Duan Yuan
Why does Stereo Triangulation Not Work in UAV Distance Estimation
Jun 15, 2023



Abstract:UAV distance estimation plays an important role for path planning of swarm UAVs and collision avoidance. However, the lack of annotated data seriously hinder the related studies. In this paper, we build and present a UAVDE dataset for UAV distance estimation, in which distance between two UAVs is obtained by UWB sensors. During experiments, we surprisingly observe that the commonly used stereo triangulation can not stand for UAV scenes. The core reason is the position deviation issue of UAVs due to long shooting distance and camera vibration, which is common in UAV scenes. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel position correction module (PCM), which can directly predict the offset between the image positions and the actual ones of UAVs and perform calculation compensation in stereo triangulation. Besides, to further boost performance on hard samples, we propose a dynamic iterative correction mechanism, which is composed of multiple stacked PCMs and a gating mechanism to adaptively determine whether further correction is required according to the difficulty of data samples. Consequently, the position deviation issue can be effectively alleviated. We conduct extensive experiments on UAVDE, and our proposed method can achieve a 38.84% performance improvement, which demonstrates its effectiveness and superiority. The code and dataset would be released.
RHA-Net: An Encoder-Decoder Network with Residual Blocks and Hybrid Attention Mechanisms for Pavement Crack Segmentation
Jul 28, 2022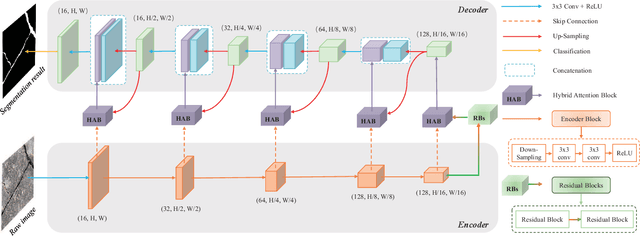
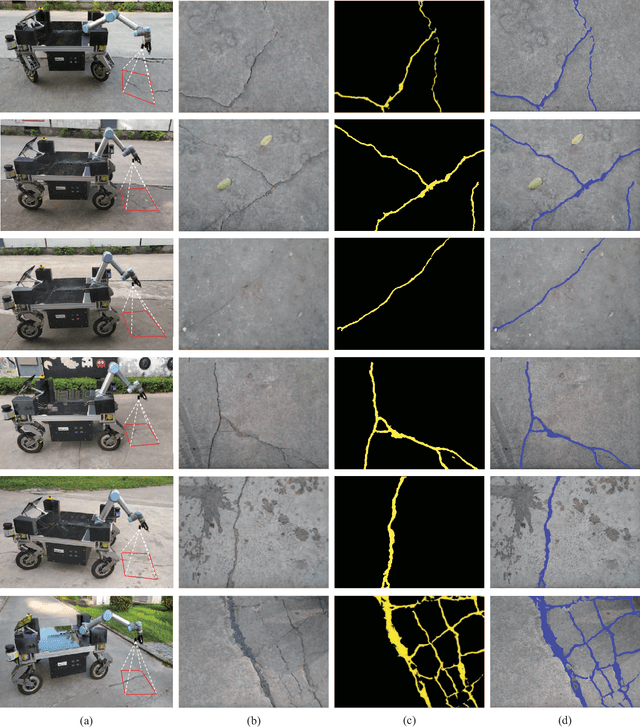

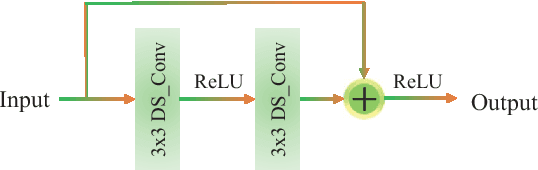
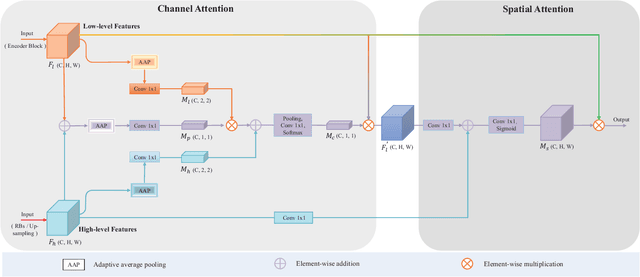
Abstract:The acquisition and evaluation of pavement surface data play an essential role in pavement condition evaluation. In this paper, an efficient and effective end-to-end network for automatic pavement crack segmentation, called RHA-Net, is proposed to improve the pavement crack segmentation accuracy. The RHA-Net is built by integrating residual blocks (ResBlocks) and hybrid attention blocks into the encoder-decoder architecture. The ResBlocks are used to improve the ability of RHA-Net to extract high-level abstract features. The hybrid attention blocks are designed to fuse both low-level features and high-level features to help the model focus on correct channels and areas of cracks, thereby improving the feature presentation ability of RHA-Net. An image data set containing 789 pavement crack images collected by a self-designed mobile robot is constructed and used for training and evaluating the proposed model. Compared with other state-of-the-art networks, the proposed model achieves better performance and the functionalities of adding residual blocks and hybrid attention mechanisms are validated in a comprehensive ablation study. Additionally, a light-weighted version of the model generated by introducing depthwise separable convolution achieves better a performance and a much faster processing speed with 1/30 of the number of U-Net parameters. The developed system can segment pavement crack in real-time on an embedded device Jetson TX2 (25 FPS). The video taken in real-time experiments is released at https://youtu.be/3XIogk0fiG4.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge