Miguel A. Otaduy
SNUG: Self-Supervised Neural Dynamic Garments
Apr 05, 2022



Abstract:We present a self-supervised method to learn dynamic 3D deformations of garments worn by parametric human bodies. State-of-the-art data-driven approaches to model 3D garment deformations are trained using supervised strategies that require large datasets, usually obtained by expensive physics-based simulation methods or professional multi-camera capture setups. In contrast, we propose a new training scheme that removes the need for ground-truth samples, enabling self-supervised training of dynamic 3D garment deformations. Our key contribution is to realize that physics-based deformation models, traditionally solved in a frame-by-frame basis by implicit integrators, can be recasted as an optimization problem. We leverage such optimization-based scheme to formulate a set of physics-based loss terms that can be used to train neural networks without precomputing ground-truth data. This allows us to learn models for interactive garments, including dynamic deformations and fine wrinkles, with two orders of magnitude speed up in training time compared to state-of-the-art supervised methods
RGB2Hands: Real-Time Tracking of 3D Hand Interactions from Monocular RGB Video
Jun 22, 2021

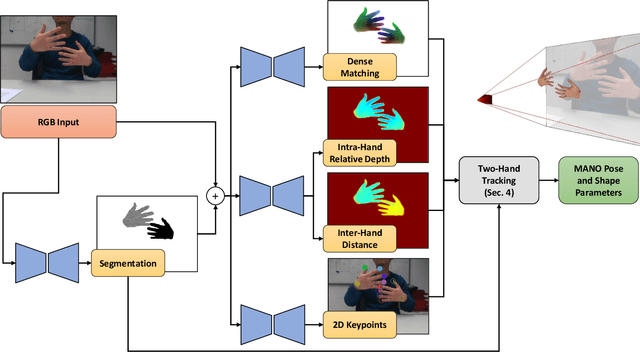
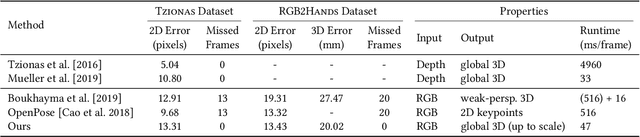
Abstract:Tracking and reconstructing the 3D pose and geometry of two hands in interaction is a challenging problem that has a high relevance for several human-computer interaction applications, including AR/VR, robotics, or sign language recognition. Existing works are either limited to simpler tracking settings (e.g., considering only a single hand or two spatially separated hands), or rely on less ubiquitous sensors, such as depth cameras. In contrast, in this work we present the first real-time method for motion capture of skeletal pose and 3D surface geometry of hands from a single RGB camera that explicitly considers close interactions. In order to address the inherent depth ambiguities in RGB data, we propose a novel multi-task CNN that regresses multiple complementary pieces of information, including segmentation, dense matchings to a 3D hand model, and 2D keypoint positions, together with newly proposed intra-hand relative depth and inter-hand distance maps. These predictions are subsequently used in a generative model fitting framework in order to estimate pose and shape parameters of a 3D hand model for both hands. We experimentally verify the individual components of our RGB two-hand tracking and 3D reconstruction pipeline through an extensive ablation study. Moreover, we demonstrate that our approach offers previously unseen two-hand tracking performance from RGB, and quantitatively and qualitatively outperforms existing RGB-based methods that were not explicitly designed for two-hand interactions. Moreover, our method even performs on-par with depth-based real-time methods.
* SIGGRAPH Asia 2020
Real-time Pose and Shape Reconstruction of Two Interacting Hands With a Single Depth Camera
Jun 15, 2021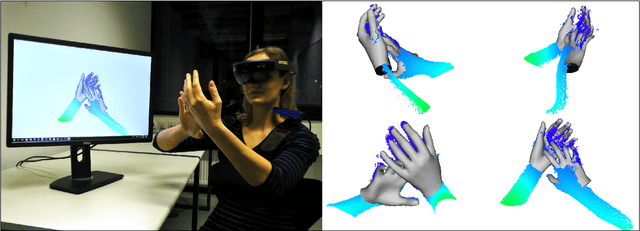
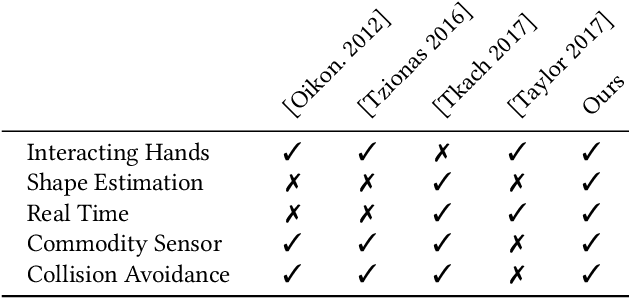
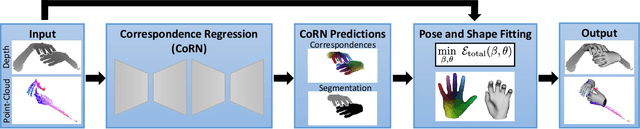
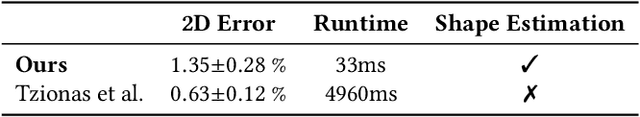
Abstract:We present a novel method for real-time pose and shape reconstruction of two strongly interacting hands. Our approach is the first two-hand tracking solution that combines an extensive list of favorable properties, namely it is marker-less, uses a single consumer-level depth camera, runs in real time, handles inter- and intra-hand collisions, and automatically adjusts to the user's hand shape. In order to achieve this, we embed a recent parametric hand pose and shape model and a dense correspondence predictor based on a deep neural network into a suitable energy minimization framework. For training the correspondence prediction network, we synthesize a two-hand dataset based on physical simulations that includes both hand pose and shape annotations while at the same time avoiding inter-hand penetrations. To achieve real-time rates, we phrase the model fitting in terms of a nonlinear least-squares problem so that the energy can be optimized based on a highly efficient GPU-based Gauss-Newton optimizer. We show state-of-the-art results in scenes that exceed the complexity level demonstrated by previous work, including tight two-hand grasps, significant inter-hand occlusions, and gesture interaction.
Self-Supervised Collision Handling via Generative 3D Garment Models for Virtual Try-On
May 13, 2021



Abstract:We propose a new generative model for 3D garment deformations that enables us to learn, for the first time, a data-driven method for virtual try-on that effectively addresses garment-body collisions. In contrast to existing methods that require an undesirable postprocessing step to fix garment-body interpenetrations at test time, our approach directly outputs 3D garment configurations that do not collide with the underlying body. Key to our success is a new canonical space for garments that removes pose-and-shape deformations already captured by a new diffused human body model, which extrapolates body surface properties such as skinning weights and blendshapes to any 3D point. We leverage this representation to train a generative model with a novel self-supervised collision term that learns to reliably solve garment-body interpenetrations. We extensively evaluate and compare our results with recently proposed data-driven methods, and show that our method is the first to successfully address garment-body contact in unseen body shapes and motions, without compromising realism and detail.
SoftSMPL: Data-driven Modeling of Nonlinear Soft-tissue Dynamics for Parametric Humans
Apr 01, 2020



Abstract:We present SoftSMPL, a learning-based method to model realistic soft-tissue dynamics as a function of body shape and motion. Datasets to learn such task are scarce and expensive to generate, which makes training models prone to overfitting. At the core of our method there are three key contributions that enable us to model highly realistic dynamics and better generalization capabilities than state-of-the-art methods, while training on the same data. First, a novel motion descriptor that disentangles the standard pose representation by removing subject-specific features; second, a neural-network-based recurrent regressor that generalizes to unseen shapes and motions; and third, a highly efficient nonlinear deformation subspace capable of representing soft-tissue deformations of arbitrary shapes. We demonstrate qualitative and quantitative improvements over existing methods and, additionally, we show the robustness of our method on a variety of motion capture databases.
Learning-Based Animation of Clothing for Virtual Try-On
Mar 17, 2019



Abstract:This paper presents a learning-based clothing animation method for highly efficient virtual try-on simulation. Given a garment, we preprocess a rich database of physically-based dressed character simulations, for multiple body shapes and animations. Then, using this database, we train a learning-based model of cloth drape and wrinkles, as a function of body shape and dynamics. We propose a model that separates global garment fit, due to body shape, from local garment wrinkles, due to both pose dynamics and body shape. We use a recurrent neural network to regress garment wrinkles, and we achieve highly plausible nonlinear effects, in contrast to the blending artifacts suffered by previous methods. At runtime, dynamic virtual try-on animations are produced in just a few milliseconds for garments with thousands of triangles. We show qualitative and quantitative analysis of results
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge