Matěj Karásek
An Experimental Study of Wind Resistance and Power Consumption in MAVs with a Low-Speed Multi-Fan Wind System
Feb 14, 2022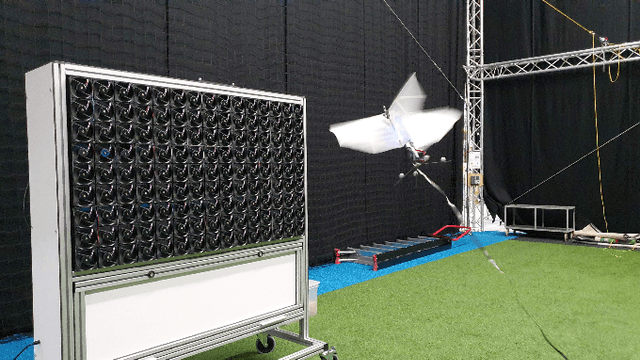
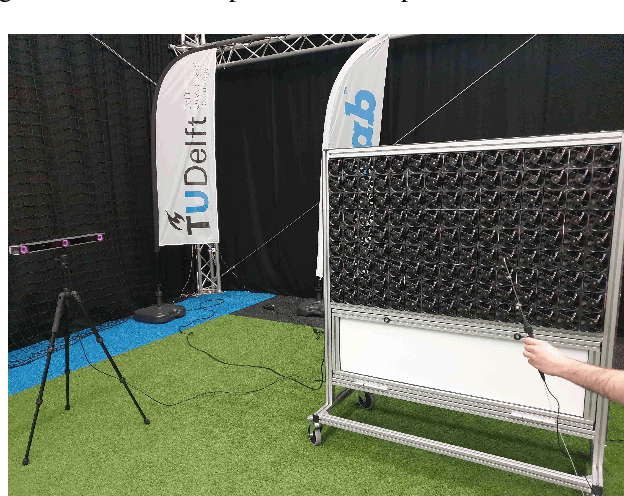
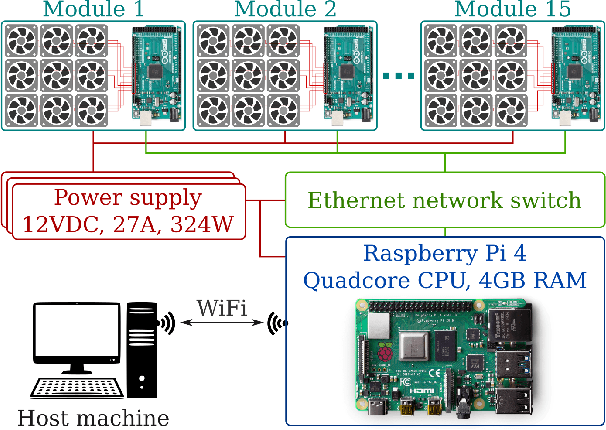

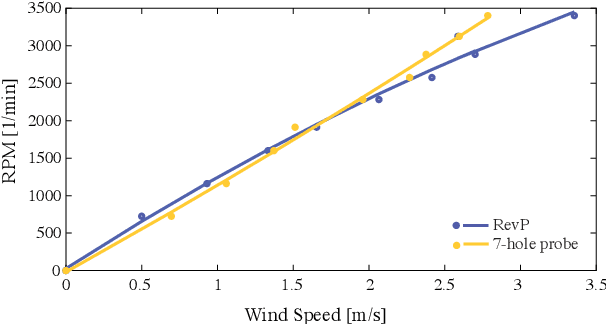
Abstract:This paper discusses a low-cost, open-source and open-hardware design and performance evaluation of a low-speed, multi-fan wind system dedicated to micro air vehicle (MAV) testing. In addition, a set of experiments with a flapping wing MAV and rotorcraft is presented, demonstrating the capabilities of the system and the properties of these different types of drones in response to various types of wind. We performed two sets of experiments where a MAV is flying into the wake of the fan system, gathering data about states, battery voltage and current. Firstly, we focus on steady wind conditions with wind speeds ranging from 0.5 m/s to 3.4 m/s. During the second set of experiments, we introduce wind gusts, by periodically modulating the wind speed from 1.3 m/s to 3.4 m/s with wind gust oscillations of 0.5 Hz, 0.25 Hz and 0.125 Hz. The "Flapper" flapping wing MAV requires much larger pitch angles to counter wind than the "CrazyFlie" quadrotor. This is due to the Flapper's larger wing surface. In forward flight, its wings do provide extra lift, considerably reducing the power consumption. In contrast, the CrazyFlie's power consumption stays more constant for different wind speeds. The experiments with the varying wind show a quicker gust response by the CrazyFlie compared with the Flapper drone, but both their responses could be further improved. We expect that the proposed wind gust system will provide a useful tool to the community to achieve such improvements.
First free-flight flow visualisation of a flapping-wing robot
Dec 22, 2016
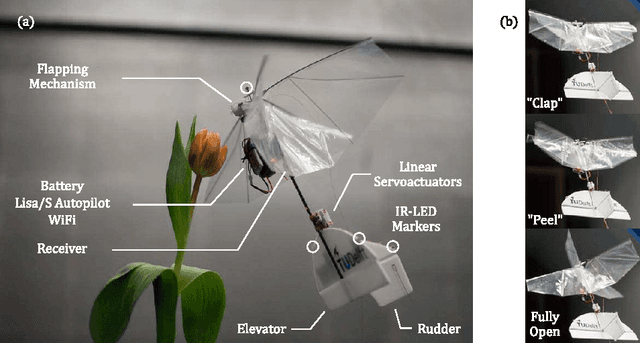

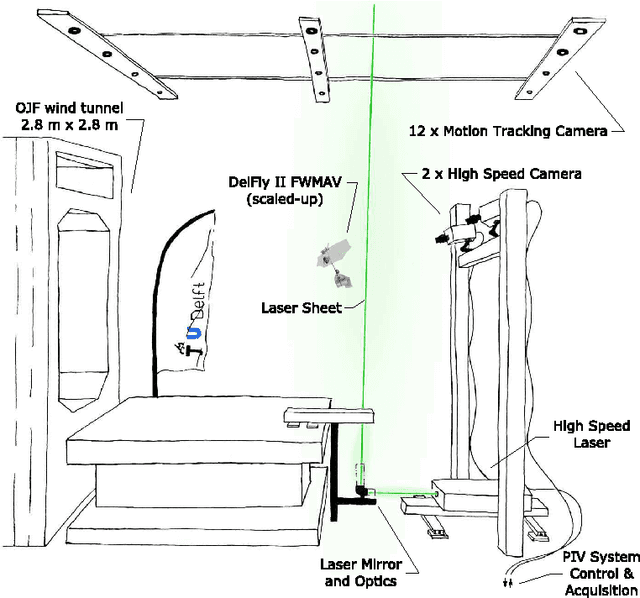
Abstract:Flow visualisations are essential to better understand the unsteady aerodynamics of flapping wing flight. The issues inherent to animal experiments, such as poor controllability and unnatural flapping when tethered, can be avoided by using robotic flyers. Such an approach holds a promise for a more systematic and repeatable methodology for flow visualisation, through a better controlled flight. Such experiments require high precision position control, however, and until now this was not possible due to the challenging flight dynamics and payload restrictions of flapping wing Micro Air Vehicles (FWMAV). Here, we present a new FWMAV-specific control approach that, by employing an external motion tracking system, achieved autonomous wind tunnel flight with a maximum root-mean-square position error of 28 mm at low speeds (0.8 - 1.2 m/s) and 75 mm at high speeds (2 - 2.4 m/s). This allowed the first free-flight flow visualisation experiments to be conducted with an FWMAV. Time-resolved stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) was used to reconstruct the 3D flow patterns of the FWMAV wake. A good qualitative match was found in comparison to a tethered configuration at similar conditions, suggesting that the obtained free-flight measurements are reliable and meaningful.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge