Miao Song
Can we enhance prosocial behavior? Using post-ride feedback to improve micromobility interactions
Sep 05, 2024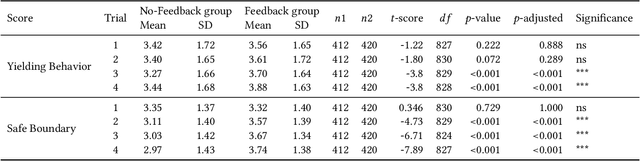
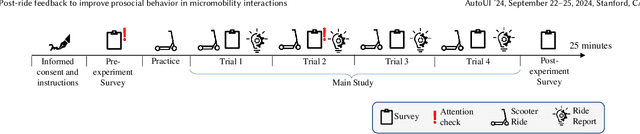
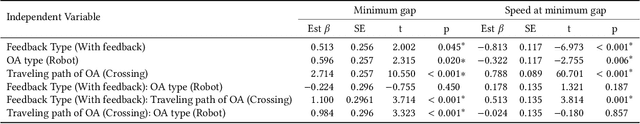
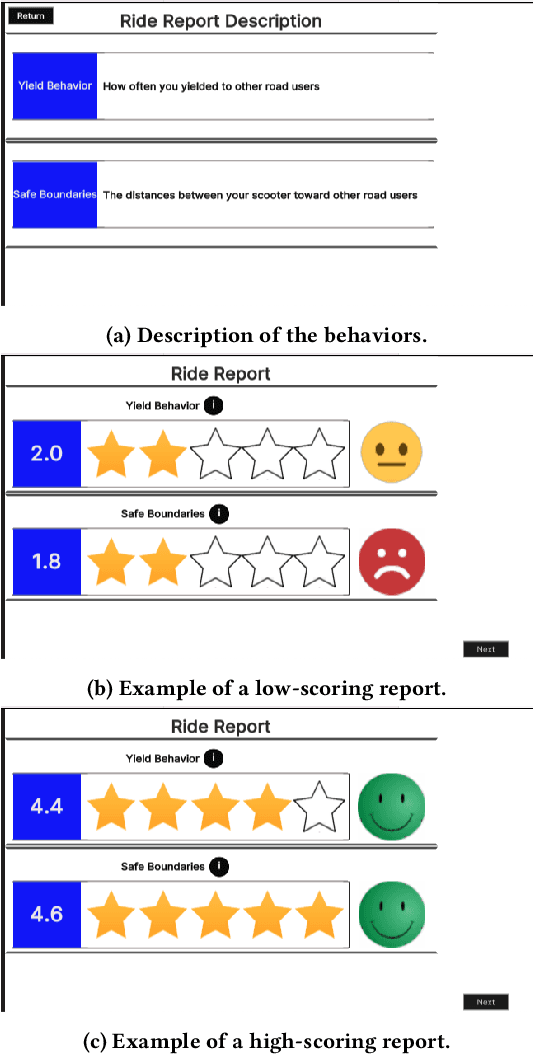
Abstract:Micromobility devices, such as e-scooters and delivery robots, hold promise for eco-friendly and cost-effective alternatives for future urban transportation. However, their lack of societal acceptance remains a challenge. Therefore, we must consider ways to promote prosocial behavior in micromobility interactions. We investigate how post-ride feedback can encourage the prosocial behavior of e-scooter riders while interacting with sidewalk users, including pedestrians and delivery robots. Using a web-based platform, we measure the prosocial behavior of e-scooter riders. Results found that post-ride feedback can successfully promote prosocial behavior, and objective measures indicated better gap behavior, lower speeds at interaction, and longer stopping time around other sidewalk actors. The findings of this study demonstrate the efficacy of post-ride feedback and provide a step toward designing methodologies to improve the prosocial behavior of mobility users.
Toward Multimodal Interaction in Scalable Visual Digital Evidence Visualization Using Computer Vision Techniques and ISS
Aug 01, 2018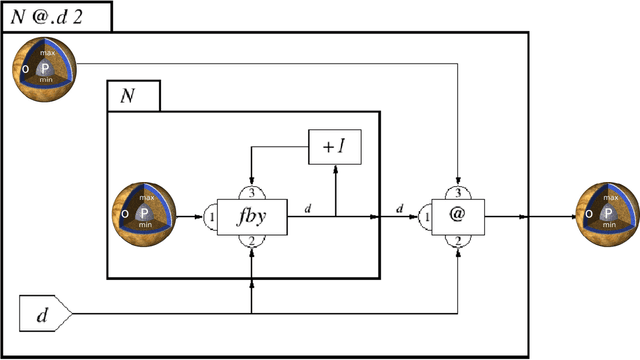


Abstract:Visualization requirements in Forensic Lucid have to do with different levels of case knowledge abstraction, representation, aggregation, as well as the operational aspects as the final long-term goal of this proposal. It encompasses anything from the finer detailed representation of hierarchical contexts to Forensic Lucid programs, to the documented evidence and its management, its linkage to programs, to evaluation, and to the management of GIPSY software networks. This includes an ability to arbitrarily switch between those views combined with usable multimodal interaction. The purpose is to determine how the findings can be applied to Forensic Lucid and investigation case management. It is also natural to want a convenient and usable evidence visualization, its semantic linkage and the reasoning machinery for it. Thus, we propose a scalable management, visualization, and evaluation of digital evidence using the modified interactive 3D documentary system - Illimitable Space System - (ISS) to represent, semantically link, and provide a usable interface to digital investigators that is navigable via different multimodal interaction techniques using Computer Vision techniques including gestures, as well as eye-gaze and audio.
Writer Identification Using Inexpensive Signal Processing Techniques
Dec 30, 2009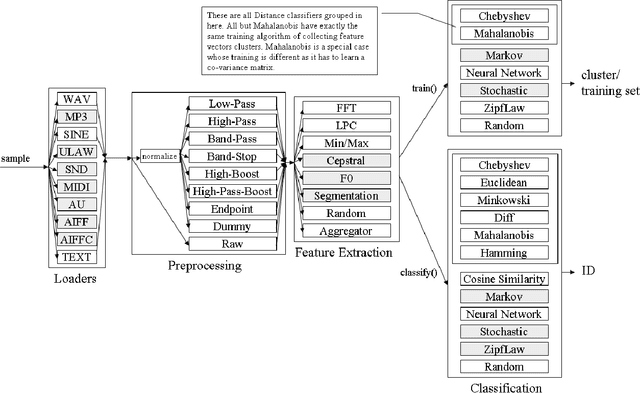
Abstract:We propose to use novel and classical audio and text signal-processing and otherwise techniques for "inexpensive" fast writer identification tasks of scanned hand-written documents "visually". The "inexpensive" refers to the efficiency of the identification process in terms of CPU cycles while preserving decent accuracy for preliminary identification. This is a comparative study of multiple algorithm combinations in a pattern recognition pipeline implemented in Java around an open-source Modular Audio Recognition Framework (MARF) that can do a lot more beyond audio. We present our preliminary experimental findings in such an identification task. We simulate "visual" identification by "looking" at the hand-written document as a whole rather than trying to extract fine-grained features out of it prior classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge