Md Rashedul Islam
Predictive Analytics for Dementia: Machine Learning on Healthcare Data
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Dementia is a complex syndrome impacting cognitive and emotional functions, with Alzheimer's disease being the most common form. This study focuses on enhancing dementia prediction using machine learning (ML) techniques on patient health data. Supervised learning algorithms are applied in this study, including K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), and Gaussian Process Classifiers. To address class imbalance and improve model performance, techniques such as Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) and Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) vectorization were employed. Among the models, LDA achieved the highest testing accuracy of 98%. This study highlights the importance of model interpretability and the correlation of dementia with features such as the presence of the APOE-epsilon4 allele and chronic conditions like diabetes. This research advocates for future ML innovations, particularly in integrating explainable AI approaches, to further improve predictive capabilities in dementia care.
CAGN-GAT Fusion: A Hybrid Contrastive Attentive Graph Neural Network for Network Intrusion Detection
Mar 02, 2025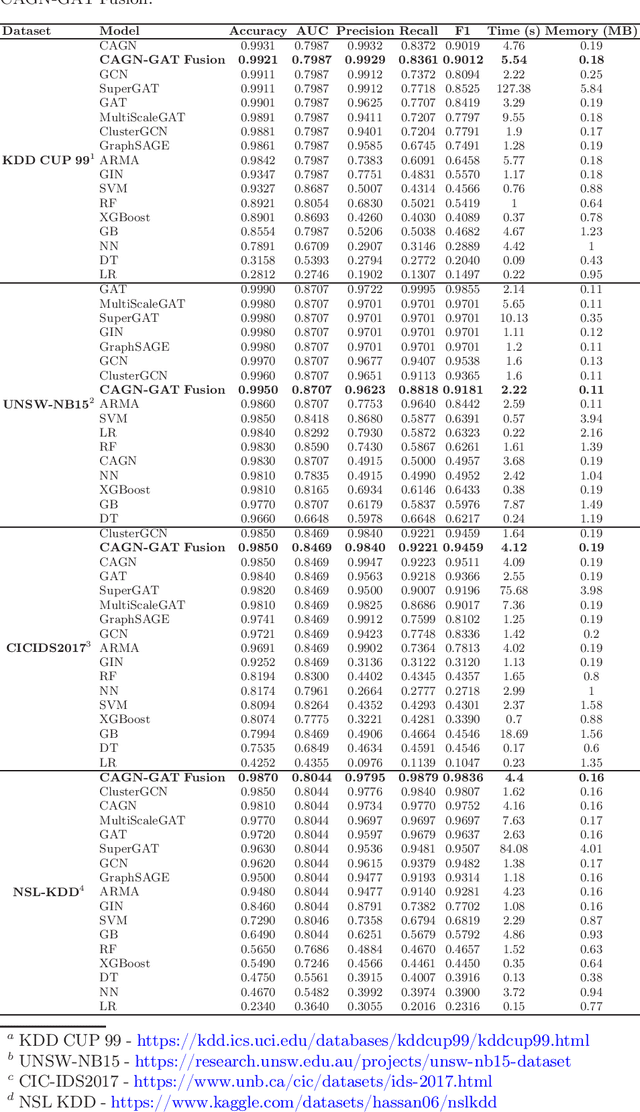
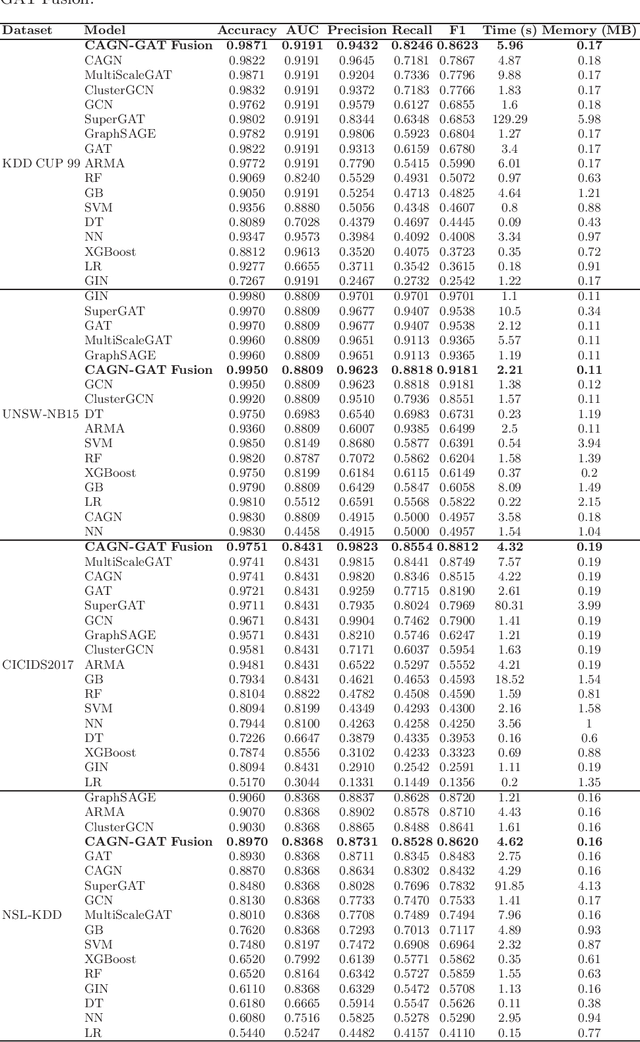
Abstract:Cybersecurity threats are growing, making network intrusion detection essential. Traditional machine learning models remain effective in resource-limited environments due to their efficiency, requiring fewer parameters and less computational time. However, handling short and highly imbalanced datasets remains challenging. In this study, we propose the fusion of a Contrastive Attentive Graph Network and Graph Attention Network (CAGN-GAT Fusion) and benchmark it against 15 other models, including both Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and traditional ML models. Our evaluation is conducted on four benchmark datasets (KDD-CUP-1999, NSL-KDD, UNSW-NB15, and CICIDS2017) using a short and proportionally imbalanced dataset with a constant size of 5000 samples to ensure fairness in comparison. Results show that CAGN-GAT Fusion demonstrates stable and competitive accuracy, recall, and F1-score, even though it does not achieve the highest performance in every dataset. Our analysis also highlights the impact of adaptive graph construction techniques, including small changes in connections (edge perturbation) and selective hiding of features (feature masking), improving detection performance. The findings confirm that GNNs, particularly CAGN-GAT Fusion, are robust and computationally efficient, making them well-suited for resource-constrained environments. Future work will explore GraphSAGE layers and multiview graph construction techniques to further enhance adaptability and detection accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge