Masha Zorin
URET: Universal Robustness Evaluation Toolkit (for Evasion)
Aug 03, 2023
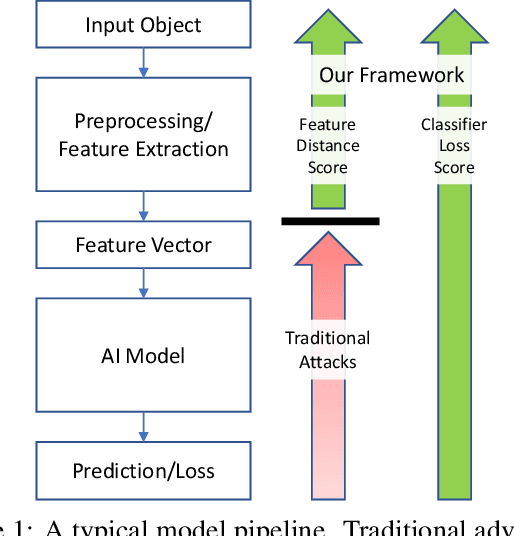
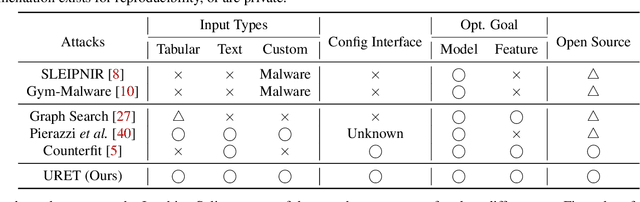
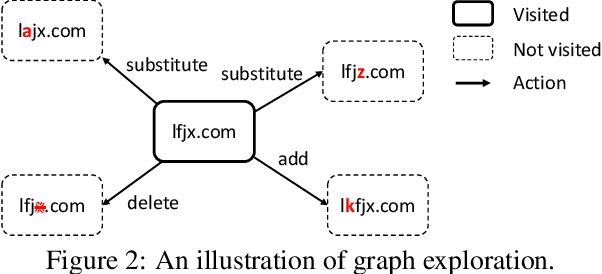
Abstract:Machine learning models are known to be vulnerable to adversarial evasion attacks as illustrated by image classification models. Thoroughly understanding such attacks is critical in order to ensure the safety and robustness of critical AI tasks. However, most evasion attacks are difficult to deploy against a majority of AI systems because they have focused on image domain with only few constraints. An image is composed of homogeneous, numerical, continuous, and independent features, unlike many other input types to AI systems used in practice. Furthermore, some input types include additional semantic and functional constraints that must be observed to generate realistic adversarial inputs. In this work, we propose a new framework to enable the generation of adversarial inputs irrespective of the input type and task domain. Given an input and a set of pre-defined input transformations, our framework discovers a sequence of transformations that result in a semantically correct and functional adversarial input. We demonstrate the generality of our approach on several diverse machine learning tasks with various input representations. We also show the importance of generating adversarial examples as they enable the deployment of mitigation techniques.
Deep Neural Networks Improve Radiologists' Performance in Breast Cancer Screening
Mar 20, 2019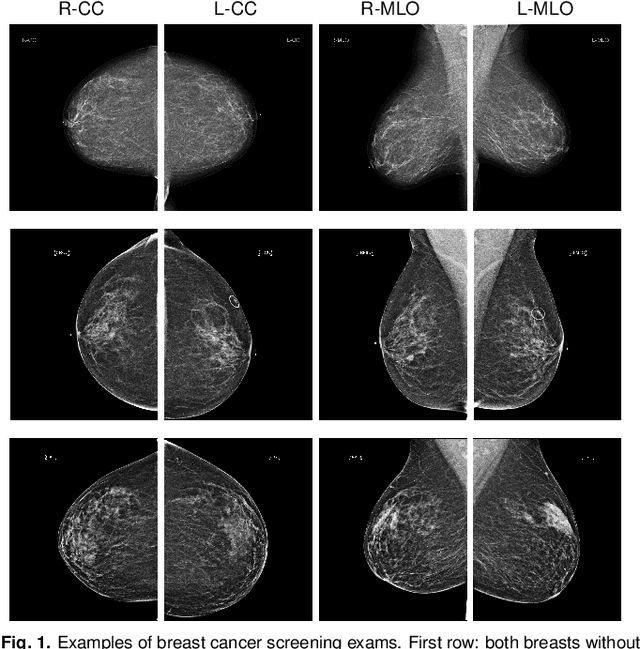
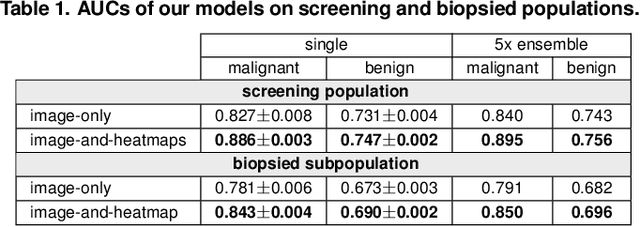
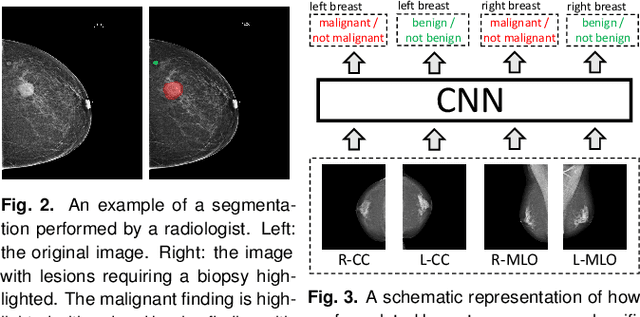
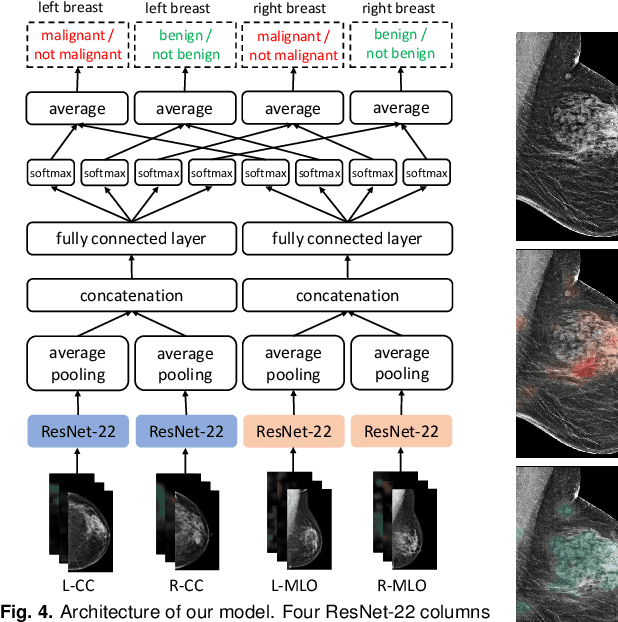
Abstract:We present a deep convolutional neural network for breast cancer screening exam classification, trained and evaluated on over 200,000 exams (over 1,000,000 images). Our network achieves an AUC of 0.895 in predicting whether there is a cancer in the breast, when tested on the screening population. We attribute the high accuracy of our model to a two-stage training procedure, which allows us to use a very high-capacity patch-level network to learn from pixel-level labels alongside a network learning from macroscopic breast-level labels. To validate our model, we conducted a reader study with 14 readers, each reading 720 screening mammogram exams, and find our model to be as accurate as experienced radiologists when presented with the same data. Finally, we show that a hybrid model, averaging probability of malignancy predicted by a radiologist with a prediction of our neural network, is more accurate than either of the two separately. To better understand our results, we conduct a thorough analysis of our network's performance on different subpopulations of the screening population, model design, training procedure, errors, and properties of its internal representations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge