Matan Ninio
Does your model understand genes? A benchmark of gene properties for biological and text models
Dec 05, 2024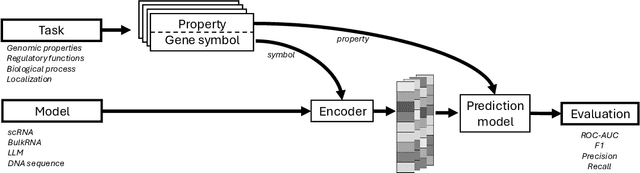
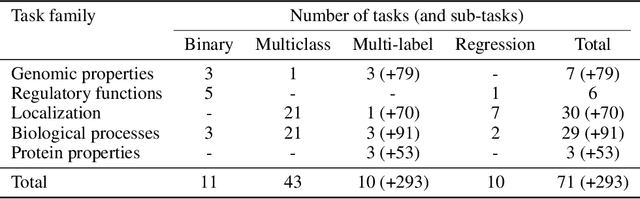
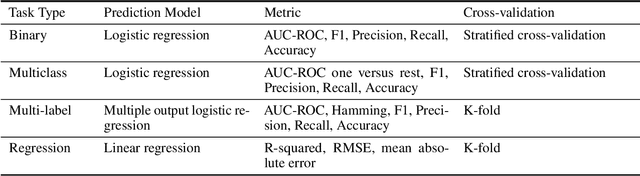

Abstract:The application of deep learning methods, particularly foundation models, in biological research has surged in recent years. These models can be text-based or trained on underlying biological data, especially omics data of various types. However, comparing the performance of these models consistently has proven to be a challenge due to differences in training data and downstream tasks. To tackle this problem, we developed an architecture-agnostic benchmarking approach that, instead of evaluating the models directly, leverages entity representation vectors from each model and trains simple predictive models for each benchmarking task. This ensures that all types of models are evaluated using the same input and output types. Here we focus on gene properties collected from professionally curated bioinformatics databases. These gene properties are categorized into five major groups: genomic properties, regulatory functions, localization, biological processes, and protein properties. Overall, we define hundreds of tasks based on these databases, which include binary, multi-label, and multi-class classification tasks. We apply these benchmark tasks to evaluate expression-based models, large language models, protein language models, DNA-based models, and traditional baselines. Our findings suggest that text-based models and protein language models generally outperform expression-based models in genomic properties and regulatory functions tasks, whereas expression-based models demonstrate superior performance in localization tasks. These results should aid in the development of more informed artificial intelligence strategies for biological understanding and therapeutic discovery. To ensure the reproducibility and transparency of our findings, we have made the source code and benchmark data publicly accessible for further investigation and expansion at github.com/BiomedSciAI/gene-benchmark.
MAMMAL -- Molecular Aligned Multi-Modal Architecture and Language
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:Drug discovery typically consists of multiple steps, including identifying a target protein key to a disease's etiology, validating that interacting with this target could prevent symptoms or cure the disease, discovering a small molecule or biologic therapeutic to interact with it, and optimizing the candidate molecule through a complex landscape of required properties. Drug discovery related tasks often involve prediction and generation while considering multiple entities that potentially interact, which poses a challenge for typical AI models. For this purpose we present MAMMAL - Molecular Aligned Multi-Modal Architecture and Language - a method that we applied to create a versatile multi-task foundation model ibm/biomed.omics.bl.sm.ma-ted-458m that learns from large-scale biological datasets (2 billion samples) across diverse modalities, including proteins, small molecules, and genes. We introduce a prompt syntax that supports a wide range of classification, regression, and generation tasks. It allows combining different modalities and entity types as inputs and/or outputs. Our model handles combinations of tokens and scalars and enables the generation of small molecules and proteins, property prediction, and transcriptomic lab test predictions. We evaluated the model on 11 diverse downstream tasks spanning different steps within a typical drug discovery pipeline, where it reaches new SOTA in 9 tasks and is comparable to SOTA in 2 tasks. This performance is achieved while using a unified architecture serving all tasks, in contrast to the original SOTA performance achieved using tailored architectures. The model code and pretrained weights are publicly available at https://github.com/BiomedSciAI/biomed-multi-alignment and https://huggingface.co/ibm/biomed.omics.bl.sm.ma-ted-458m.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge