Michael Nirschl
Lingvo: a Modular and Scalable Framework for Sequence-to-Sequence Modeling
Feb 21, 2019
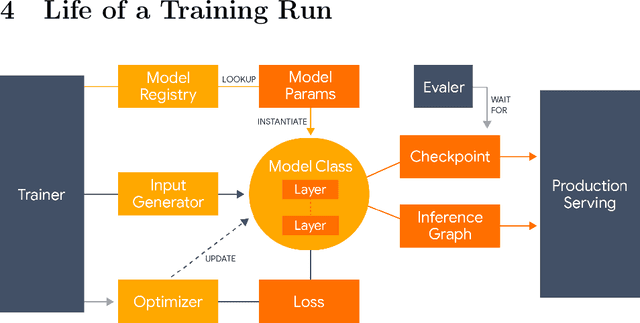
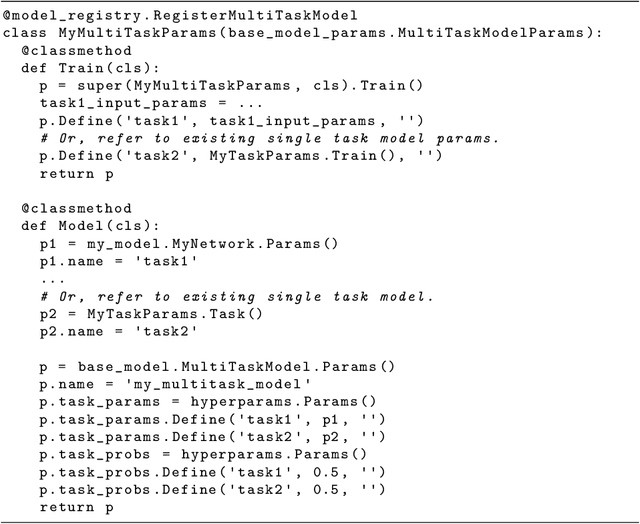
Abstract:Lingvo is a Tensorflow framework offering a complete solution for collaborative deep learning research, with a particular focus towards sequence-to-sequence models. Lingvo models are composed of modular building blocks that are flexible and easily extensible, and experiment configurations are centralized and highly customizable. Distributed training and quantized inference are supported directly within the framework, and it contains existing implementations of a large number of utilities, helper functions, and the newest research ideas. Lingvo has been used in collaboration by dozens of researchers in more than 20 papers over the last two years. This document outlines the underlying design of Lingvo and serves as an introduction to the various pieces of the framework, while also offering examples of advanced features that showcase the capabilities of the framework.
Lattice Rescoring Strategies for Long Short Term Memory Language Models in Speech Recognition
Nov 15, 2017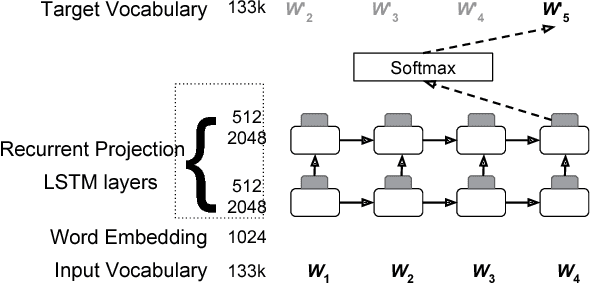
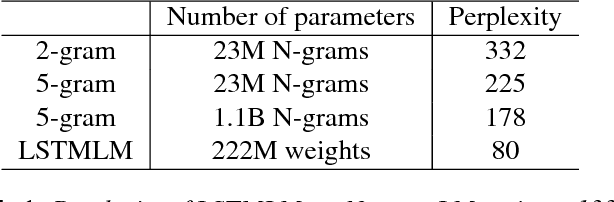
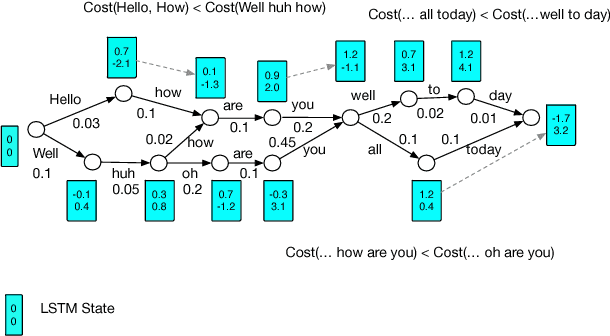
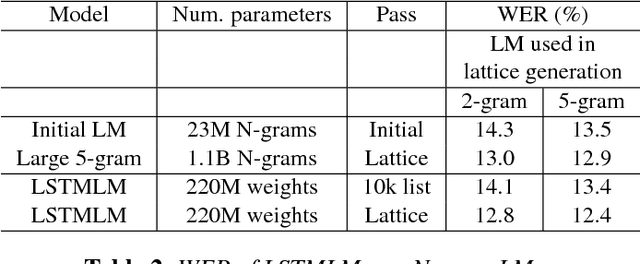
Abstract:Recurrent neural network (RNN) language models (LMs) and Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) LMs, a variant of RNN LMs, have been shown to outperform traditional N-gram LMs on speech recognition tasks. However, these models are computationally more expensive than N-gram LMs for decoding, and thus, challenging to integrate into speech recognizers. Recent research has proposed the use of lattice-rescoring algorithms using RNNLMs and LSTMLMs as an efficient strategy to integrate these models into a speech recognition system. In this paper, we evaluate existing lattice rescoring algorithms along with new variants on a YouTube speech recognition task. Lattice rescoring using LSTMLMs reduces the word error rate (WER) for this task by 8\% relative to the WER obtained using an N-gram LM.
* Accepted at ASRU 2017
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge