Meihua Wang
RHA-Net: An Encoder-Decoder Network with Residual Blocks and Hybrid Attention Mechanisms for Pavement Crack Segmentation
Jul 28, 2022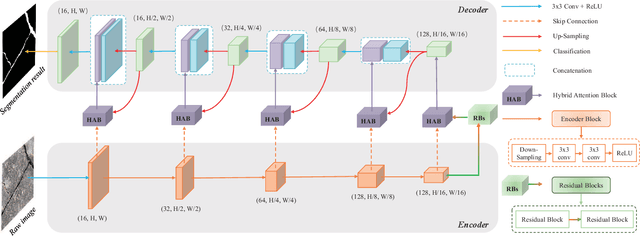
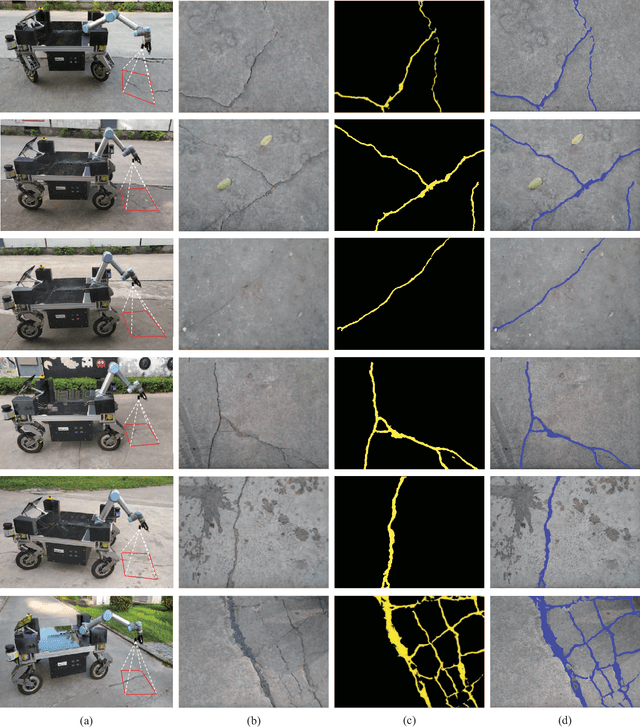

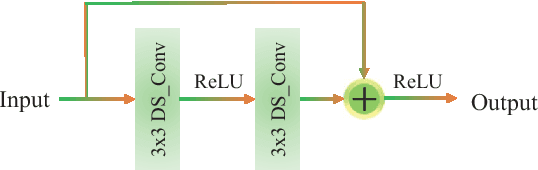
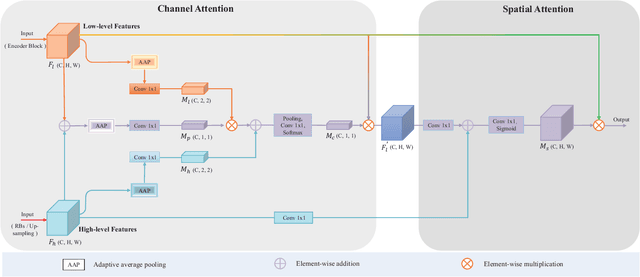
Abstract:The acquisition and evaluation of pavement surface data play an essential role in pavement condition evaluation. In this paper, an efficient and effective end-to-end network for automatic pavement crack segmentation, called RHA-Net, is proposed to improve the pavement crack segmentation accuracy. The RHA-Net is built by integrating residual blocks (ResBlocks) and hybrid attention blocks into the encoder-decoder architecture. The ResBlocks are used to improve the ability of RHA-Net to extract high-level abstract features. The hybrid attention blocks are designed to fuse both low-level features and high-level features to help the model focus on correct channels and areas of cracks, thereby improving the feature presentation ability of RHA-Net. An image data set containing 789 pavement crack images collected by a self-designed mobile robot is constructed and used for training and evaluating the proposed model. Compared with other state-of-the-art networks, the proposed model achieves better performance and the functionalities of adding residual blocks and hybrid attention mechanisms are validated in a comprehensive ablation study. Additionally, a light-weighted version of the model generated by introducing depthwise separable convolution achieves better a performance and a much faster processing speed with 1/30 of the number of U-Net parameters. The developed system can segment pavement crack in real-time on an embedded device Jetson TX2 (25 FPS). The video taken in real-time experiments is released at https://youtu.be/3XIogk0fiG4.
Component-Based Distributed Framework for Coherent and Real-Time Video Dehazing
Sep 09, 2016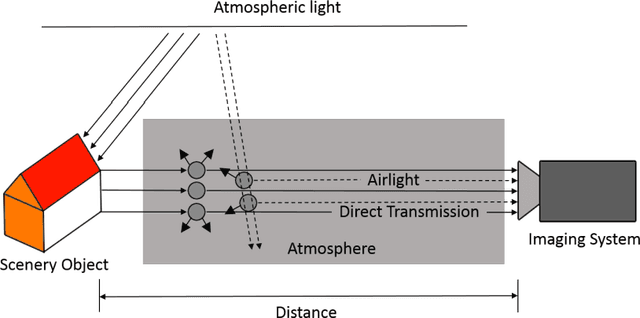

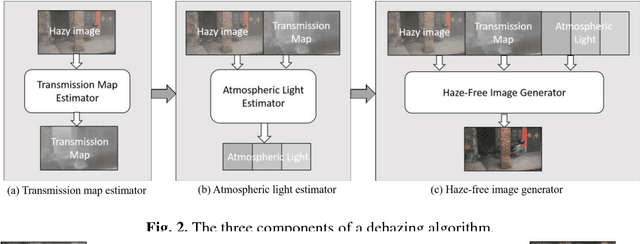

Abstract:Traditional dehazing techniques, as a well studied topic in image processing, are now widely used to eliminate the haze effects from individual images. However, even the state-of-the-art dehazing algorithms may not provide sufficient support to video analytics, as a crucial pre-processing step for video-based decision making systems (e.g., robot navigation), due to the limitations of these algorithms on poor result coherence and low processing efficiency. This paper presents a new framework, particularly designed for video dehazing, to output coherent results in real time, with two novel techniques. Firstly, we decompose the dehazing algorithms into three generic components, namely transmission map estimator, atmospheric light estimator and haze-free image generator. They can be simultaneously processed by multiple threads in the distributed system, such that the processing efficiency is optimized by automatic CPU resource allocation based on the workloads. Secondly, a cross-frame normalization scheme is proposed to enhance the coherence among consecutive frames, by sharing the parameters of atmospheric light from consecutive frames in the distributed computation platform. The combination of these techniques enables our framework to generate highly consistent and accurate dehazing results in real-time, by using only 3 PCs connected by Ethernet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge