Kelvin C. P. Wang
CrackCLF: Automatic Pavement Crack Detection based on Closed-Loop Feedback
Nov 20, 2023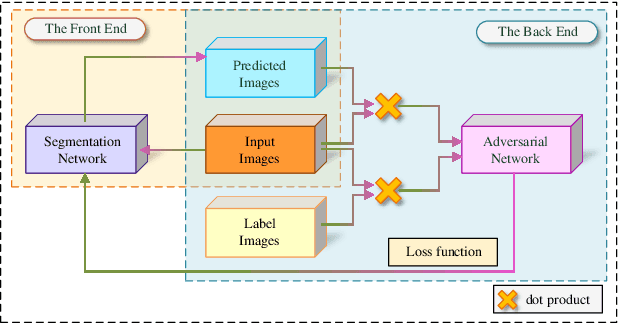

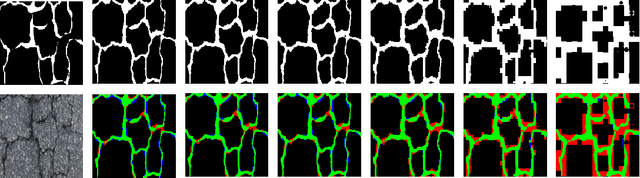
Abstract:Automatic pavement crack detection is an important task to ensure the functional performances of pavements during their service life. Inspired by deep learning (DL), the encoder-decoder framework is a powerful tool for crack detection. However, these models are usually open-loop (OL) systems that tend to treat thin cracks as the background. Meanwhile, these models can not automatically correct errors in the prediction, nor can it adapt to the changes of the environment to automatically extract and detect thin cracks. To tackle this problem, we embed closed-loop feedback (CLF) into the neural network so that the model could learn to correct errors on its own, based on generative adversarial networks (GAN). The resulting model is called CrackCLF and includes the front and back ends, i.e. segmentation and adversarial network. The front end with U-shape framework is employed to generate crack maps, and the back end with a multi-scale loss function is used to correct higher-order inconsistencies between labels and crack maps (generated by the front end) to address open-loop system issues. Empirical results show that the proposed CrackCLF outperforms others methods on three public datasets. Moreover, the proposed CLF can be defined as a plug and play module, which can be embedded into different neural network models to improve their performances.
RHA-Net: An Encoder-Decoder Network with Residual Blocks and Hybrid Attention Mechanisms for Pavement Crack Segmentation
Jul 28, 2022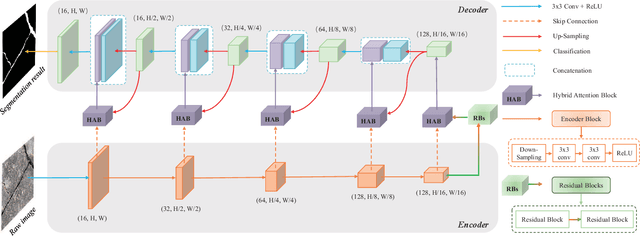
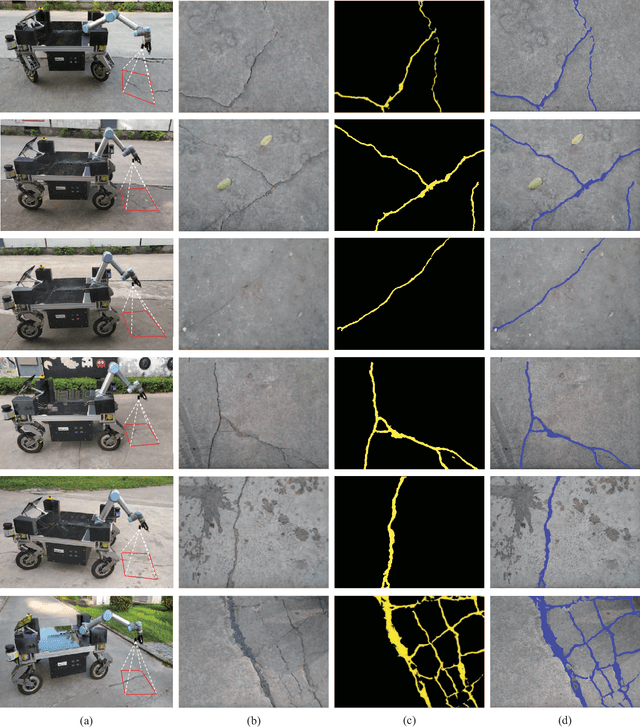

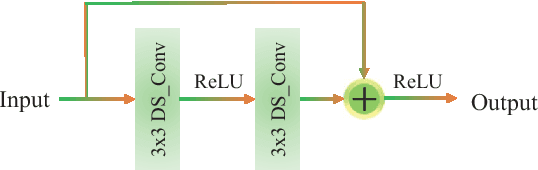
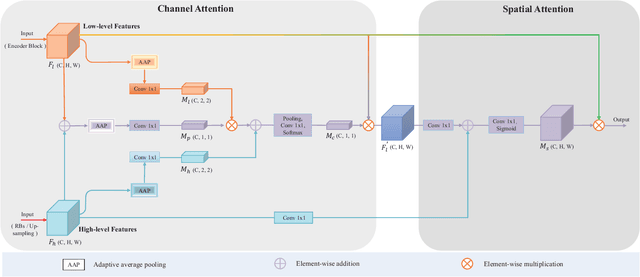
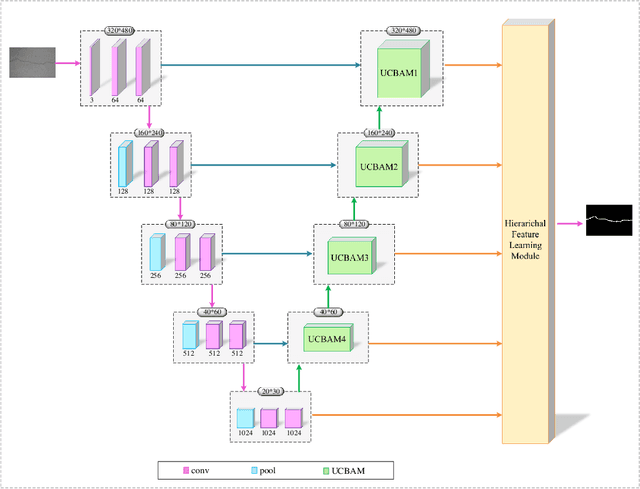
Abstract:The acquisition and evaluation of pavement surface data play an essential role in pavement condition evaluation. In this paper, an efficient and effective end-to-end network for automatic pavement crack segmentation, called RHA-Net, is proposed to improve the pavement crack segmentation accuracy. The RHA-Net is built by integrating residual blocks (ResBlocks) and hybrid attention blocks into the encoder-decoder architecture. The ResBlocks are used to improve the ability of RHA-Net to extract high-level abstract features. The hybrid attention blocks are designed to fuse both low-level features and high-level features to help the model focus on correct channels and areas of cracks, thereby improving the feature presentation ability of RHA-Net. An image data set containing 789 pavement crack images collected by a self-designed mobile robot is constructed and used for training and evaluating the proposed model. Compared with other state-of-the-art networks, the proposed model achieves better performance and the functionalities of adding residual blocks and hybrid attention mechanisms are validated in a comprehensive ablation study. Additionally, a light-weighted version of the model generated by introducing depthwise separable convolution achieves better a performance and a much faster processing speed with 1/30 of the number of U-Net parameters. The developed system can segment pavement crack in real-time on an embedded device Jetson TX2 (25 FPS). The video taken in real-time experiments is released at https://youtu.be/3XIogk0fiG4.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge