Exploring Gap Filling as a Cheaper Alternative to Reading Comprehension Questionnaires when Evaluating Machine Translation for Gisting
Paper and Code
Sep 02, 2018
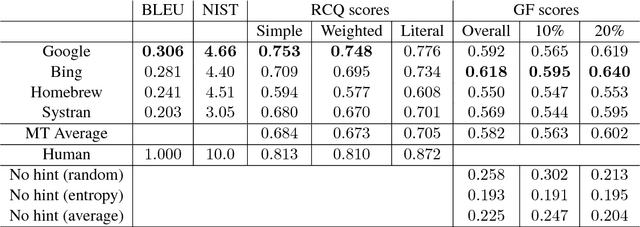

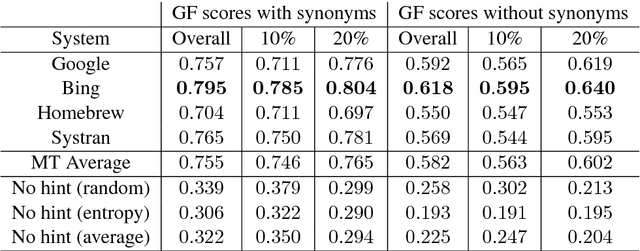
A popular application of machine translation (MT) is gisting: MT is consumed as is to make sense of text in a foreign language. Evaluation of the usefulness of MT for gisting is surprisingly uncommon. The classical method uses reading comprehension questionnaires (RCQ), in which informants are asked to answer professionally-written questions in their language about a foreign text that has been machine-translated into their language. Recently, gap-filling (GF), a form of cloze testing, has been proposed as a cheaper alternative to RCQ. In GF, certain words are removed from reference translations and readers are asked to fill the gaps left using the machine-translated text as a hint. This paper reports, for thefirst time, a comparative evaluation, using both RCQ and GF, of translations from multiple MT systems for the same foreign texts, and a systematic study on the effect of variables such as gap density, gap-selection strategies, and document context in GF. The main findings of the study are: (a) both RCQ and GF clearly identify MT to be useful, (b) global RCQ and GF rankings for the MT systems are mostly in agreement, (c) GF scores vary very widely across informants, making comparisons among MT systems hard, and (d) unlike RCQ, which is framed around documents, GF evaluation can be framed at the sentence level. These findings support the use of GF as a cheaper alternative to RCQ.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge