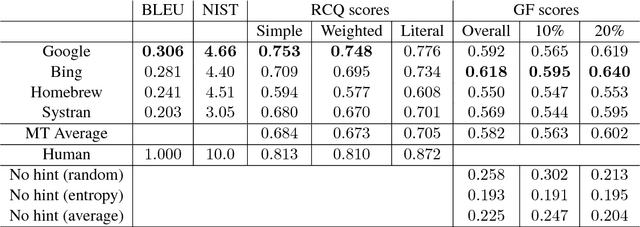

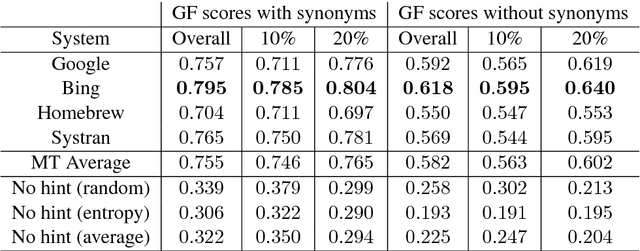
Abstract:A popular application of machine translation (MT) is gisting: MT is consumed as is to make sense of text in a foreign language. Evaluation of the usefulness of MT for gisting is surprisingly uncommon. The classical method uses reading comprehension questionnaires (RCQ), in which informants are asked to answer professionally-written questions in their language about a foreign text that has been machine-translated into their language. Recently, gap-filling (GF), a form of cloze testing, has been proposed as a cheaper alternative to RCQ. In GF, certain words are removed from reference translations and readers are asked to fill the gaps left using the machine-translated text as a hint. This paper reports, for thefirst time, a comparative evaluation, using both RCQ and GF, of translations from multiple MT systems for the same foreign texts, and a systematic study on the effect of variables such as gap density, gap-selection strategies, and document context in GF. The main findings of the study are: (a) both RCQ and GF clearly identify MT to be useful, (b) global RCQ and GF rankings for the MT systems are mostly in agreement, (c) GF scores vary very widely across informants, making comparisons among MT systems hard, and (d) unlike RCQ, which is framed around documents, GF evaluation can be framed at the sentence level. These findings support the use of GF as a cheaper alternative to RCQ.
A Maturity Model for Public Administration as Open Translation Data Providers
Jul 07, 2016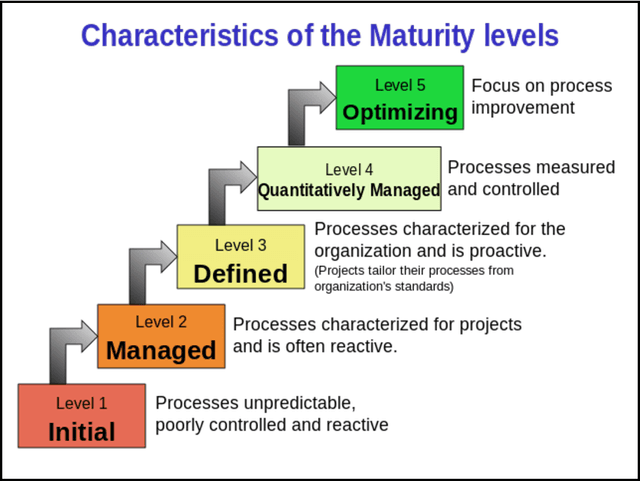
Abstract:Any public administration that produces translation data can be a provider of useful reusable data to meet its own translation needs and the ones of other public organizations and private companies that work with texts of the same domain. These data can also be crucial to produce domain-tuned Machine Translation systems. The organization's management of the translation process, the characteristics of the archives of the generated resources and of the infrastructure available to support them determine the efficiency and the effectiveness with which the materials produced can be converted into reusable data. However, it is of utmost importance that the organizations themselves first become aware of the goods they are producing and, second, adapt their internal processes to become optimal providers. In this article, we propose a Maturity Model to help these organizations to achieve it by identifying the different stages of the management of translation data that determine the path to the aforementioned goal.
A Light Sliding-Window Part-of-Speech Tagger for the Apertium Free/Open-Source Machine Translation Platform
Sep 18, 2015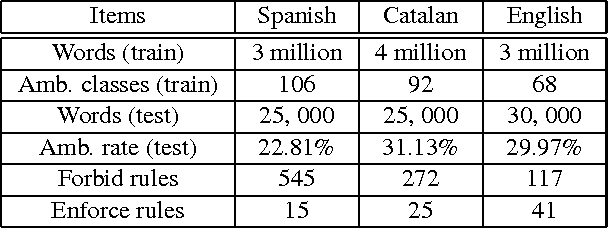
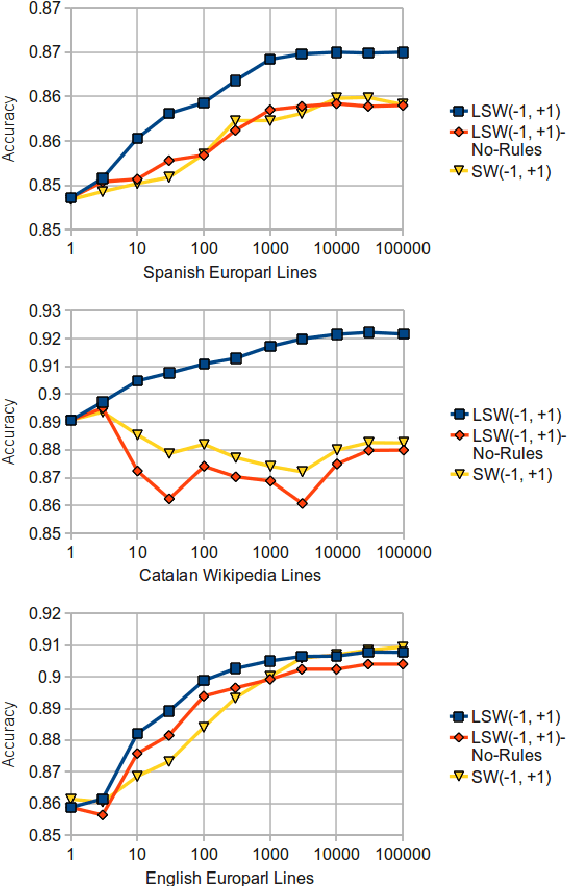
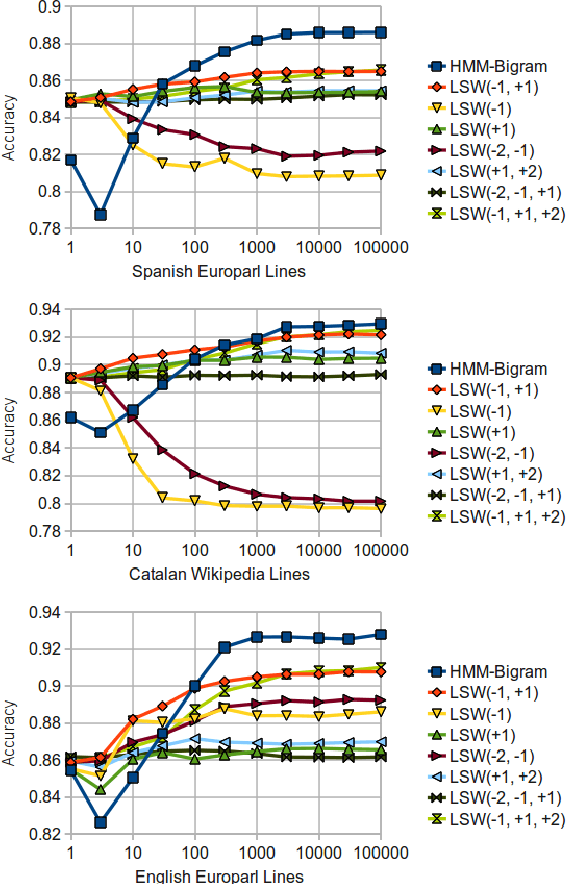
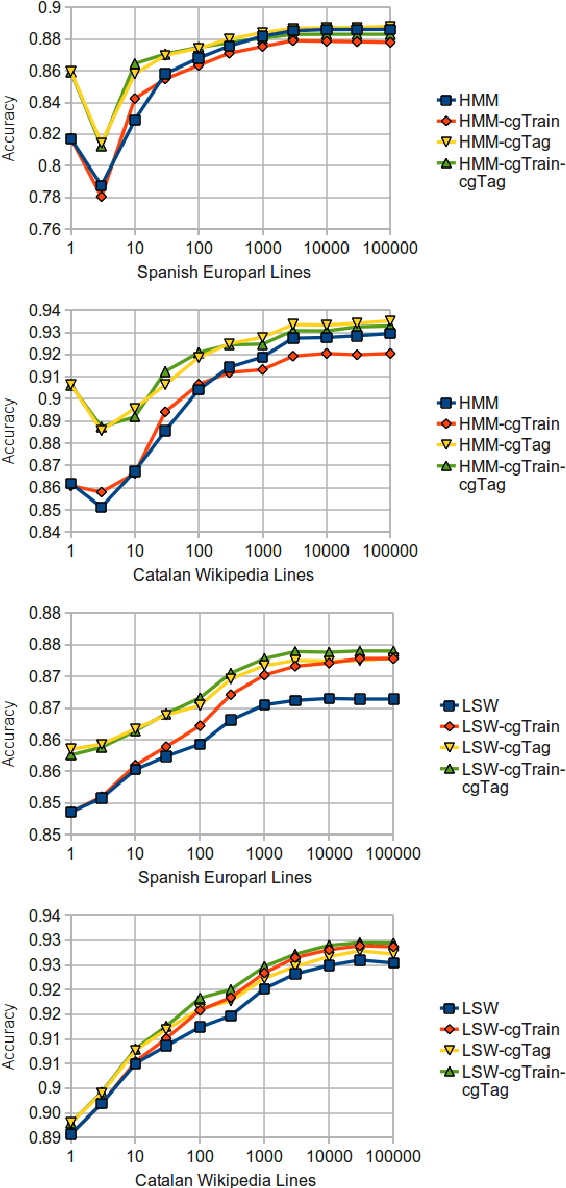
Abstract:This paper describes a free/open-source implementation of the light sliding-window (LSW) part-of-speech tagger for the Apertium free/open-source machine translation platform. Firstly, the mechanism and training process of the tagger are reviewed, and a new method for incorporating linguistic rules is proposed. Secondly, experiments are conducted to compare the performances of the tagger under different window settings, with or without Apertium-style "forbid" rules, with or without Constraint Grammar, and also with respect to the traditional HMM tagger in Apertium.
Inferring Shallow-Transfer Machine Translation Rules from Small Parallel Corpora
Jan 15, 2014
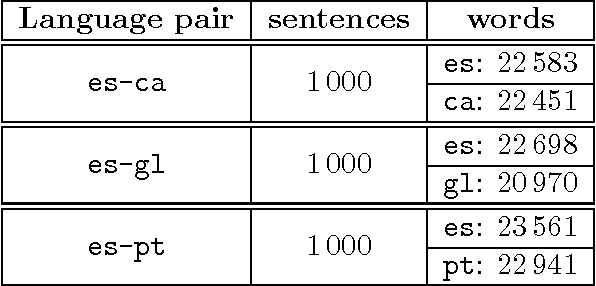

Abstract:This paper describes a method for the automatic inference of structural transfer rules to be used in a shallow-transfer machine translation (MT) system from small parallel corpora. The structural transfer rules are based on alignment templates, like those used in statistical MT. Alignment templates are extracted from sentence-aligned parallel corpora and extended with a set of restrictions which are derived from the bilingual dictionary of the MT system and control their application as transfer rules. The experiments conducted using three different language pairs in the free/open-source MT platform Apertium show that translation quality is improved as compared to word-for-word translation (when no transfer rules are used), and that the resulting translation quality is close to that obtained using hand-coded transfer rules. The method we present is entirely unsupervised and benefits from information in the rest of modules of the MT system in which the inferred rules are applied.
Using external sources of bilingual information for on-the-fly word alignment
Dec 07, 2012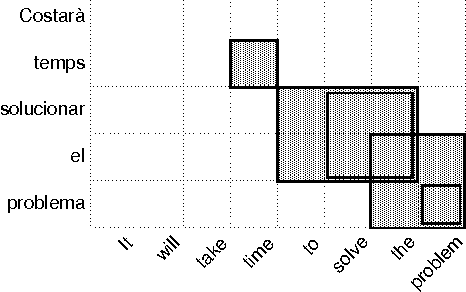
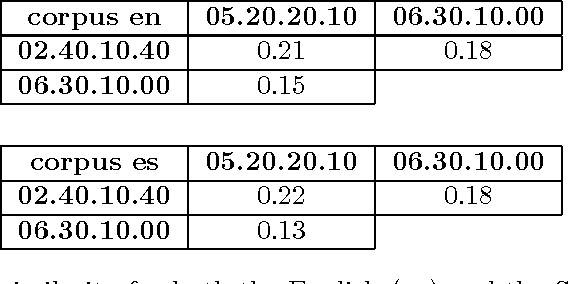
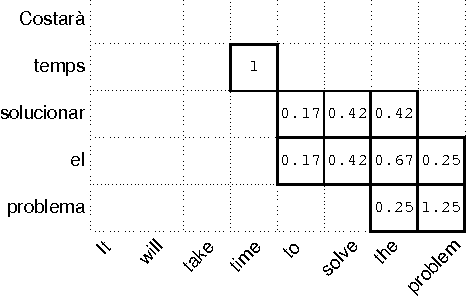
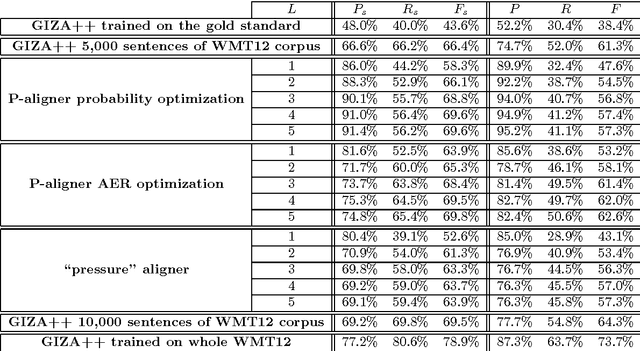
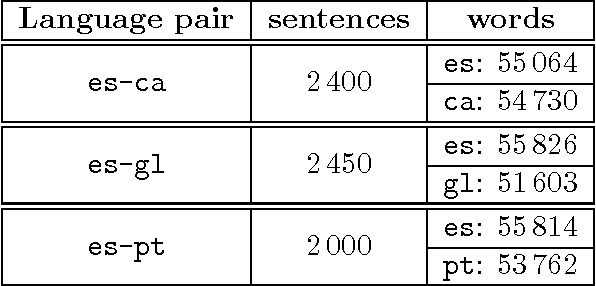
Abstract:In this paper we present a new and simple language-independent method for word-alignment based on the use of external sources of bilingual information such as machine translation systems. We show that the few parameters of the aligner can be trained on a very small corpus, which leads to results comparable to those obtained by the state-of-the-art tool GIZA++ in terms of precision. Regarding other metrics, such as alignment error rate or F-measure, the parametric aligner, when trained on a very small gold-standard (450 pairs of sentences), provides results comparable to those produced by GIZA++ when trained on an in-domain corpus of around 10,000 pairs of sentences. Furthermore, the results obtained indicate that the training is domain-independent, which enables the use of the trained aligner 'on the fly' on any new pair of sentences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge