Mehran Ebrahimi
Optimal Design of Continuum Robots with Reachability Constraints
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:While multi-joint continuum robots are highly dexterous and flexible, designing an optimal robot can be challenging due to its kinematics involving curvatures. Hence, the current work presents a computational method developed to find optimal designs of continuum robots given reachability constraints. First, we leverage both forward and inverse kinematic computations to perform reachability analysis in an efficient yet accurate manner. While implementing inverse kinematics, we also integrate torque minimization at joints such that robot configurations with the minimum actuator torque required to reach a given workspace could be found. Lastly, we apply an estimation of distribution algorithm (EDA) to find optimal robot dimensions while considering reachability, where the objective function could be the total length of the robot or the actuator torque required to operate the robot. Through three application problems, we show that the EDA is superior to a genetic algorithm (GA) in finding better solutions within a given number of iterations, as the objective values of the best solutions found by the EDA are 4-15\% lower than those found by the GA.
Configuration Design of Mechanical Assemblies using an Estimation of Distribution Algorithm and Constraint Programming
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:A configuration design problem in mechanical engineering involves finding an optimal assembly of components and joints that realizes some desired performance criteria. Such a problem is a discrete, constrained, and black-box optimization problem. A novel method is developed to solve the problem by applying Bivariate Marginal Distribution Algorithm (BMDA) and constraint programming (CP). BMDA is a type of Estimation of Distribution Algorithm (EDA) that exploits the dependency knowledge learned between design variables without requiring too many fitness evaluations, which tend to be expensive for the current application. BMDA is extended with adaptive chi-square testing to identify dependencies and Gibbs sampling to generate new solutions. Also, repair operations based on CP are used to deal with infeasible solutions found during search. The method is applied to a vehicle suspension design problem and is found to be more effective in converging to good solutions than a genetic algorithm and other EDAs. These contributions are significant steps towards solving the difficult problem of configuration design in mechanical engineering with evolutionary computation.
Single MR Image Super-Resolution using Generative Adversarial Network
Jul 16, 2022



Abstract:Spatial resolution of medical images can be improved using super-resolution methods. Real Enhanced Super Resolution Generative Adversarial Network (Real-ESRGAN) is one of the recent effective approaches utilized to produce higher resolution images, given input images of lower resolution. In this paper, we apply this method to enhance the spatial resolution of 2D MR images. In our proposed approach, we slightly modify the structure of the Real-ESRGAN to train 2D Magnetic Resonance images (MRI) taken from the Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge (BraTS) 2018 dataset. The obtained results are validated qualitatively and quantitatively by computing SSIM (Structural Similarity Index Measure), NRMSE (Normalized Root Mean Square Error), MAE (Mean Absolute Error), and VIF (Visual Information Fidelity) values.
Multi-Modality Image Super-Resolution using Generative Adversarial Networks
Jun 22, 2022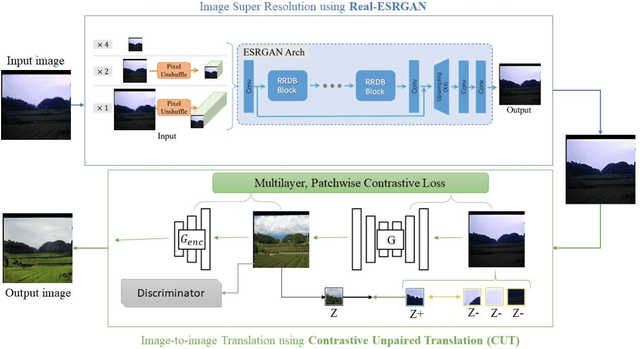
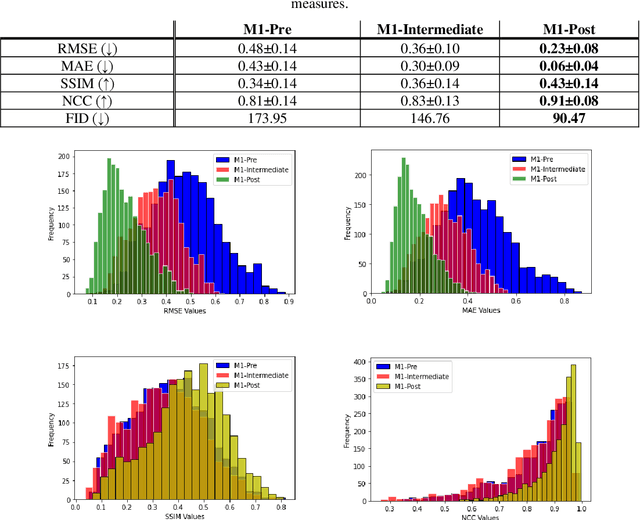
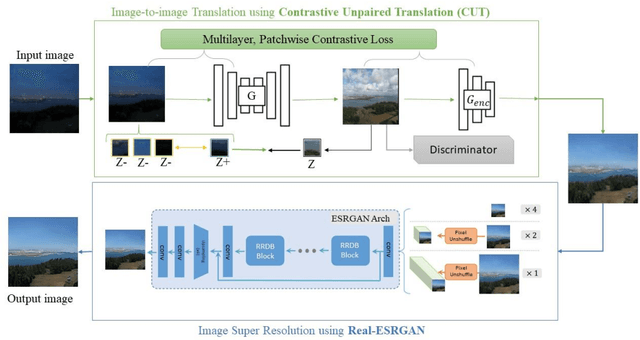
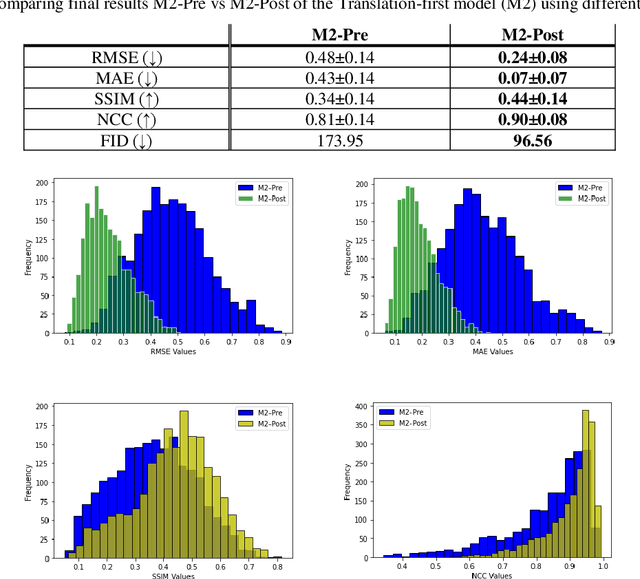
Abstract:Over the past few years deep learning-based techniques such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have significantly improved solutions to image super-resolution and image-to-image translation problems. In this paper, we propose a solution to the joint problem of image super-resolution and multi-modality image-to-image translation. The problem can be stated as the recovery of a high-resolution image in a modality, given a low-resolution observation of the same image in an alternative modality. Our paper offers two models to address this problem and will be evaluated on the recovery of high-resolution day images given low-resolution night images of the same scene. Promising qualitative and quantitative results will be presented for each model.
Multi-Modality Image Inpainting using Generative Adversarial Networks
Jun 22, 2022



Abstract:Deep learning techniques, especially Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have significantly improved image inpainting and image-to-image translation tasks over the past few years. To the best of our knowledge, the problem of combining the image inpainting task with the multi-modality image-to-image translation remains intact. In this paper, we propose a model to address this problem. The model will be evaluated on combined night-to-day image translation and inpainting, along with promising qualitative and quantitative results.
Deep Learning-Based MR Image Re-parameterization
Jun 11, 2022



Abstract:Magnetic resonance (MR) image re-parameterization refers to the process of generating via simulations of an MR image with a new set of MRI scanning parameters. Different parameter values generate distinct contrast between different tissues, helping identify pathologic tissue. Typically, more than one scan is required for diagnosis; however, acquiring repeated scans can be costly, time-consuming, and difficult for patients. Thus, using MR image re-parameterization to predict and estimate the contrast in these imaging scans can be an effective alternative. In this work, we propose a novel deep learning (DL) based convolutional model for MRI re-parameterization. Based on our preliminary results, DL-based techniques hold the potential to learn the non-linearities that govern the re-parameterization.
Artist-Guided Semiautomatic Animation Colorization
Jun 25, 2020


Abstract:There is a delicate balance between automating repetitive work in creative domains while staying true to an artist's vision. The animation industry regularly outsources large animation workloads to foreign countries where labor is inexpensive and long hours are common. Automating part of this process can be incredibly useful for reducing costs and creating manageable workloads for major animation studios and outsourced artists. We present a method for automating line art colorization by keeping artists in the loop to successfully reduce this workload while staying true to an artist's vision. By incorporating color hints and temporal information to an adversarial image-to-image framework, we show that it is possible to meet the balance between automation and authenticity through artist's input to generate colored frames with temporal consistency.
* This article supersedes our previous work arXiv:1904.09527
Edge-Informed Single Image Super-Resolution
Sep 11, 2019



Abstract:The recent increase in the extensive use of digital imaging technologies has brought with it a simultaneous demand for higher-resolution images. We develop a novel edge-informed approach to single image super-resolution (SISR). The SISR problem is reformulated as an image inpainting task. We use a two-stage inpainting model as a baseline for super-resolution and show its effectiveness for different scale factors (x2, x4, x8) compared to basic interpolation schemes. This model is trained using a joint optimization of image contents (texture and color) and structures (edges). Quantitative and qualitative comparisons are included and the proposed model is compared with current state-of-the-art techniques. We show that our method of decoupling structure and texture reconstruction improves the quality of the final reconstructed high-resolution image. Code and models available at: https://github.com/knazeri/edge-informed-sisr
Automatic Temporally Coherent Video Colorization
Apr 21, 2019



Abstract:Greyscale image colorization for applications in image restoration has seen significant improvements in recent years. Many of these techniques that use learning-based methods struggle to effectively colorize sparse inputs. With the consistent growth of the anime industry, the ability to colorize sparse input such as line art can reduce significant cost and redundant work for production studios by eliminating the in-between frame colorization process. Simply using existing methods yields inconsistent colors between related frames resulting in a flicker effect in the final video. In order to successfully automate key areas of large-scale anime production, the colorization of line arts must be temporally consistent between frames. This paper proposes a method to colorize line art frames in an adversarial setting, to create temporally coherent video of large anime by improving existing image to image translation methods. We show that by adding an extra condition to the generator and discriminator, we can effectively create temporally consistent video sequences from anime line arts. Code and models available at: https://github.com/Harry-Thasarathan/TCVC
EdgeConnect: Generative Image Inpainting with Adversarial Edge Learning
Jan 11, 2019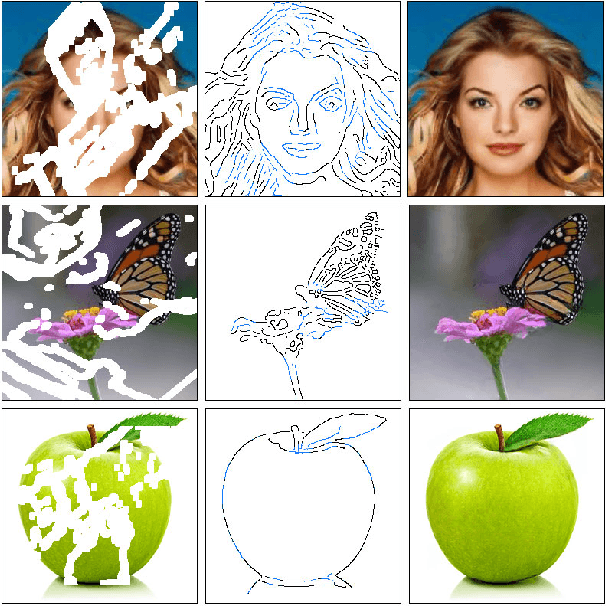
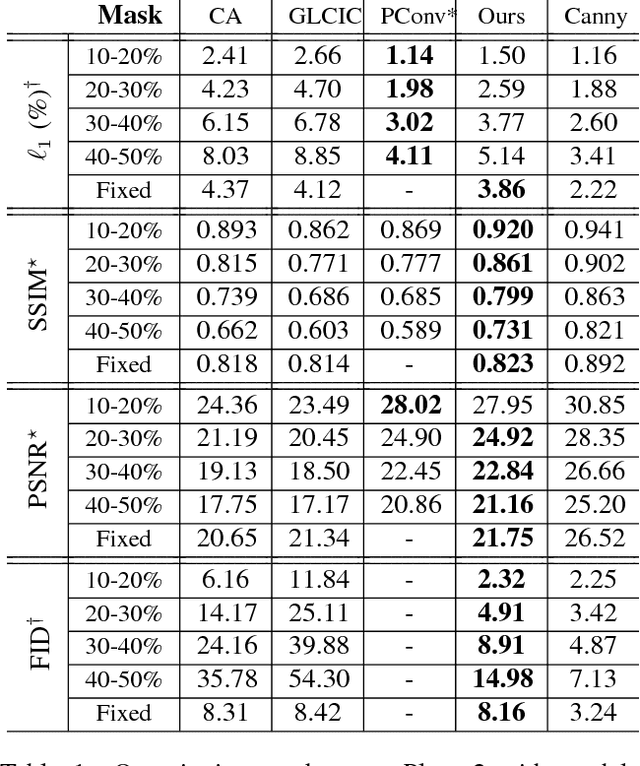
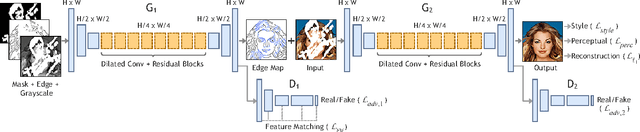
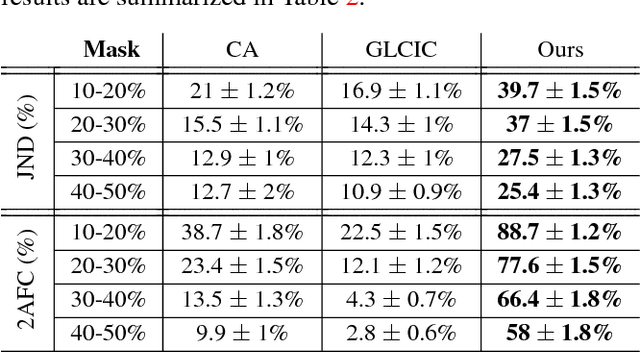
Abstract:Over the last few years, deep learning techniques have yielded significant improvements in image inpainting. However, many of these techniques fail to reconstruct reasonable structures as they are commonly over-smoothed and/or blurry. This paper develops a new approach for image inpainting that does a better job of reproducing filled regions exhibiting fine details. We propose a two-stage adversarial model EdgeConnect that comprises of an edge generator followed by an image completion network. The edge generator hallucinates edges of the missing region (both regular and irregular) of the image, and the image completion network fills in the missing regions using hallucinated edges as a priori. We evaluate our model end-to-end over the publicly available datasets CelebA, Places2, and Paris StreetView, and show that it outperforms current state-of-the-art techniques quantitatively and qualitatively. Code and models available at: https://github.com/knazeri/edge-connect
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge