Md. Kishor Morol
Predictive Analytics for Dementia: Machine Learning on Healthcare Data
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Dementia is a complex syndrome impacting cognitive and emotional functions, with Alzheimer's disease being the most common form. This study focuses on enhancing dementia prediction using machine learning (ML) techniques on patient health data. Supervised learning algorithms are applied in this study, including K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA), Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), and Gaussian Process Classifiers. To address class imbalance and improve model performance, techniques such as Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) and Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF) vectorization were employed. Among the models, LDA achieved the highest testing accuracy of 98%. This study highlights the importance of model interpretability and the correlation of dementia with features such as the presence of the APOE-epsilon4 allele and chronic conditions like diabetes. This research advocates for future ML innovations, particularly in integrating explainable AI approaches, to further improve predictive capabilities in dementia care.
Small Language Models: Architectures, Techniques, Evaluation, Problems and Future Adaptation
May 26, 2025Abstract:Small Language Models (SLMs) have gained substantial attention due to their ability to execute diverse language tasks successfully while using fewer computer resources. These models are particularly ideal for deployment in limited environments, such as mobile devices, on-device processing, and edge systems. In this study, we present a complete assessment of SLMs, focussing on their design frameworks, training approaches, and techniques for lowering model size and complexity. We offer a novel classification system to organize the optimization approaches applied for SLMs, encompassing strategies like pruning, quantization, and model compression. Furthermore, we assemble SLM's studies of evaluation suite with some existing datasets, establishing a rigorous platform for measuring SLM capabilities. Alongside this, we discuss the important difficulties that remain unresolved in this sector, including trade-offs between efficiency and performance, and we suggest directions for future study. We anticipate this study to serve as a beneficial guide for researchers and practitioners who aim to construct compact, efficient, and high-performing language models.
Multilingual Question Answering in Low-Resource Settings: A Dzongkha-English Benchmark for Foundation Models
May 24, 2025Abstract:In this work, we provide DZEN, a dataset of parallel Dzongkha and English test questions for Bhutanese middle and high school students. The over 5K questions in our collection span a variety of scientific topics and include factual, application, and reasoning-based questions. We use our parallel dataset to test a number of Large Language Models (LLMs) and find a significant performance difference between the models in English and Dzongkha. We also look at different prompting strategies and discover that Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting works well for reasoning questions but less well for factual ones. We also find that adding English translations enhances the precision of Dzongkha question responses. Our results point to exciting avenues for further study to improve LLM performance in Dzongkha and, more generally, in low-resource languages. We release the dataset at: https://github.com/kraritt/llm_dzongkha_evaluation.
ConvoWaste: An Automatic Waste Segregation Machine Using Deep Learning
Feb 06, 2023Abstract:Nowadays, proper urban waste management is one of the biggest concerns for maintaining a green and clean environment. An automatic waste segregation system can be a viable solution to improve the sustainability of the country and boost the circular economy. This paper proposes a machine to segregate waste into different parts with the help of a smart object detection algorithm using ConvoWaste in the field of deep convolutional neural networks (DCNN) and image processing techniques. In this paper, deep learning and image processing techniques are applied to precisely classify the waste, and the detected waste is placed inside the corresponding bins with the help of a servo motor-based system. This machine has the provision to notify the responsible authority regarding the waste level of the bins and the time to trash out the bins filled with garbage by using the ultrasonic sensors placed in each bin and the dual-band GSM-based communication technology. The entire system is controlled remotely through an Android app in order to dump the separated waste in the desired place thanks to its automation properties. The use of this system can aid in the process of recycling resources that were initially destined to become waste, utilizing natural resources, and turning these resources back into usable products. Thus, the system helps fulfill the criteria of a circular economy through resource optimization and extraction. Finally, the system is designed to provide services at a low cost while maintaining a high level of accuracy in terms of technological advancement in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). We have gotten 98% accuracy for our ConvoWaste deep learning model.
convoHER2: A Deep Neural Network for Multi-Stage Classification of HER2 Breast Cancer
Nov 19, 2022



Abstract:Generally, human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2) breast cancer is more aggressive than other kinds of breast cancer. Currently, HER2 breast cancer is detected using expensive medical tests are most expensive. Therefore, the aim of this study was to develop a computational model named convoHER2 for detecting HER2 breast cancer with image data using convolution neural network (CNN). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immunohistochemical (IHC) stained images has been used as raw data from the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) benchmark dataset. This dataset consists of 4873 images of H&E and IHC. Among all images of the dataset, 3896 and 977 images are applied to train and test the convoHER2 model, respectively. As all the images are in high resolution, we resize them so that we can feed them in our convoHER2 model. The cancerous samples images are classified into four classes based on the stage of the cancer (0+, 1+, 2+, 3+). The convoHER2 model is able to detect HER2 cancer and its grade with accuracy 85% and 88% using H&E images and IHC images, respectively. The outcomes of this study determined that the HER2 cancer detecting rates of the convoHER2 model are much enough to provide better diagnosis to the patient for recovering their HER2 breast cancer in future.
A comparative analysis of Graph Neural Networks and commonly used machine learning algorithms on fake news detection
Mar 26, 2022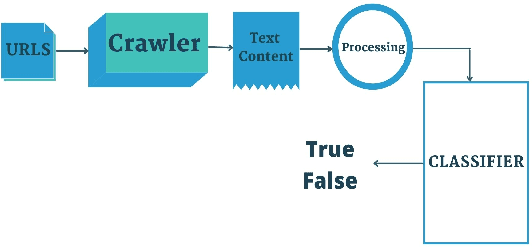
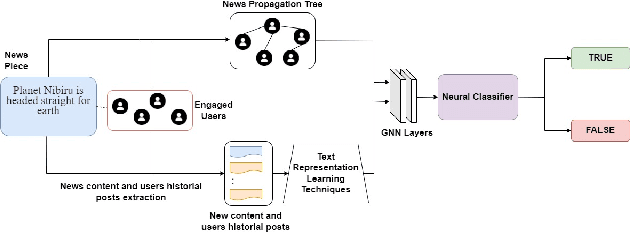
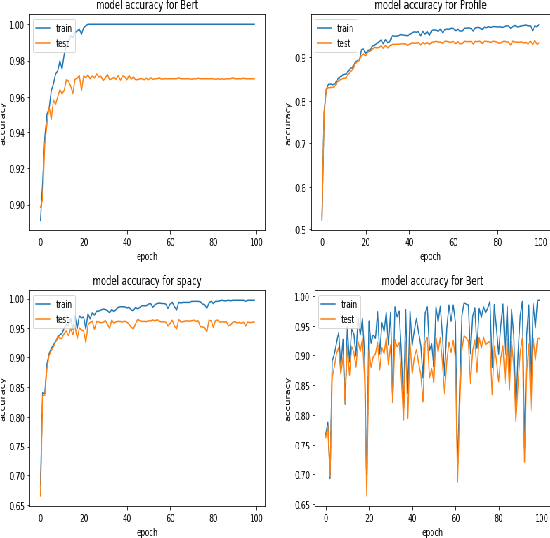
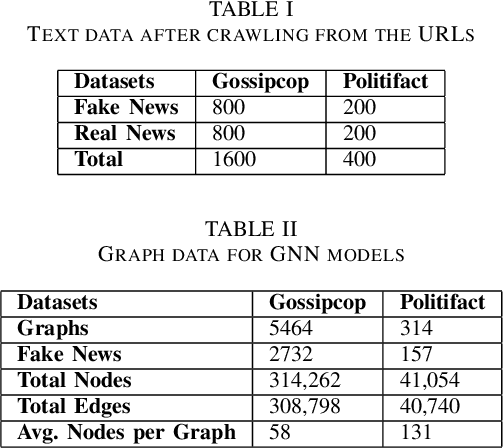
Abstract:Fake news on social media is increasingly regarded as one of the most concerning issues. Low cost, simple accessibility via social platforms, and a plethora of low-budget online news sources are some of the factors that contribute to the spread of false news. Most of the existing fake news detection algorithms are solely focused on the news content only but engaged users prior posts or social activities provide a wealth of information about their views on news and have significant ability to improve fake news identification. Graph Neural Networks are a form of deep learning approach that conducts prediction on graph-described data. Social media platforms are followed graph structure in their representation, Graph Neural Network are special types of neural networks that could be usually applied to graphs, making it much easier to execute edge, node, and graph-level prediction. Therefore, in this paper, we present a comparative analysis among some commonly used machine learning algorithms and Graph Neural Networks for detecting the spread of false news on social media platforms. In this study, we take the UPFD dataset and implement several existing machine learning algorithms on text data only. Besides this, we create different GNN layers for fusing graph-structured news propagation data and the text data as the node feature in our GNN models. GNNs provide the best solutions to the dilemma of identifying false news in our research.
A Systematic Review on Interactive Virtual Reality Laboratory
Mar 26, 2022
Abstract:Virtual Reality has become a significant element of education throughout the years. To understand the quality and advantages of these techniques, it is important to understand how they were developed and evaluated. Since COVID-19, the education system has drastically changed a lot. It has shifted from being in a classroom with a whiteboard and projectors to having your own room in front of your laptop in a virtual meeting. In this respect, virtual reality in the laboratory or Virtual Laboratory is the main focus of this research, which is intended to comprehend the work done in quality education from a distance using VR. As per the findings of the study, adopting virtual reality in education can help students learn more effectively and also help them increase perspective, enthusiasm, and knowledge of complex notions by offering them an interactive experience in which they can engage and learn more effectively. This highlights the importance of a significant expansion of VR use in learning, the majority of which employ scientific comparison approaches to compare students who use VR to those who use the traditional method for learning.
A Deep Learning Framework to Reconstruct Face under Mask
Mar 23, 2022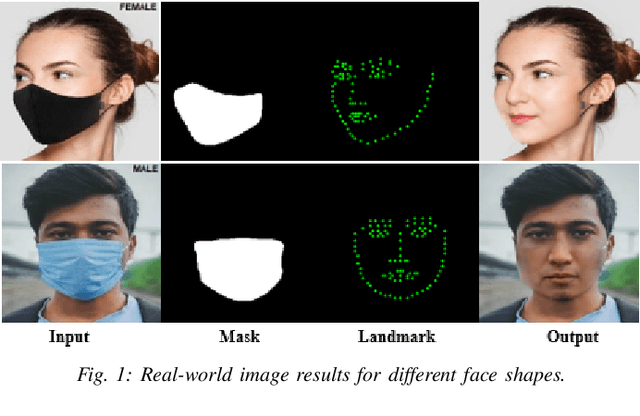
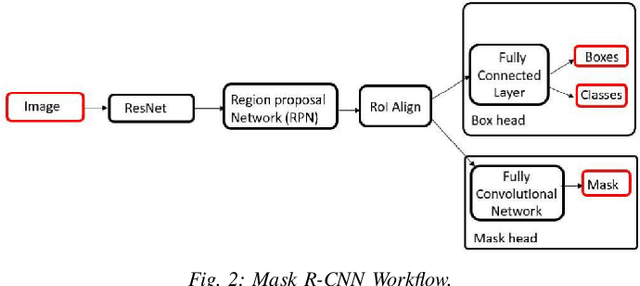
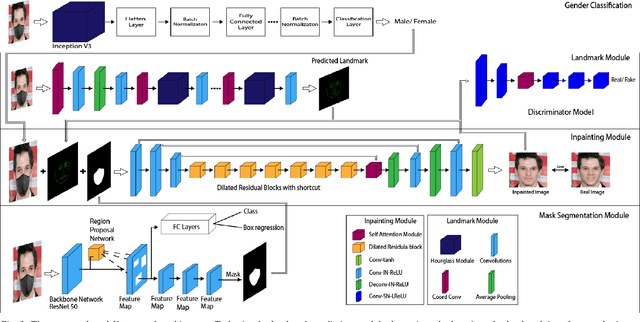
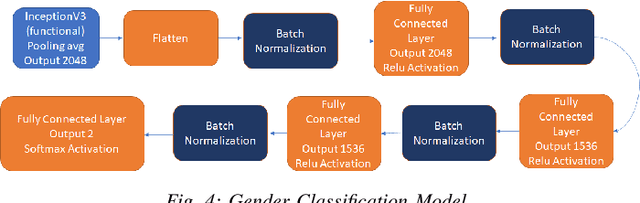
Abstract:While deep learning-based image reconstruction methods have shown significant success in removing objects from pictures, they have yet to achieve acceptable results for attributing consistency to gender, ethnicity, expression, and other characteristics like the topological structure of the face. The purpose of this work is to extract the mask region from a masked image and rebuild the area that has been detected. This problem is complex because (i) it is difficult to determine the gender of an image hidden behind a mask, which causes the network to become confused and reconstruct the male face as a female or vice versa; (ii) we may receive images from multiple angles, making it extremely difficult to maintain the actual shape, topological structure of the face and a natural image; and (iii) there are problems with various mask forms because, in some cases, the area of the mask cannot be anticipated precisely; certain parts of the mask remain on the face after completion. To solve this complex task, we split the problem into three phases: landmark detection, object detection for the targeted mask area, and inpainting the addressed mask region. To begin, to solve the first problem, we have used gender classification, which detects the actual gender behind a mask, then we detect the landmark of the masked facial image. Second, we identified the non-face item, i.e., the mask, and used the Mask R-CNN network to create the binary mask of the observed mask area. Thirdly, we developed an inpainting network that uses anticipated landmarks to create realistic images. To segment the mask, this article uses a mask R-CNN and offers a binary segmentation map for identifying the mask area. Additionally, we generated the image utilizing landmarks as structural guidance through a GAN-based network. The studies presented in this paper use the FFHQ and CelebA datasets.
A Real-time Junk Food Recognition System based on Machine Learning
Mar 22, 2022

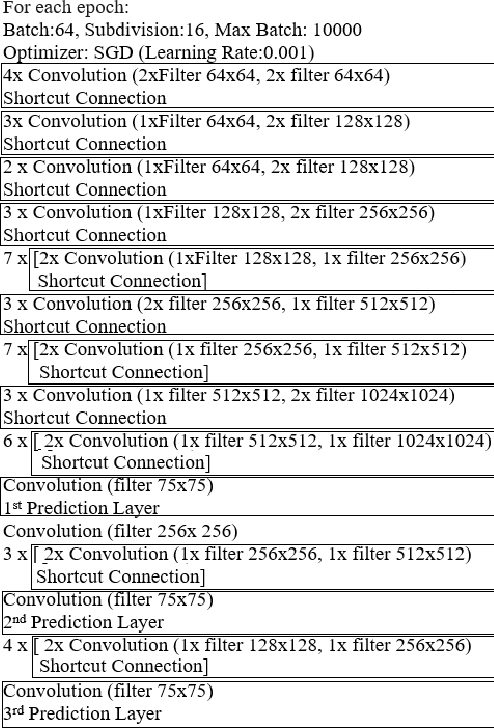

Abstract:$ $As a result of bad eating habits, humanity may be destroyed. People are constantly on the lookout for tasty foods, with junk foods being the most common source. As a consequence, our eating patterns are shifting, and we're gravitating toward junk food more than ever, which is bad for our health and increases our risk of acquiring health problems. Machine learning principles are applied in every aspect of our lives, and one of them is object recognition via image processing. However, because foods vary in nature, this procedure is crucial, and traditional methods like ANN, SVM, KNN, PLS etc., will result in a low accuracy rate. All of these issues were defeated by the Deep Neural Network. In this work, we created a fresh dataset of 10,000 data points from 20 junk food classifications to try to recognize junk foods. All of the data in the data set was gathered using the Google search engine, which is thought to be one-of-a-kind in every way. The goal was achieved using Convolution Neural Network (CNN) technology, which is well-known for image processing. We achieved a 98.05\% accuracy rate throughout the research, which was satisfactory. In addition, we conducted a test based on a real-life event, and the outcome was extraordinary. Our goal is to advance this research to the next level, so that it may be applied to a future study. Our ultimate goal is to create a system that would encourage people to avoid eating junk food and to be health-conscious. \keywords{ Machine Learning \and junk food \and object detection \and YOLOv3 \and custom food dataset.}
Approaches for Improving the Performance of Fake News Detection in Bangla: Imbalance Handling and Model Stacking
Mar 22, 2022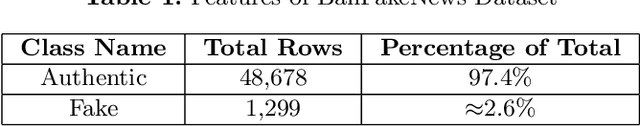
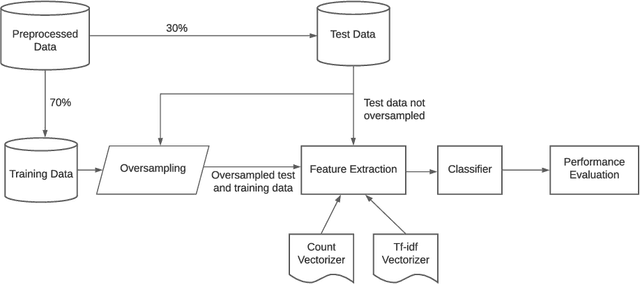
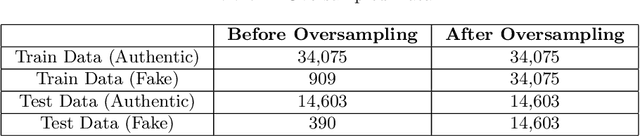
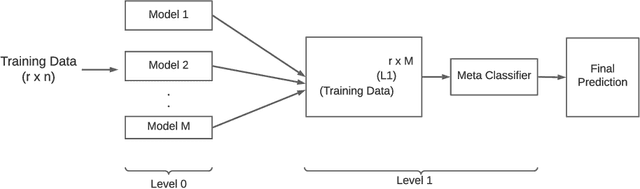
Abstract:Imbalanced datasets can lead to biasedness into the detection of fake news. In this work, we present several strategies for resolving the imbalance issue for fake news detection in Bangla with a comparative assessment of proposed methodologies. Additionally, we propose a technique for improving performance even when the dataset is imbalanced. We applied our proposed approaches to BanFakeNews, a dataset developed for the purpose of detecting fake news in Bangla comprising of 50K instances but is significantly skewed, with 97% of majority instances. We obtained a 93.1% F1-score using data manipulation manipulation techniques such as SMOTE, and a 79.1% F1-score using without data manipulation approaches such as Stacked Generalization. Without implementing these techniques, the F1-score would have been 67.6% for baseline models. We see this work as an important step towards paving the way of fake news detection in Bangla. By implementing these strategies the obstacles of imbalanced dataset can be removed and improvement in the performance can be achieved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge