Writer Identification Using Inexpensive Signal Processing Techniques
Paper and Code
Dec 30, 2009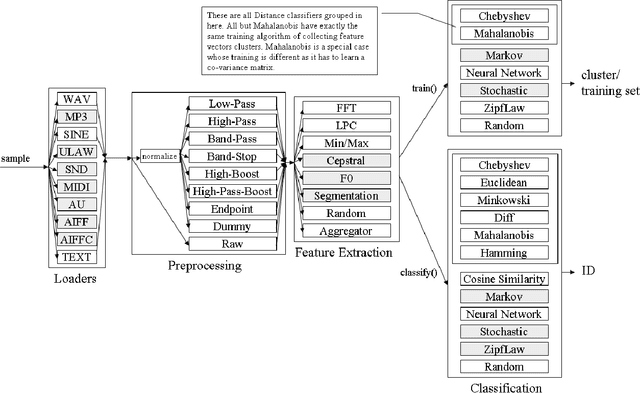
We propose to use novel and classical audio and text signal-processing and otherwise techniques for "inexpensive" fast writer identification tasks of scanned hand-written documents "visually". The "inexpensive" refers to the efficiency of the identification process in terms of CPU cycles while preserving decent accuracy for preliminary identification. This is a comparative study of multiple algorithm combinations in a pattern recognition pipeline implemented in Java around an open-source Modular Audio Recognition Framework (MARF) that can do a lot more beyond audio. We present our preliminary experimental findings in such an identification task. We simulate "visual" identification by "looking" at the hand-written document as a whole rather than trying to extract fine-grained features out of it prior classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge