Matej Ulčar
Sequence to sequence pretraining for a less-resourced Slovenian language
Jul 28, 2022



Abstract:Large pretrained language models have recently conquered the area of natural language processing. As an alternative to predominant masked language modelling introduced in BERT, the T5 model has introduced a more general training objective, namely sequence to sequence transformation, which includes masked language model but more naturally fits text generation tasks such as machine translation, summarization, open-domain question answering, text simplification, dialogue systems, etc. The monolingual variants of T5 models have been limited to well-resourced languages, while the massively multilingual T5 model supports 101 languages. In contrast, we trained two different sized T5-type sequence to sequence models for morphologically rich Slovene language with much less resources and analyzed their behavior. Concerning classification tasks, the SloT5 models mostly lag behind the monolingual Slovene SloBERTa model but are to be considered for the generative tasks.
Training dataset and dictionary sizes matter in BERT models: the case of Baltic languages
Dec 20, 2021



Abstract:Large pretrained masked language models have become state-of-the-art solutions for many NLP problems. While studies have shown that monolingual models produce better results than multilingual models, the training datasets must be sufficiently large. We trained a trilingual LitLat BERT-like model for Lithuanian, Latvian, and English, and a monolingual Est-RoBERTa model for Estonian. We evaluate their performance on four downstream tasks: named entity recognition, dependency parsing, part-of-speech tagging, and word analogy. To analyze the importance of focusing on a single language and the importance of a large training set, we compare created models with existing monolingual and multilingual BERT models for Estonian, Latvian, and Lithuanian. The results show that the newly created LitLat BERT and Est-RoBERTa models improve the results of existing models on all tested tasks in most situations.
Cross-lingual alignments of ELMo contextual embeddings
Jul 22, 2021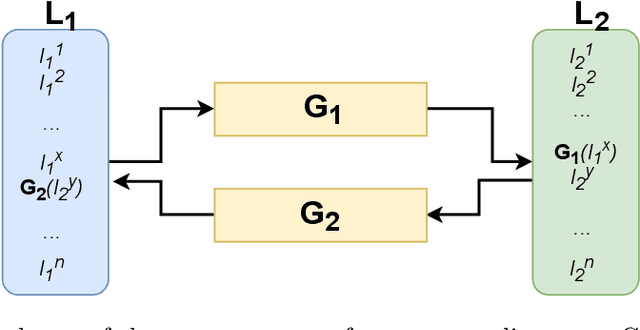
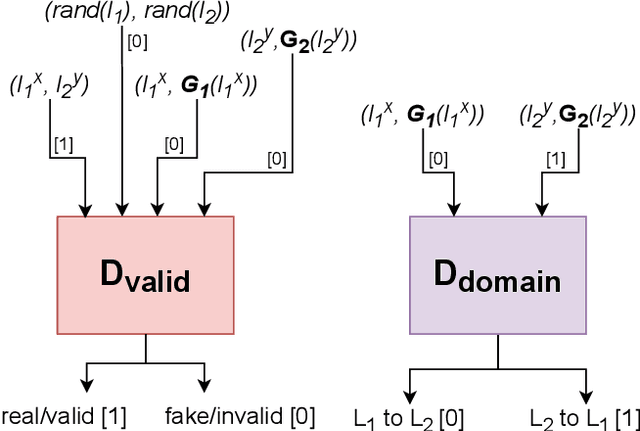
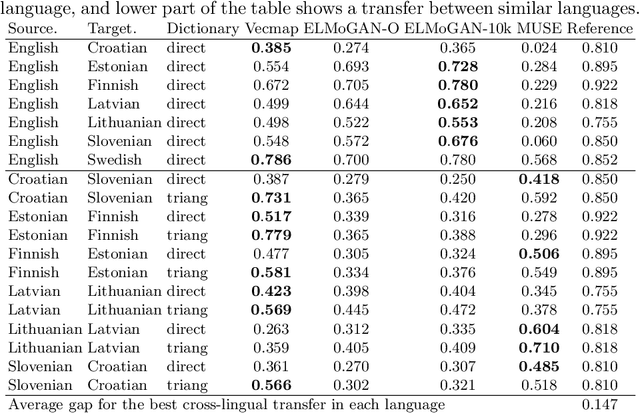
Abstract:Building machine learning prediction models for a specific NLP task requires sufficient training data, which can be difficult to obtain for less-resourced languages. Cross-lingual embeddings map word embeddings from a less-resourced language to a resource-rich language so that a prediction model trained on data from the resource-rich language can also be used in the less-resourced language. To produce cross-lingual mappings of recent contextual embeddings, anchor points between the embedding spaces have to be words in the same context. We address this issue with a novel method for creating cross-lingual contextual alignment datasets. Based on that, we propose several cross-lingual mapping methods for ELMo embeddings. The proposed linear mapping methods use existing Vecmap and MUSE alignments on contextual ELMo embeddings. Novel nonlinear ELMoGAN mapping methods are based on GANs and do not assume isomorphic embedding spaces. We evaluate the proposed mapping methods on nine languages, using four downstream tasks: named entity recognition (NER), dependency parsing (DP), terminology alignment, and sentiment analysis. The ELMoGAN methods perform very well on the NER and terminology alignment tasks, with a lower cross-lingual loss for NER compared to the direct training on some languages. In DP and sentiment analysis, linear contextual alignment variants are more successful.
Evaluation of contextual embeddings on less-resourced languages
Jul 22, 2021



Abstract:The current dominance of deep neural networks in natural language processing is based on contextual embeddings such as ELMo, BERT, and BERT derivatives. Most existing work focuses on English; in contrast, we present here the first multilingual empirical comparison of two ELMo and several monolingual and multilingual BERT models using 14 tasks in nine languages. In monolingual settings, our analysis shows that monolingual BERT models generally dominate, with a few exceptions such as the dependency parsing task, where they are not competitive with ELMo models trained on large corpora. In cross-lingual settings, BERT models trained on only a few languages mostly do best, closely followed by massively multilingual BERT models.
FinEst BERT and CroSloEngual BERT: less is more in multilingual models
Jun 14, 2020



Abstract:Large pretrained masked language models have become state-of-the-art solutions for many NLP problems. The research has been mostly focused on English language, though. While massively multilingual models exist, studies have shown that monolingual models produce much better results. We train two trilingual BERT-like models, one for Finnish, Estonian, and English, the other for Croatian, Slovenian, and English. We evaluate their performance on several downstream tasks, NER, POS-tagging, and dependency parsing, using the multilingual BERT and XLM-R as baselines. The newly created FinEst BERT and CroSloEngual BERT improve the results on all tasks in most monolingual and cross-lingual situations
CoSimLex: A Resource for Evaluating Graded Word Similarity in Context
Dec 18, 2019



Abstract:State of the art natural language processing tools are built on context-dependent word embeddings, but no direct method for evaluating these representations currently exists. Standard tasks and datasets for intrinsic evaluation of embeddings are based on judgements of similarity, but ignore context; standard tasks for word sense disambiguation take account of context but do not provide continuous measures of meaning similarity. This paper describes an effort to build a new dataset, CoSimLex, intended to fill this gap. Building on the standard pairwise similarity task of SimLex-999, it provides context-dependent similarity measures; covers not only discrete differences in word sense but more subtle, graded changes in meaning; and covers not only a well-resourced language (English) but a number of less-resourced languages. We define the task and evaluation metrics, outline the dataset collection methodology, and describe the status of the dataset so far.
High Quality ELMo Embeddings for Seven Less-Resourced Languages
Nov 22, 2019



Abstract:Recent results show that deep neural networks using contextual embeddings significantly outperform non-contextual embeddings on a majority of text classification task. We offer precomputed embeddings from popular contextual ELMo model for seven languages: Croatian, Estonian, Finnish, Latvian, Lithuanian, Slovenian, and Swedish. We demonstrate that the quality of embeddings strongly depends on the size of training set and show that existing publicly available ELMo embeddings for listed languages shall be improved. We train new ELMo embeddings on much larger training sets and show their advantage over baseline non-contextual FastText embeddings. In evaluation, we use two benchmarks, the analogy task and the NER task.
Multilingual Culture-Independent Word Analogy Datasets
Nov 22, 2019



Abstract:In text processing, deep neural networks mostly use word embeddings as an input. Embeddings have to ensure that relations between words are reflected through distances in a high-dimensional numeric space. To compare the quality of different text embeddings, typically, we use benchmark datasets. We present a collection of such datasets for the word analogy task in nine languages: Croatian, English, Estonian, Finnish, Latvian, Lithuanian, Russian, Slovenian, and Swedish. We redesigned the original monolingual analogy task to be culturally independent and also constructed cross-lingual analogy datasets for the involved languages. We present basic statistics of the created datasets and their initial evaluation using fastText embeddings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge