Can we enhance prosocial behavior? Using post-ride feedback to improve micromobility interactions
Paper and Code
Sep 05, 2024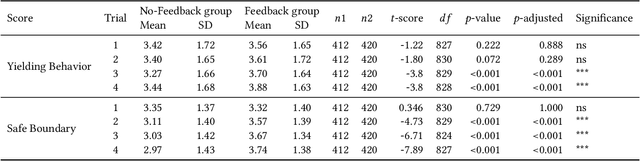
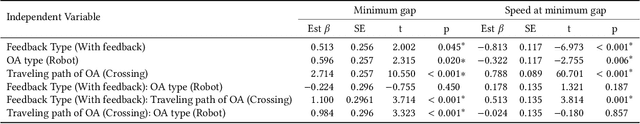
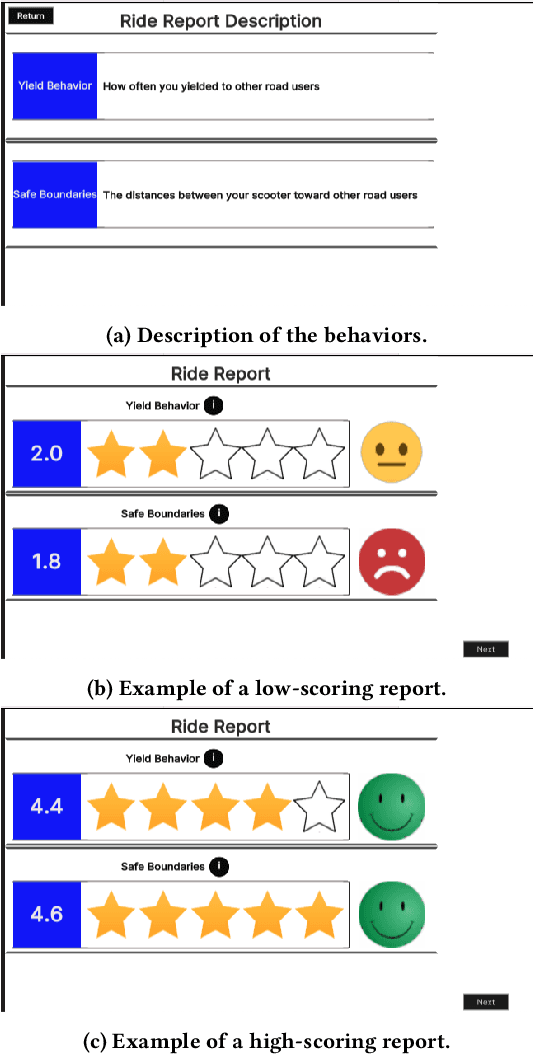
Micromobility devices, such as e-scooters and delivery robots, hold promise for eco-friendly and cost-effective alternatives for future urban transportation. However, their lack of societal acceptance remains a challenge. Therefore, we must consider ways to promote prosocial behavior in micromobility interactions. We investigate how post-ride feedback can encourage the prosocial behavior of e-scooter riders while interacting with sidewalk users, including pedestrians and delivery robots. Using a web-based platform, we measure the prosocial behavior of e-scooter riders. Results found that post-ride feedback can successfully promote prosocial behavior, and objective measures indicated better gap behavior, lower speeds at interaction, and longer stopping time around other sidewalk actors. The findings of this study demonstrate the efficacy of post-ride feedback and provide a step toward designing methodologies to improve the prosocial behavior of mobility users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge